Writing SQL for Data Query and Analysis
Lakehouse provides an integrated data processing engine to support data processing and analysis. The development language for the Lakehouse engine is SQL. This article briefly introduces how to quickly write and run SQL statements through the task development web interface of Lakehouse Studio for query analysis.
Writing and Running SQL Statements
In the page navigation, click "Development" to enter the data development interface. Under "Tasks," create a new SQL task file by selecting "SQL Script" from the new menu.
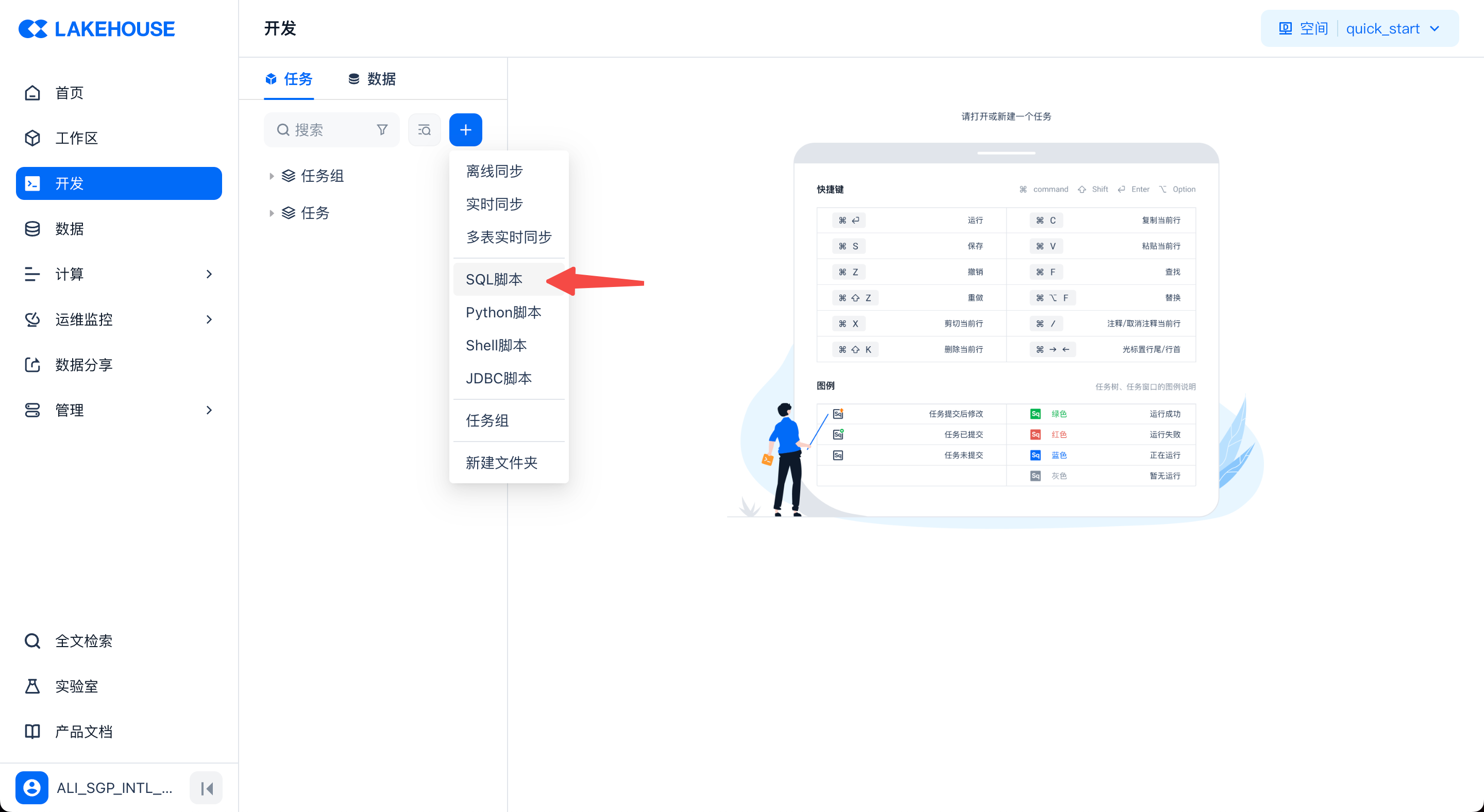
In the task file, use the following steps to write and run SQL:
-
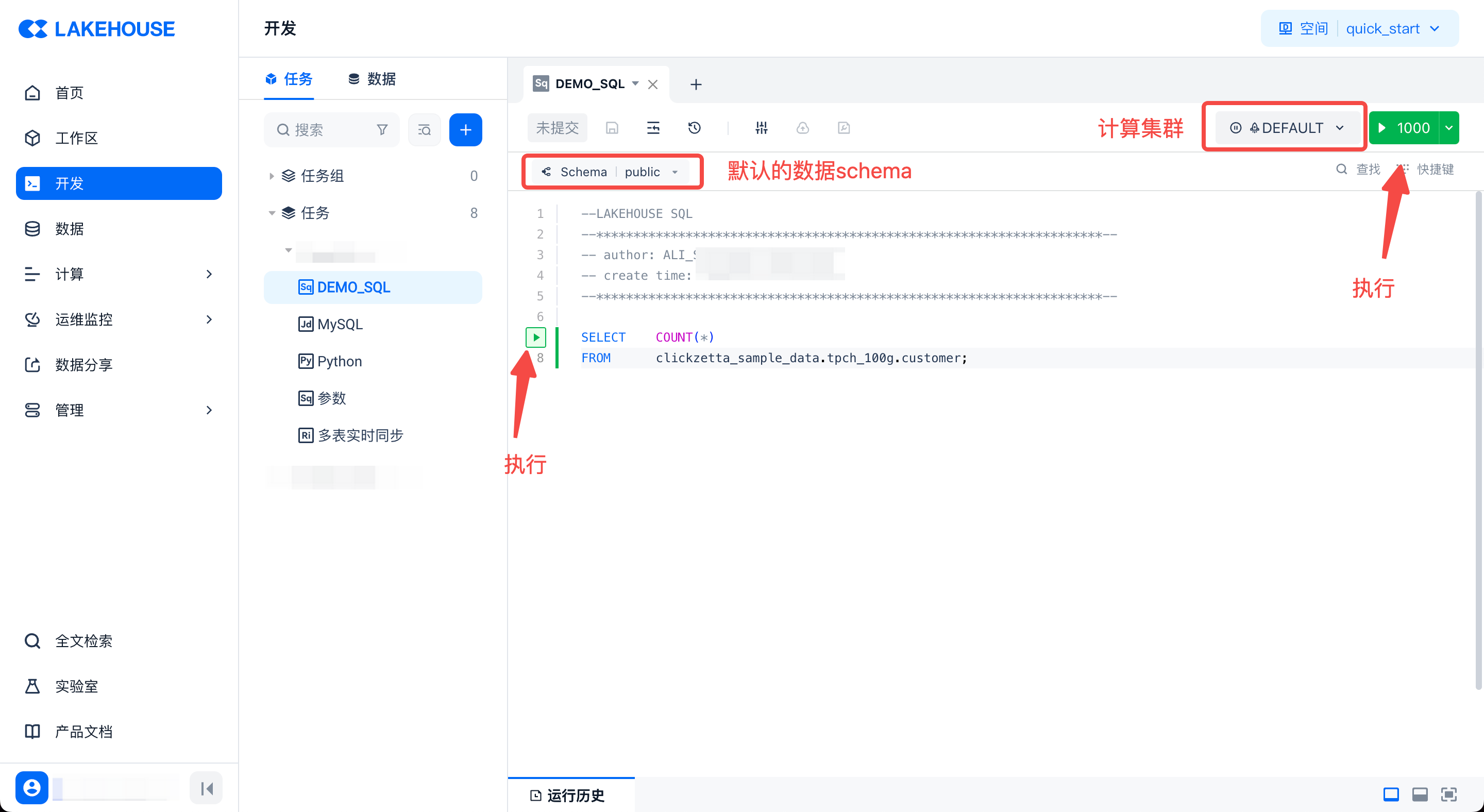
Select the correct data schema on the page. When writing code, you can directly reference the tables under the schema by their table names. Otherwise, you need to use the schema.table or workspace.schema.table format to reference tables. Usually, the system default schema is sufficient.
-
Fill in the SQL you need to run in the code editing area.
-
Choose the appropriate computing cluster. For ad-hoc temporary queries or to get faster query response times, it is recommended to choose an AP type cluster. GP type clusters are suitable for large-scale data offline periodic scheduling processing and analysis.
-
Click the run button on the left or the run button in the upper right corner to execute the code. The left button only executes the code block where the mouse is located. The upper right button executes all the code by default; you can also select part of the code and then click the upper right button to execute it.
-
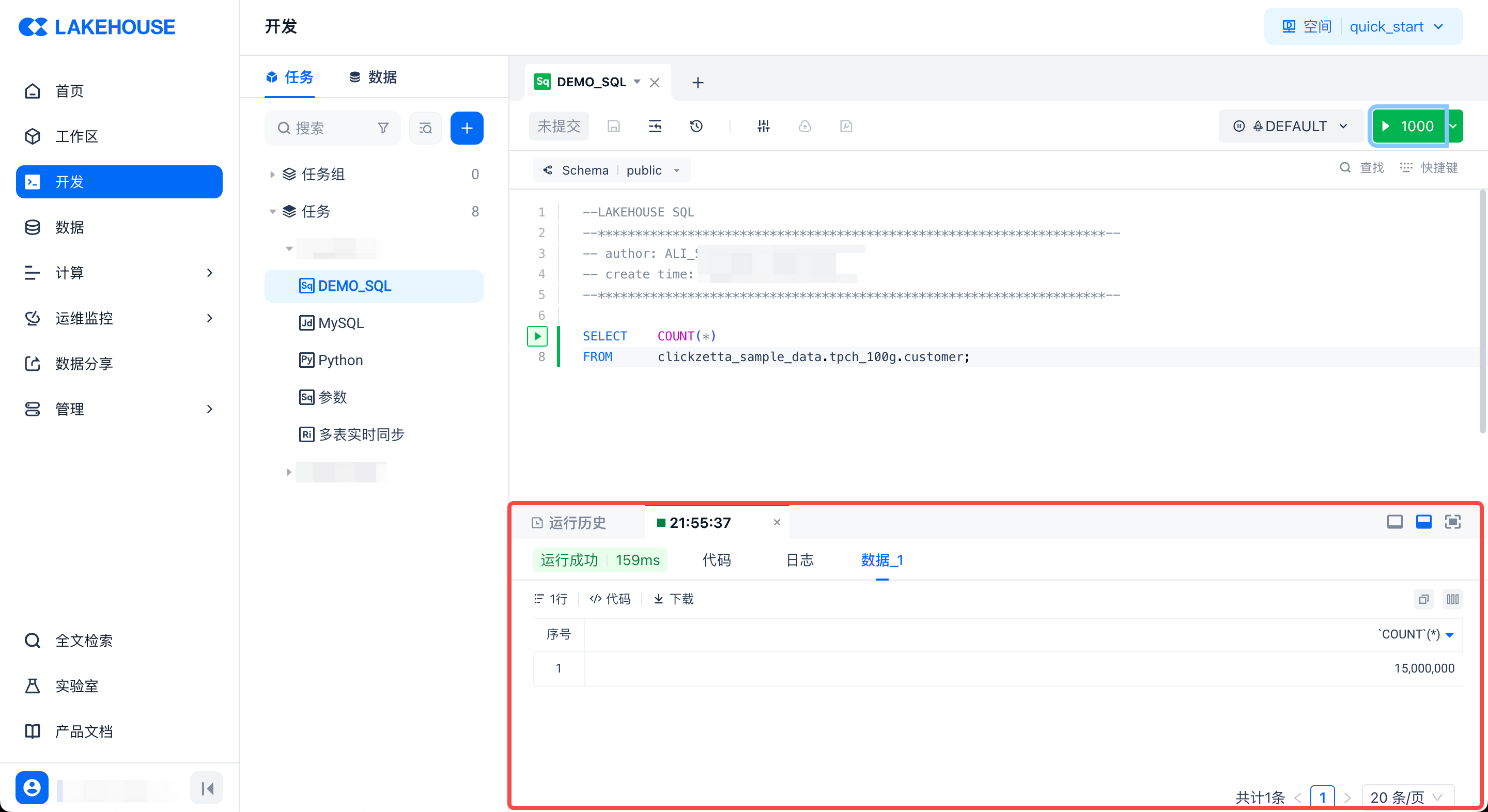
After the run is complete, you can view the results, time taken, and run logs in the area at the bottom of the page:
When writing code in the editor, you can also switch to the data tab to quickly browse and use data. After finding the required table, you can quickly insert the table name, field name, or directly generate a query sample SQL from the operation menu:
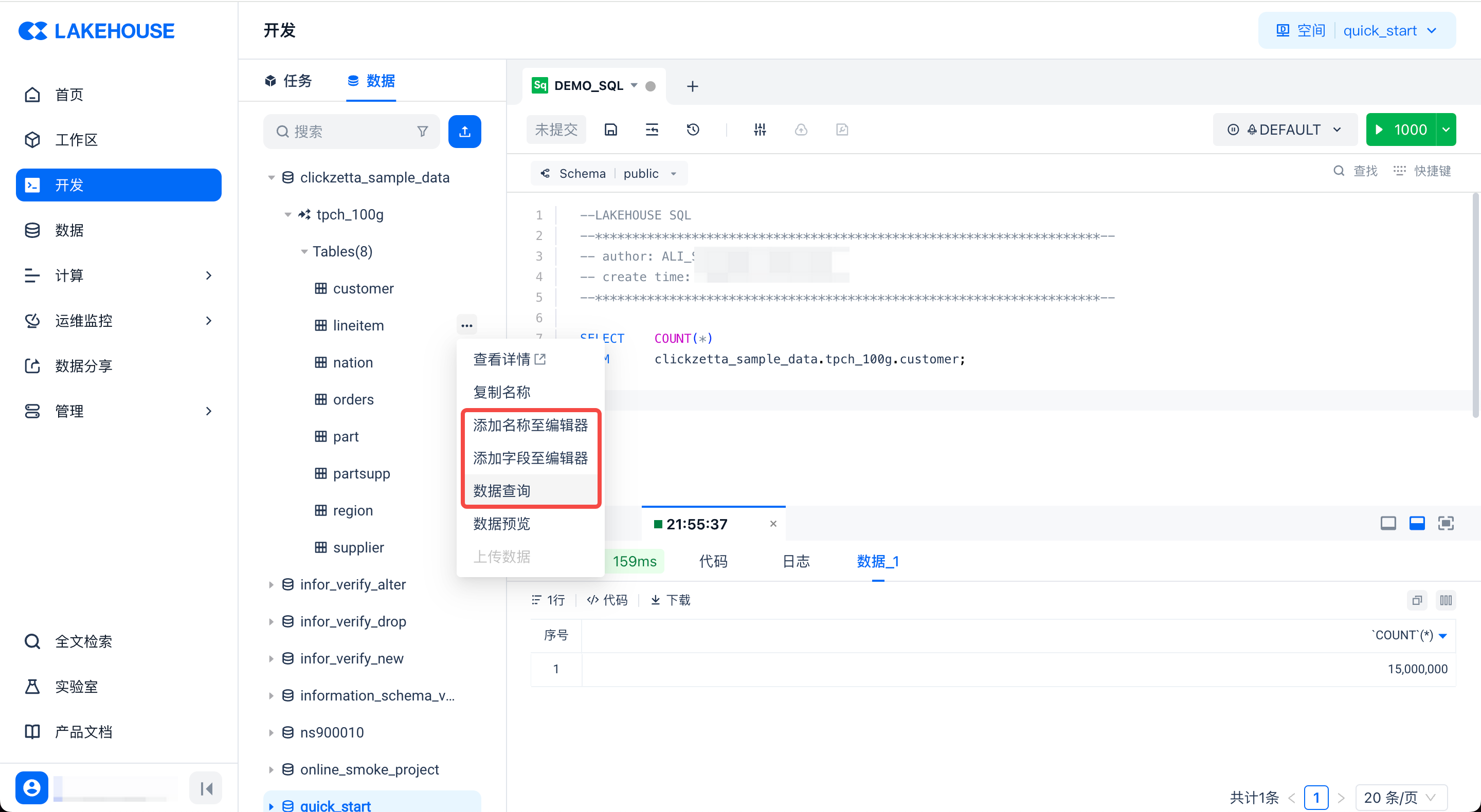
In addition, the product comes with built-in sample data that you can use. You can further understand how to perform query analysis based on sample data through the Using Sample Data to Quickly Start Query Analysis tutorial.
Other Common Operations
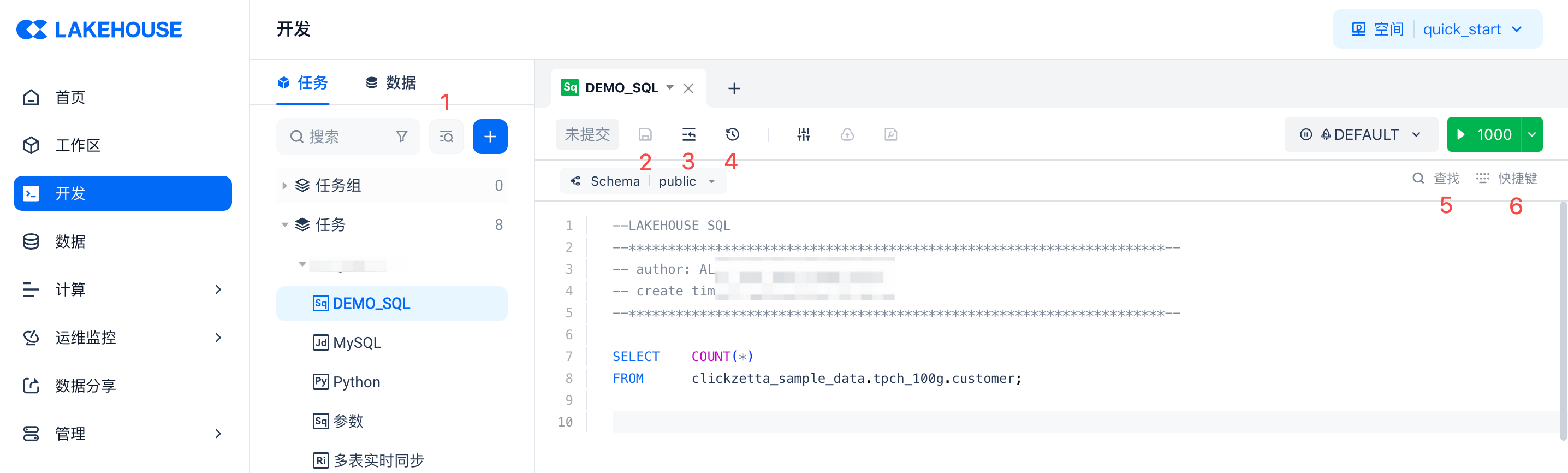
In addition to the "Run" operation, the system also provides the following functions as shown in the figure below:
- Global code search: Find files by code keywords
- Save: Save the changes made to the current file
- Format: Format the current code
- Version history: View the file's version history, and support comparison and rollback
- Find: Search for code snippets within the current file using keywords
- Shortcuts: Display supported common shortcuts
Using the Workspace
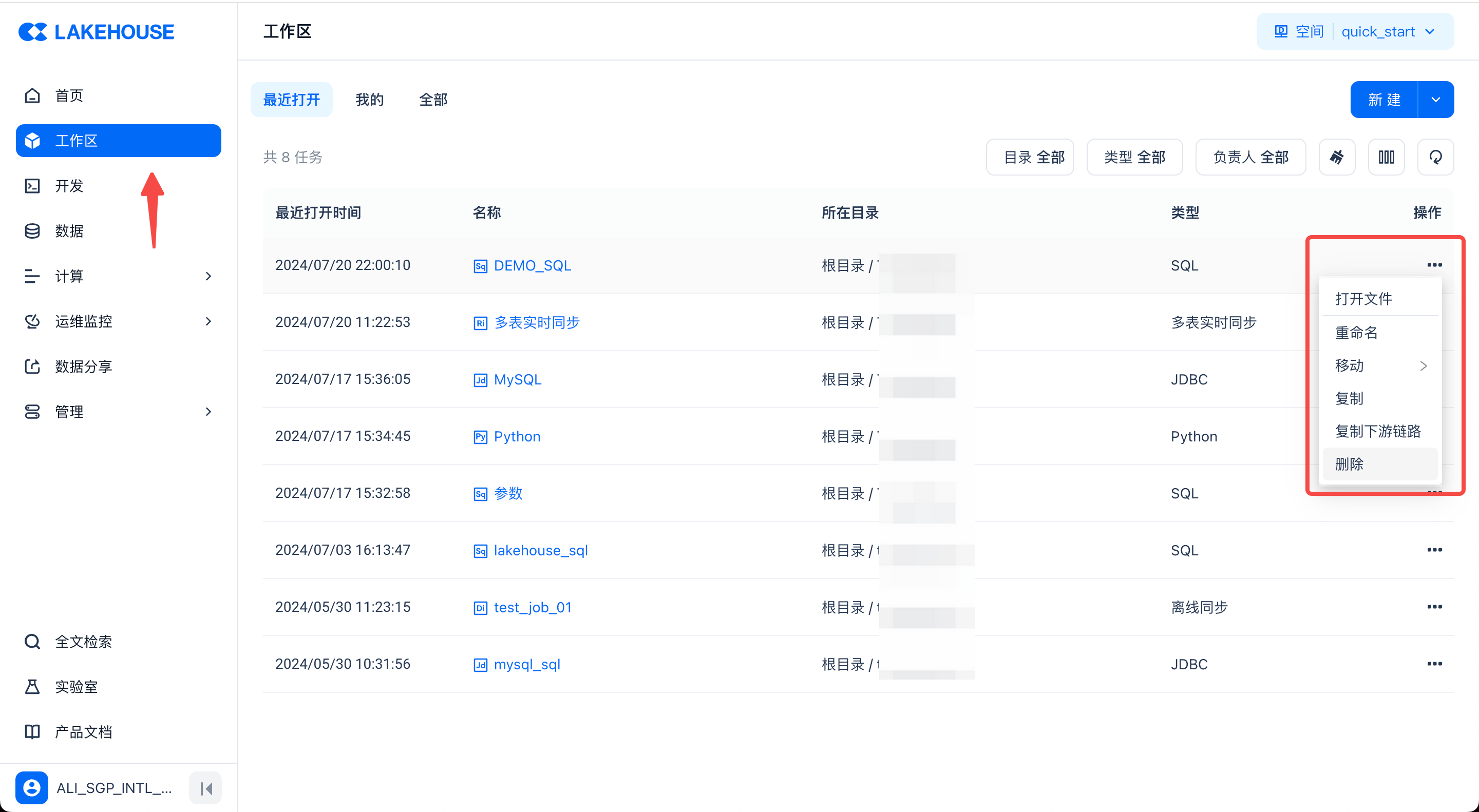
The workspace displays the files you have recently opened, as well as the tasks you manage and all task files. Here you can quickly open files or perform management operations such as renaming, moving the file directory, copying, and deleting.