Import Local Data
This document provides a detailed introduction on how to import local data into the Lakehouse platform. Currently, Lakehouse supports three main modes of local data import:
- Upload local files using the PUT command and import them into Lakehouse.
- Visual upload via the Lakehouse Studio page: Suitable for small data file uploads, providing a user-friendly interface and simplified upload process.
- Upload data using the Jdbc client: Suitable for technical users, especially those who need to batch process small amounts of data, supporting quick processing of CSV files and scripted, automated operations. (This feature has been deprecated in jdbc version 2.0.0, it is recommended to use the PUT command for uploads)
Reference Documents
Download data using the client COPY command
Application Scenarios
- Put command to upload files: Suitable for source file uploads and requires SQL for conversion. It is recommended to use SQL to convert or handle abnormal data during the upload process. Supports CSV, PARQUET, ORC.
- Lakehouse Studio page: Suitable for users who need to upload small data files, supports CSV, PARQUET, AVRO, ORC, TEXT formats, but does not include compressed file formats. It is recommended to decompress locally before uploading.
- Jdbc client: Only supports CSV file format, does not support compressed files, suitable for quick processing and automated data import tasks. In versions after JDBC 2.0.0, the local COPY command has been deprecated. We recommend using the PUT method to upload data to the volume, and then using the server-side COPY command for import.
Use Cases
Upload data using the PUT command
Lakehouse currently has some Internal Volume built-in to store files. Internal Volume currently supports two object types: USER VOLUME and TABLE VOLUME. We use the Put command to upload files to the Internal Volume and then use the COPY command to import the Volume data into the table.
Prerequisites
- Command line tool installed. Alternatively, you can use open-source tools like DBeaver, SQL Workbench/J to execute the command.
- INSERT permission on the target table.
- Execute the PUT command in the command line to upload the file to the TABLE VOLUME.
- Use the COPY INTO command to import file data into the target table
Upload Using Lakehouse Studio Page
Usage Restrictions
-
File Format Restrictions: Complex types such as ARRAY, MAP, STRUCT, JSON, INTERVAL are not supported. For complex type data, it is recommended to map using STRING type and convert through Lakehouse SQL functions.
-
File Size Restrictions: The maximum size of a single file supported by the Lakehouse Studio page and Jdbc client is 2GB.
-
COPY Command Restrictions: The COPY command cannot be used to upload local files on the Studio page. This command requires specifying the local file path, which the Studio page cannot access. In data management, the top area also provides an "Upload" function, which supports uploading local files to the Singdata Lakehouse platform.
Click the "Upload" button to easily load data from local files to the Singdata Lakehouse platform. It supports csv and txt formats, and the total size of uploaded files cannot exceed 2GB.
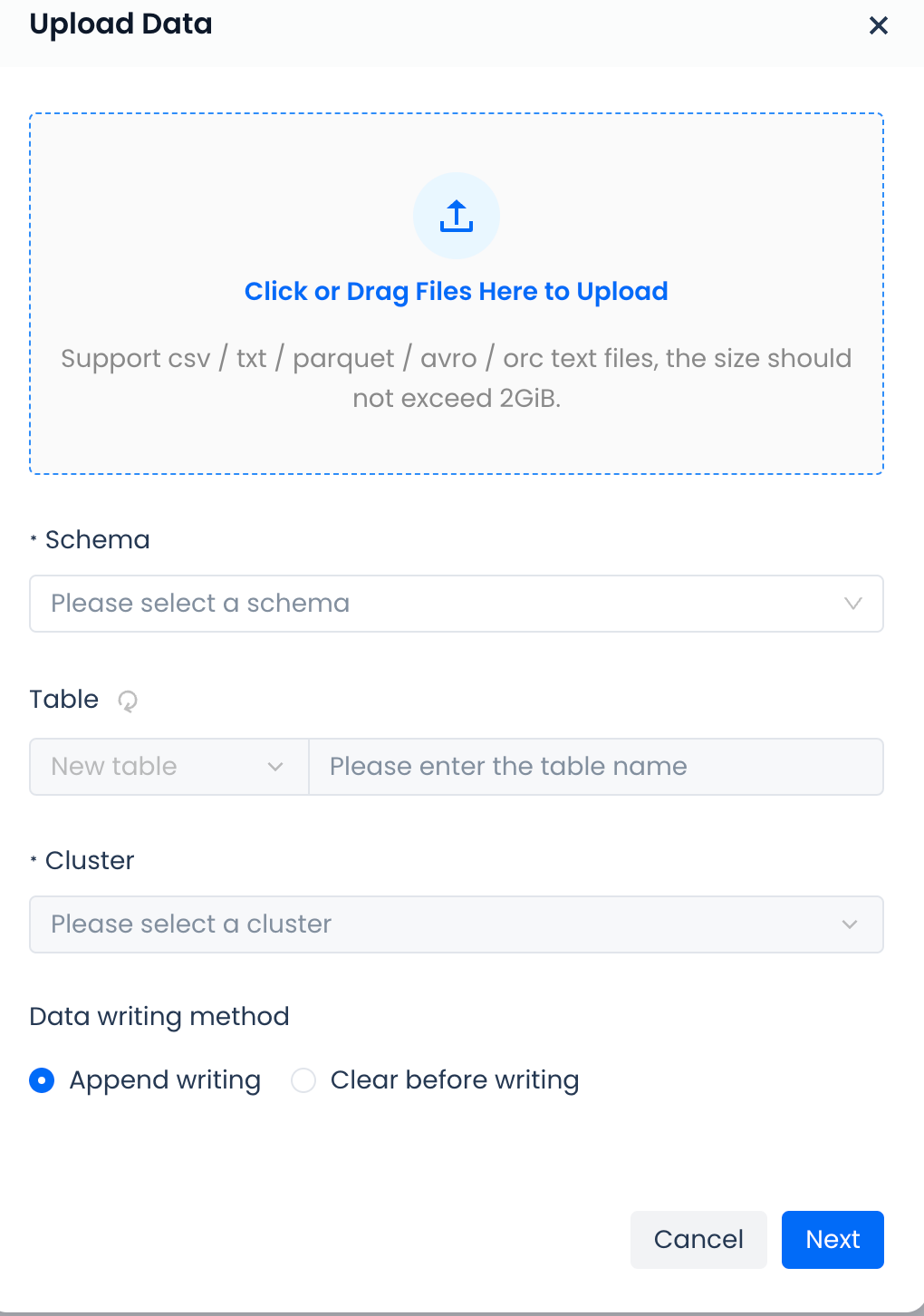
Format Description
-
Encountering Errors: How to handle error scenarios such as abnormal data in data rows.
-
Column Separator: The separator between columns, only a single character is allowed. For csv files, the default is a comma.
-
Line Break: Set the handling method for line breaks, Windows system uses \r\n, Linux, and MAC systems use \n.
-
Ignore Header: Whether to include the header in the uploaded file.
-
Null Value Representation: Specify the representation of null values in the file.
-
Cluster: Data upload can only be performed after selecting a cluster.
-
Data Write Method:
- Append Write: Directly append without processing historical data.
- Clear and Write: Clear historical data in the table first, then write data.
