Experience Performance with TPCH Queries and Sample Data
Overview
Through this tutorial, you will learn how to use the built-in sample dataset of the Lakehouse platform to quickly use SQL for query analysis and evaluate SQL functionality and performance without preparing data in advance.
Import Script
Open the "Lakehouse Tutorial" page in the console and select the "Quick Start Query Analysis with Sample Data" course. Follow the prompts on the page to import the script files needed for this course.
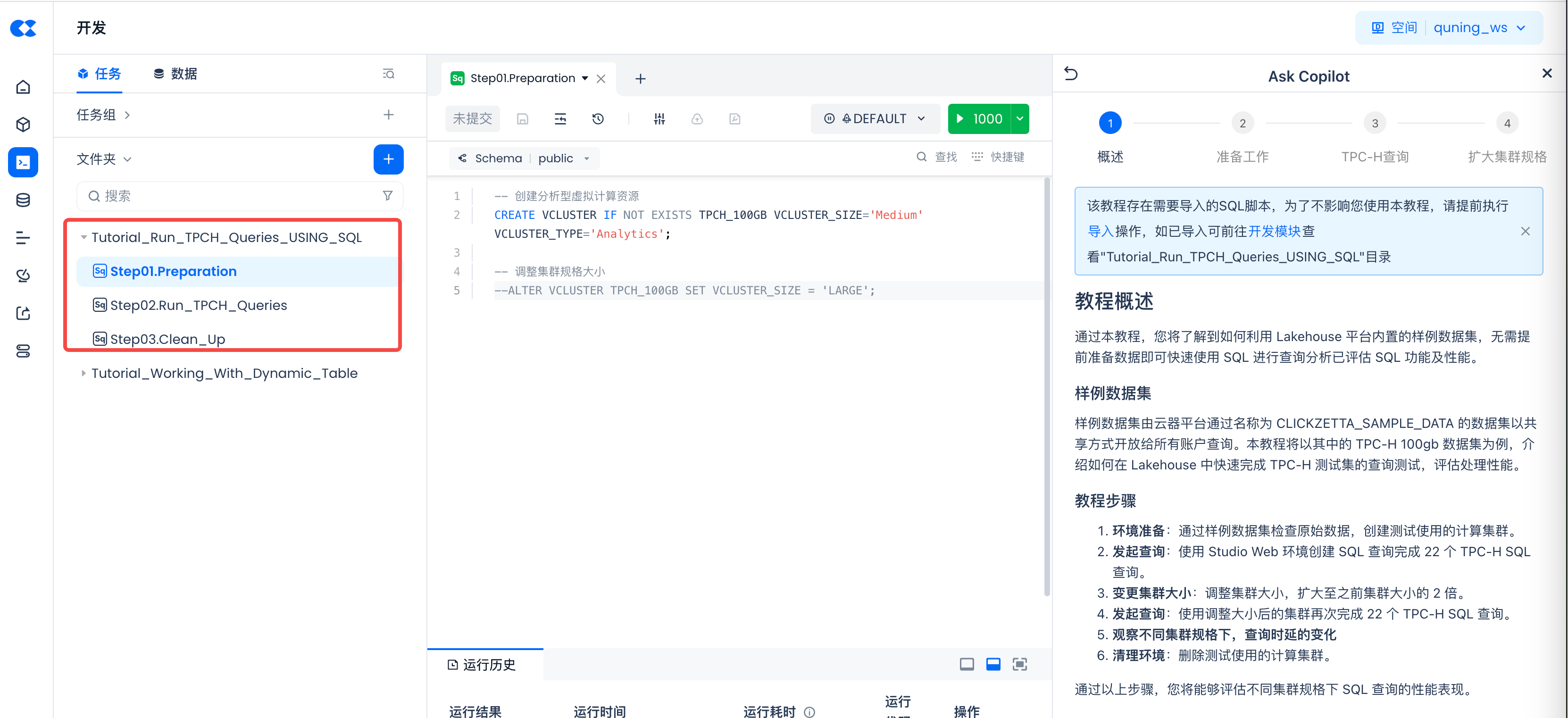
View the "Tutorial_Run_TPCH_Queries_USING_SQL" directory in the "Development Module".
Sample Dataset
The sample dataset is shared by the Singdata platform through a dataset named CLICKZETTA_SAMPLE_DATA, available for query by all accounts. This tutorial will use the TPC-H 100gb dataset within it as an example to demonstrate how to quickly complete TPC-H test set queries in Lakehouse and evaluate processing performance.
Tutorial Steps
- Environment Preparation: Check the raw data through the sample dataset and create a compute cluster for testing.
- Initiate Query: Use the Studio Web environment to create SQL queries to complete 22 TPC-H SQL queries.
- Change Cluster Size: Adjust the cluster size, doubling the previous cluster size.
- Initiate Query: Use the resized cluster to complete the 22 TPC-H SQL queries again.
- Observe the changes in query latency under different cluster specifications
- Clean Up Environment: Delete the compute cluster used for testing.
Through the above steps, you will be able to evaluate the performance of SQL queries under different cluster specifications.
Preparation
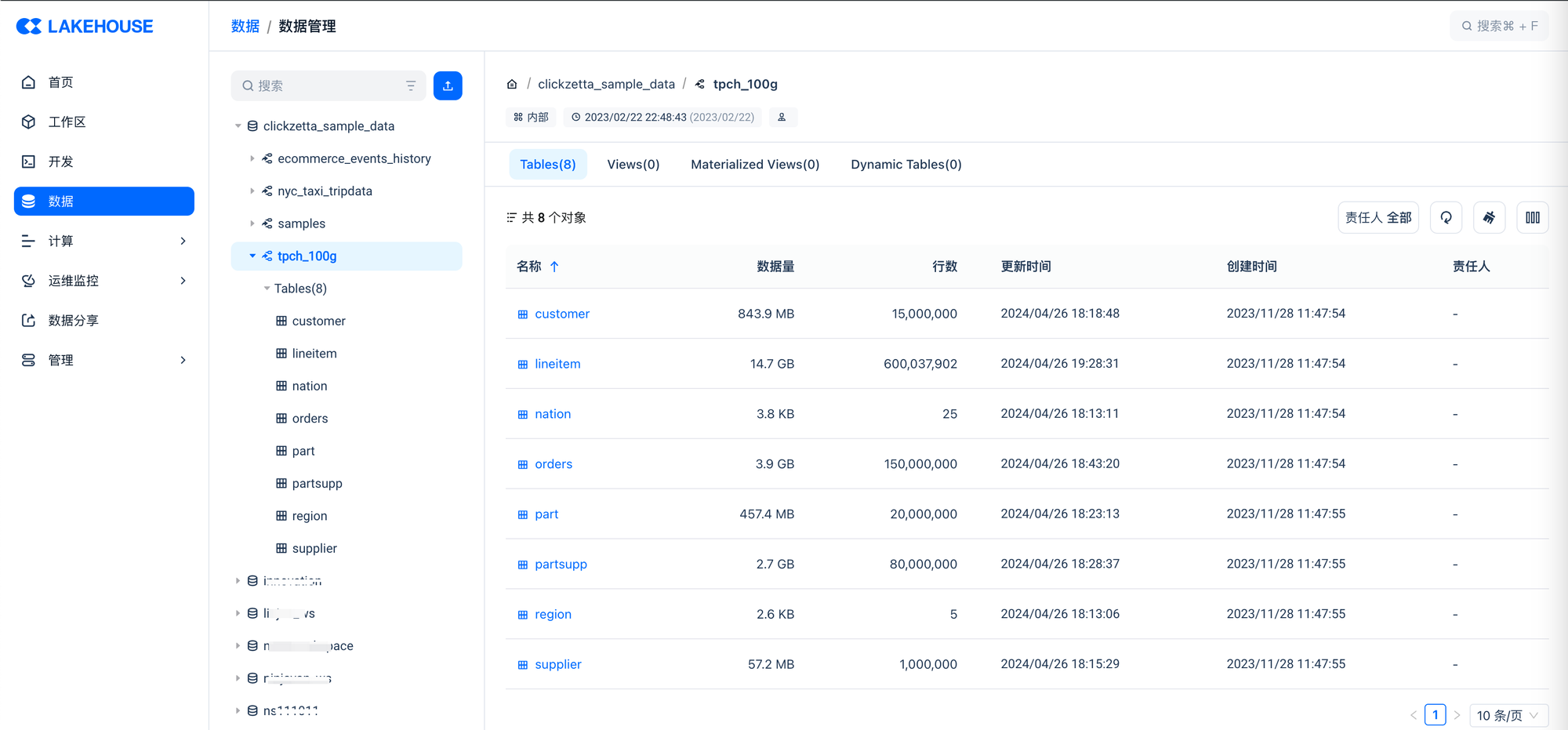
First, after logging into the Lakehouse Web console and entering the specified workspace, you can access the data module to check if the relevant tables under "clickzetta_sample_data.tpch_100g" exist in the data object list under data management.
Next, we will temporarily create an independent compute cluster for query analysis for this test. You can create a new cluster through the "Compute → Clusters" menu in the Lakehouse Web console by following the page wizard.
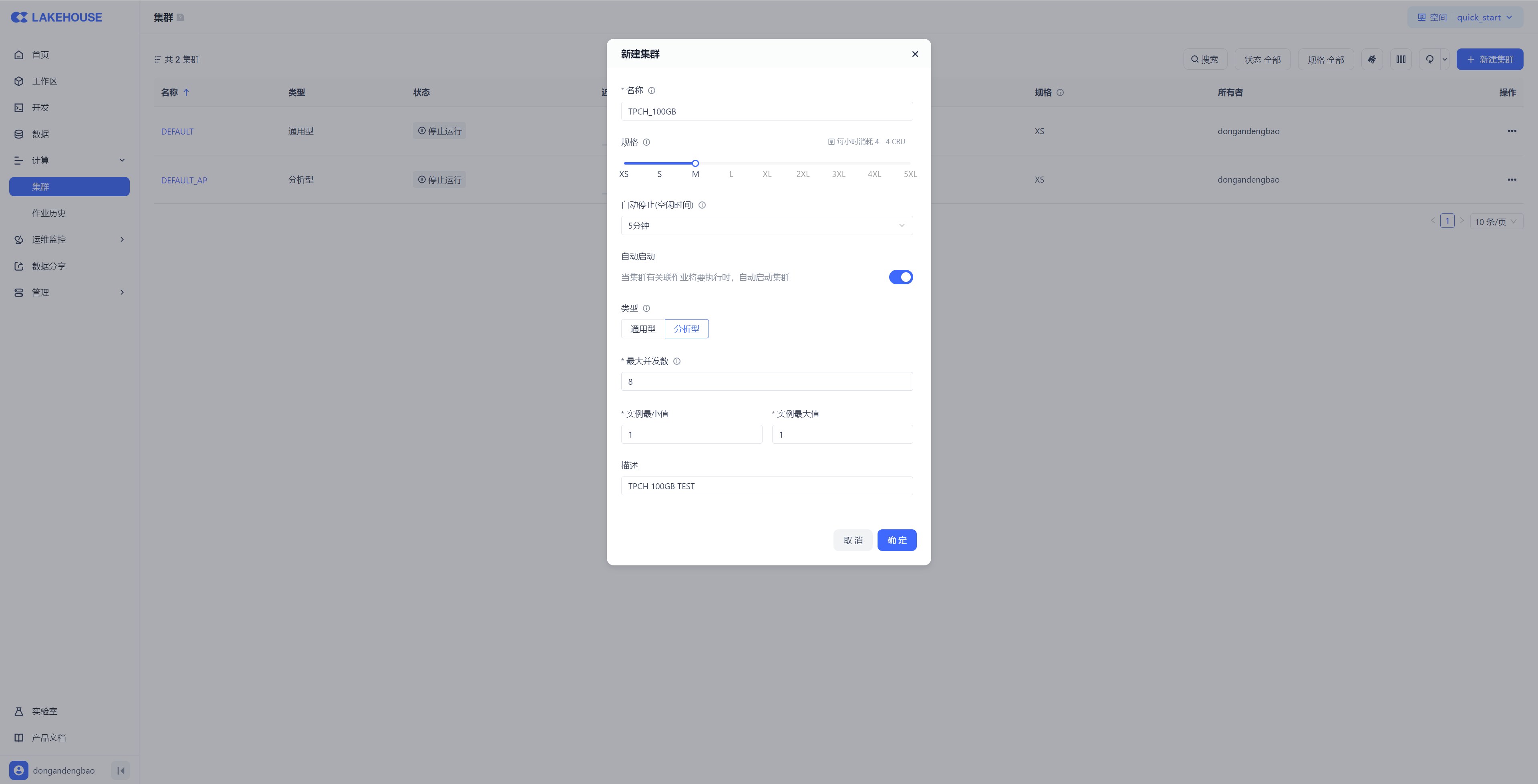
At the same time, you can also create a cluster through SQL commands. When operating through SQL commands, you can control cluster creation, scaling, pausing/resuming, and destruction actions without leaving the SQL development context, often improving the efficiency of computing resource operations during Ad-hoc or ETL development processes.
This tutorial creates the compute cluster needed for analyzing the TPCH dataset by running the [Tutorials/Tutorial_Run_TPCH_Queries_USING_SQL/Step01.Preparation] SQL script task in the "Development" module.

TPC-H Query on Sample Data
Open the [Tutorials/Tutorial_Run_TPCH_Queries_USING_SQL/Step02.Run_TPCH_Queries] SQL script file in the "Development" module. You will see that the 22 TPC-H query statements have been entered. Select the test cluster just created from the [Cluster] dropdown list, then select all scripts in the task and click the [Run] button to perform serial queries.
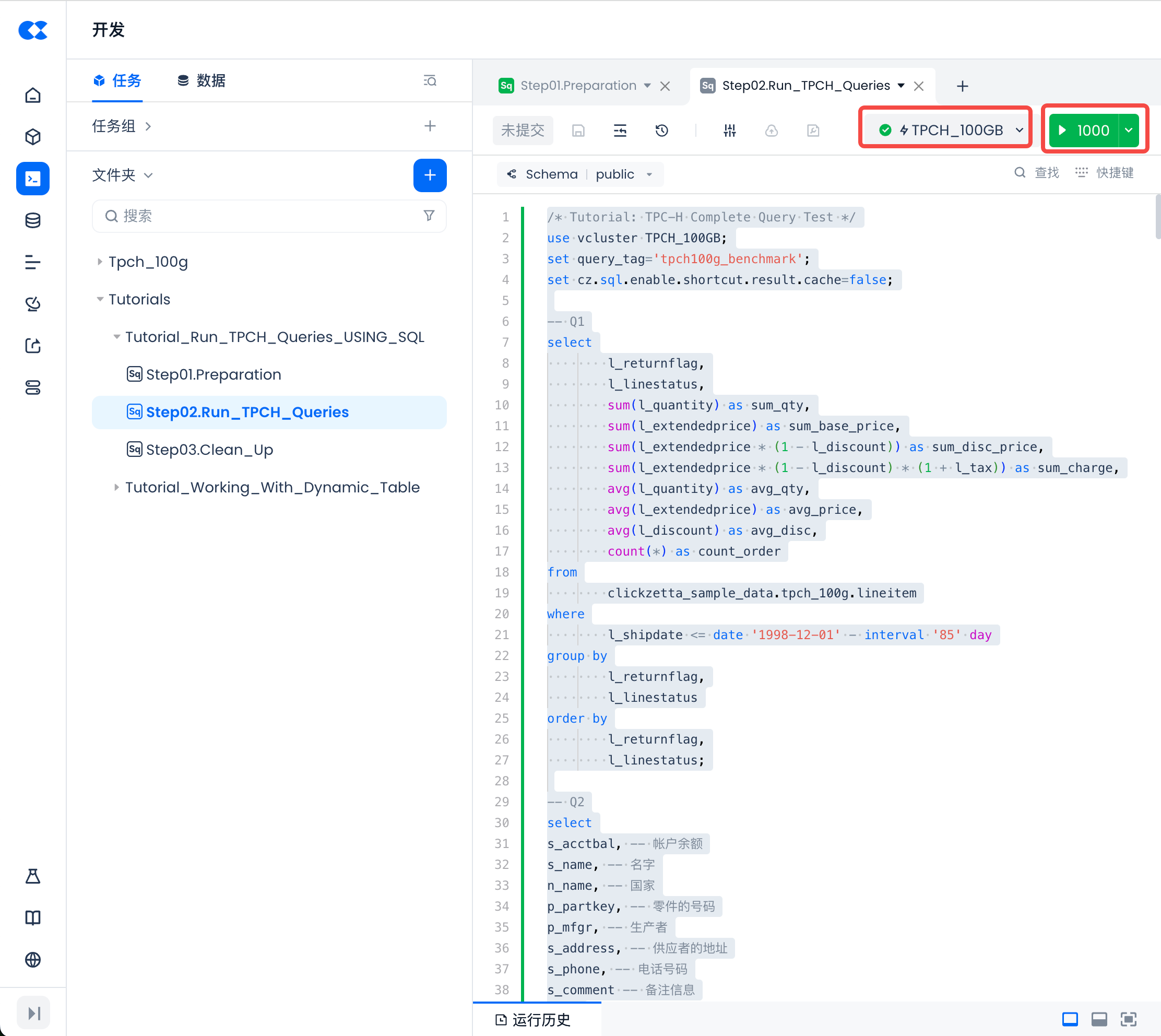
After execution, you can view the runtime of this task through the current SQL Editor's run history.
If you want to perform performance testing, you can execute the queries more than twice consecutively so that the compute cluster can fully cache the data and achieve optimal performance. The following is the result of the second run, showing a significant performance improvement after the compute cluster caches the data compared to the first run without caching.

If you want to see the execution details of each of the 22 queries, you can access Compute → Job History, filter the query history by the query tag "tpch100g_benchmark" and view it.
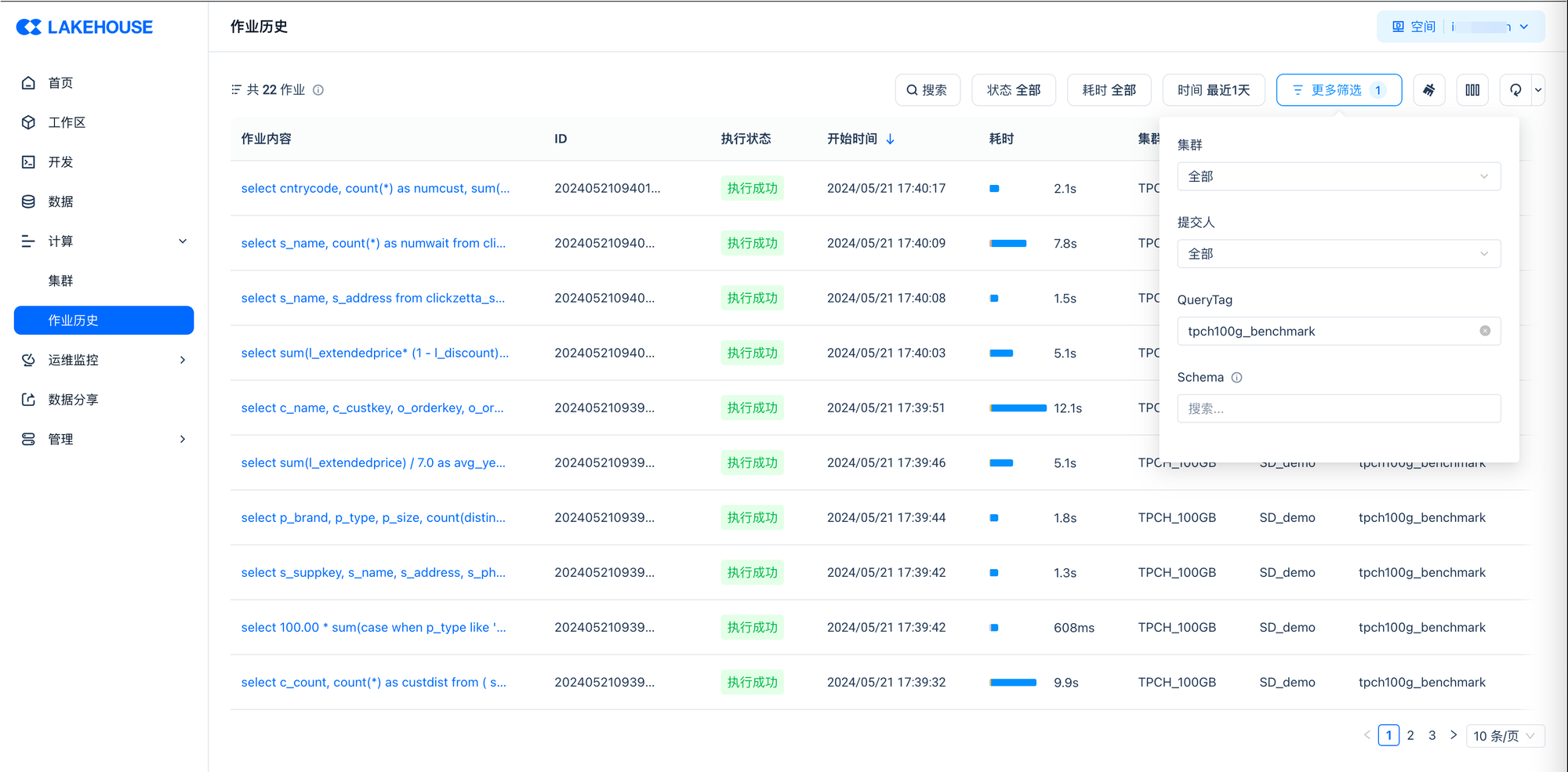
Query after expanding cluster specifications
Through the Compute → Cluster Management page, you can modify the size of the test cluster you just created, changing it from Large to XLarge, where the XLarge size is twice that of Large.

Or execute the following command in the SQL script to modify:
After modification, use the resized cluster to perform the query test again.

Environment Cleanup
Open the "Development" module [Tutorial_Run_TPCH_Queries_USING_SQL->Step03.Clean_Up] SQL script file, and execute the script to delete the test cluster for this tutorial.