Lakehouse DataGPT Quick Tour
Lakehouse DataGPT is a cutting-edge, cloud-based conversational data analysis tool that harnesses the power of natural language interactions, making data analysis as effortless as engaging in a chat. Leveraging advanced Large Language Models (LLMs), it enables users to delve into data with conversational ease, delivering precise and insightful analysis with remarkable efficiency.
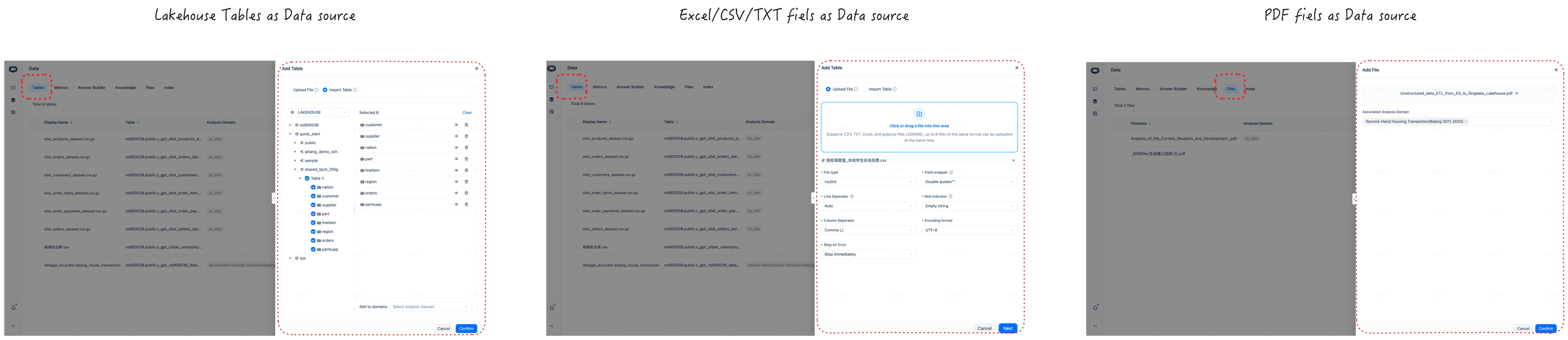
Embrace the future of data analytics with DataGPT, where the power of AI meets the versatility of data sources. Whether your data resides in the robust Singdata Lakehouse or in personal files like Excel, CSV, or PDF, DataGPT empowers you to harness its potential for analysis. This innovative tool breaks down the barriers of data accessibility, ensuring that no matter where your data is stored, you can leverage DataGPT's AI capabilities to uncover insights, make informed decisions, and drive success in the era of advanced data analytics.
To learn more about the concepts and technical architecture of DataGPT, please refer to DataGPT Introduction.
Data sources supported
Lakehouse GPT enables analysis of data already stored in Lakehouse tables. This means users can directly engage in conversational data analysis with Lakehouse GPT, expanding the application of Lakehouse from data engineering and SQL/Python-based analytics to an interactive, visual data analysis experience. This facilitates easier data exploration for users, allowing them to quickly obtain data results and the corresponding SQL code through simple question-and-answer interactions.
Lakehouse GPT also supports direct loading of files such as Excel, CSV, and PDF, with the loaded data being stored within the Lakehouse. This eliminates the need for users to worry about Lakehouse-specific concepts like schema, tables, or SQL, significantly lowering the barrier to entry for data analysis.
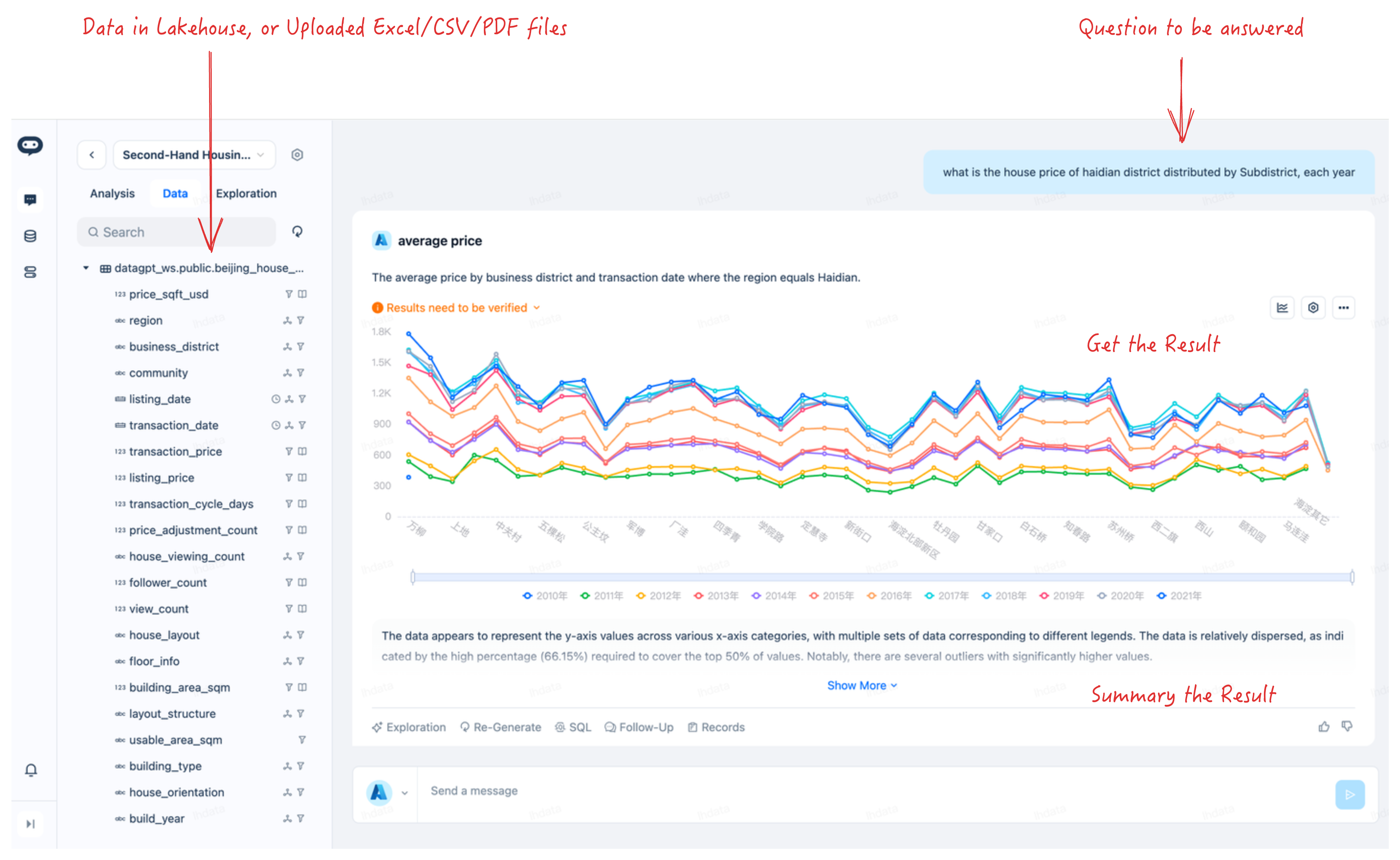
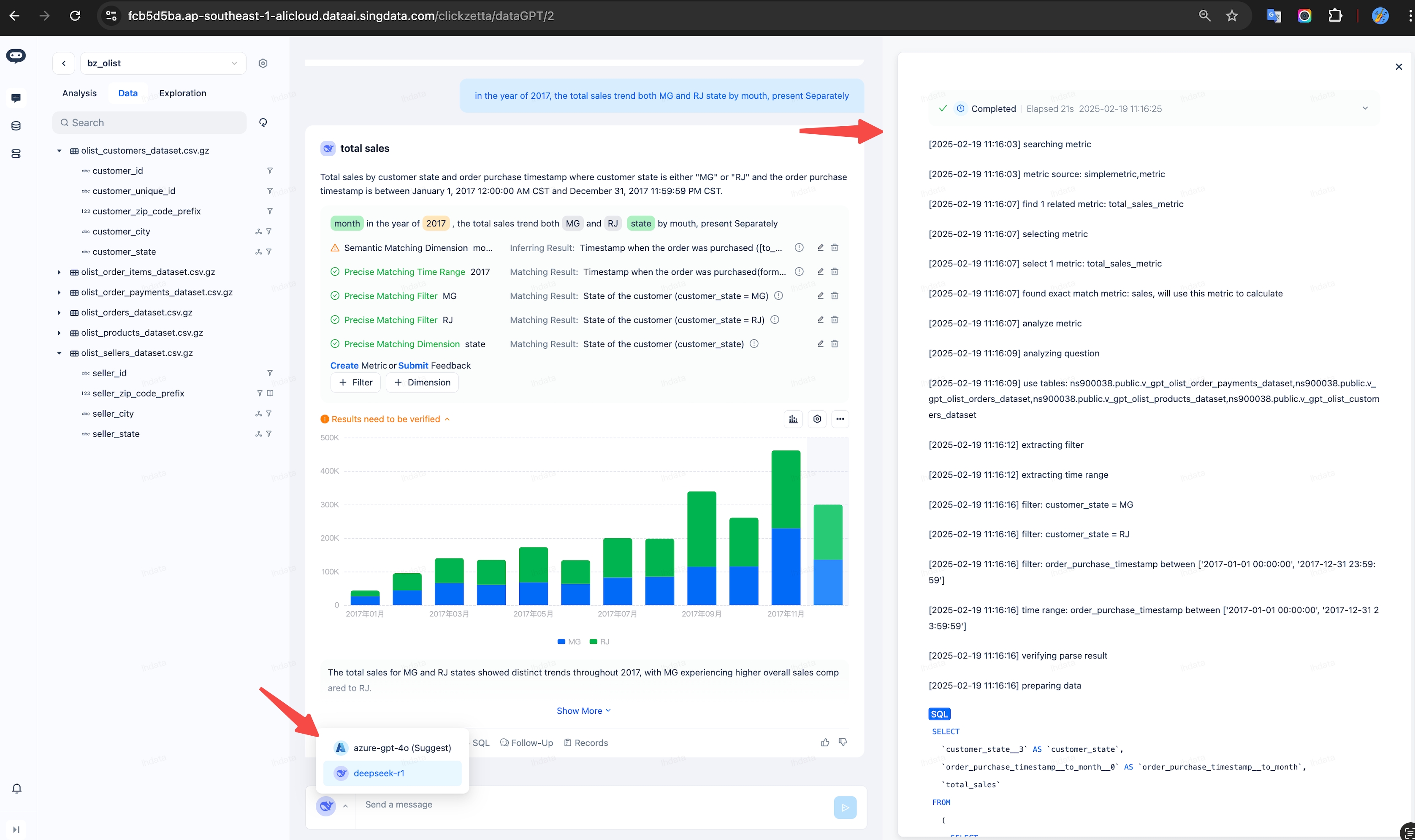
Initiate a conversation with DataGPT, and seamlessly receive comprehensive data analysis outcomes.
We received a notification indicating that "Results need to be verified." Upon investigating the details, we discovered that the query related to the "Haidian District." The Large Language Model (LLM)-powered data analysis tool, DataGPT, adeptly managed the multilingual nature of the data by interpreting "Haidian District" and correlating it with the Chinese field value "Haidian" for the region, as the table only contains district information in Chinese. DataGPT's inference capabilities enabled it to recognize the matching correlation and seamlessly align the data to yield accurate outcomes. Despite this, the tool prompted the user to verify the results for accuracy.
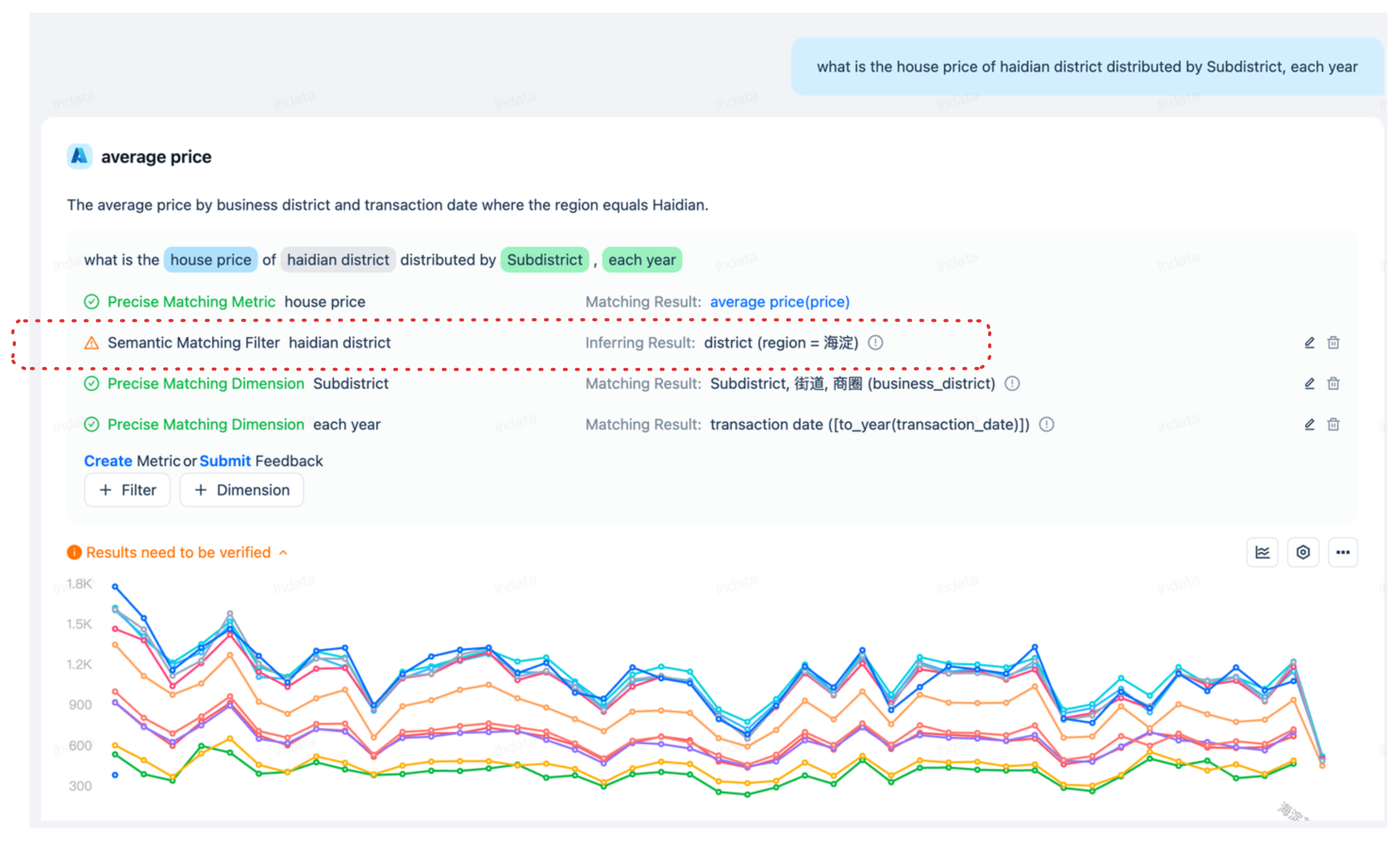
This case clearly illustrates the strength of DataGPT, which leverages the advantages of LLM to overcome challenges that traditional Business Intelligence (BI) tools often face in data analysis. By harnessing the power of LLM, DataGPT effectively addresses complex multilingual data issues, providing a solution that surpasses the limitations of conventional BI tools and enhances the overall analytical process.
Comparative analysis & multi-dimensional drilling down
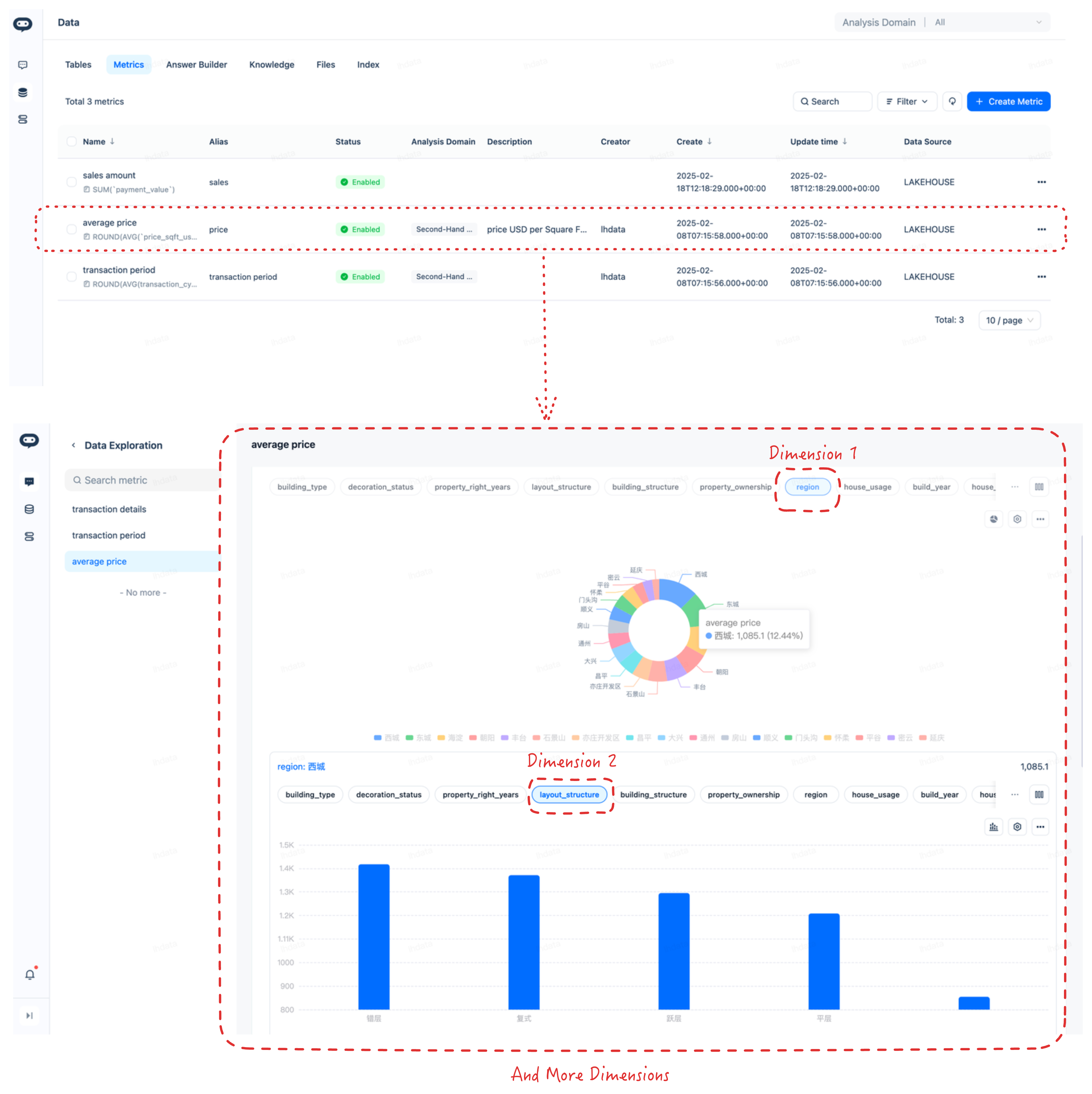
Metrics, which are computed based on database fields, are quantifiable measures used to evaluate performance, trends, and other key data points. They can be generated through aggregation, which involves summarizing large datasets into a single value or a small set of values, or by using custom code methods that apply specific algorithms or calculations to the data. DataGPT offers an automated way to create these metrics through the use of large models, streamlining the process and reducing the need for manual intervention. These metrics provide a concise way to understand complex data and make informed decisions.
Data analysis based on metrics includes comparative analysis across different time periods and multi-dimensional drilling down.
Comparative analysis
Comparative analysis involves examining changes and trends over time, such as month-over-month, year-over-year, or quarter-over-quarter, to identify patterns, growth, or decline in performance metrics. This type of analysis is essential for understanding progress and making strategic decisions.
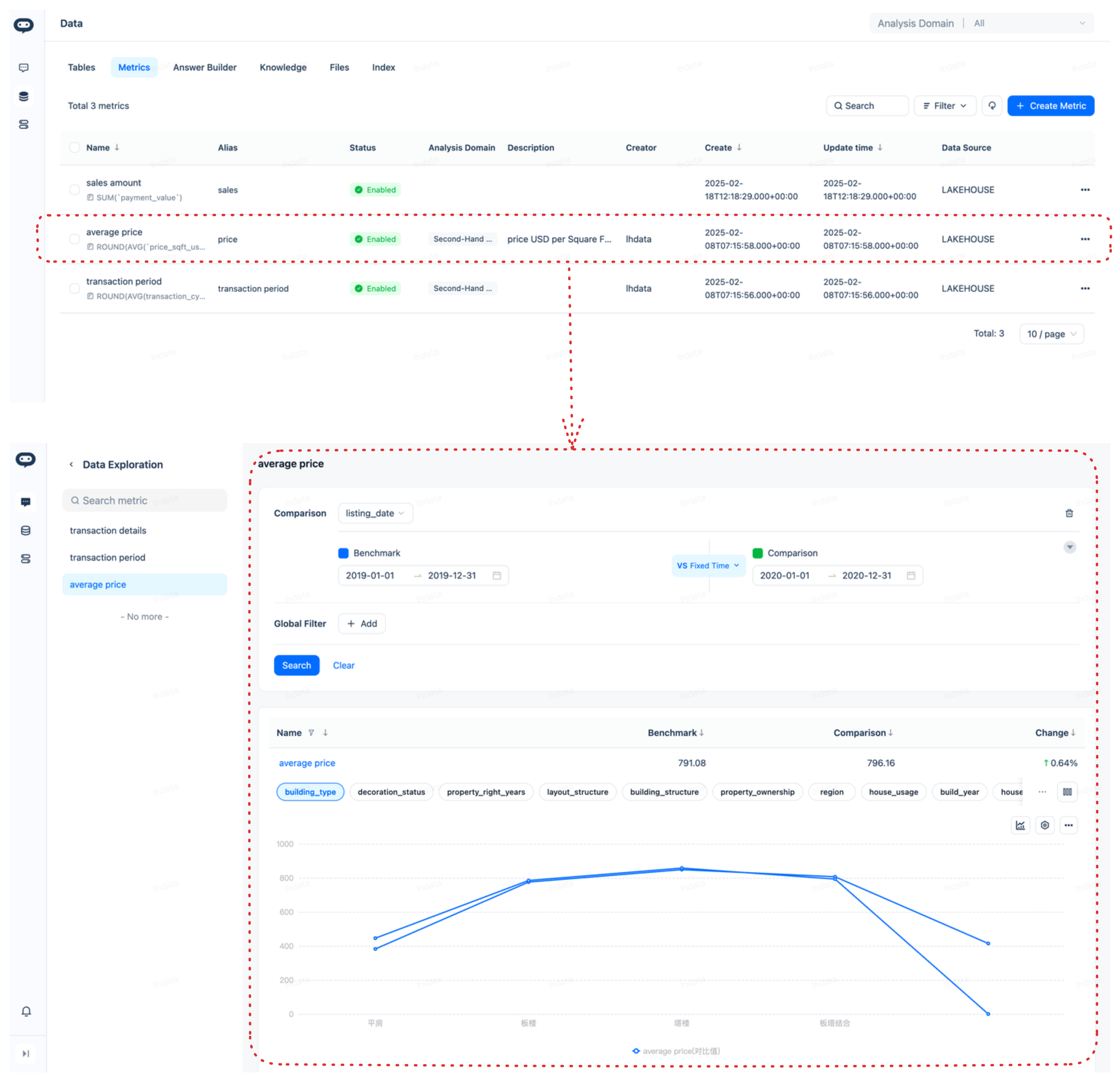
Multi-dimensional drilling down
Multi-dimensional drilling down refers to the process of exploring data from various angles or dimensions. This could involve segmenting data by region, product line, customer segment, or any other relevant category to gain deeper insights. By drilling down, analysts can uncover the factors that contribute to the overall metrics, allowing for more targeted and informed decision-making.
Quick Start
-
DataGPT Quickstart: Quickly experience conversational analytics using Sample Dataset: We have prepared a well-configured sample dataset for you, which includes a complete table configuration and indicator system. You can start asking questions directly to quickly experience the intelligent analysis capabilities. At the same time, this sample can also serve as a template to help you create an analysis domain suitable for your business scenarios.
-
DataGPT Data Source Management: Connect to Lakehouse instances in other regions.
-
Once the data is ready, you can start asking questions in natural language.
Configuration
-
Metrics and Answer Builder: For specific calculation needs, the system can provide answers using predefined SQL templates.
-
How to make answers more accurate: To improve the accuracy of DataGPT's responses.
Data Privacy
- DataGPT Data Privacy: For data privacy concerns during the Q&A process.
