Compute Cluster Cache
Lakehouse uses caching technology to accelerate query performance and efficiency. The platform provides three types of caches to improve query performance:
-
Query Result Cache (ResultCache)
-
Metadata Cache (MetadataCache)
-
Compute Cluster Local Disk Cache (Virtual Cluster Local Disk Cache)
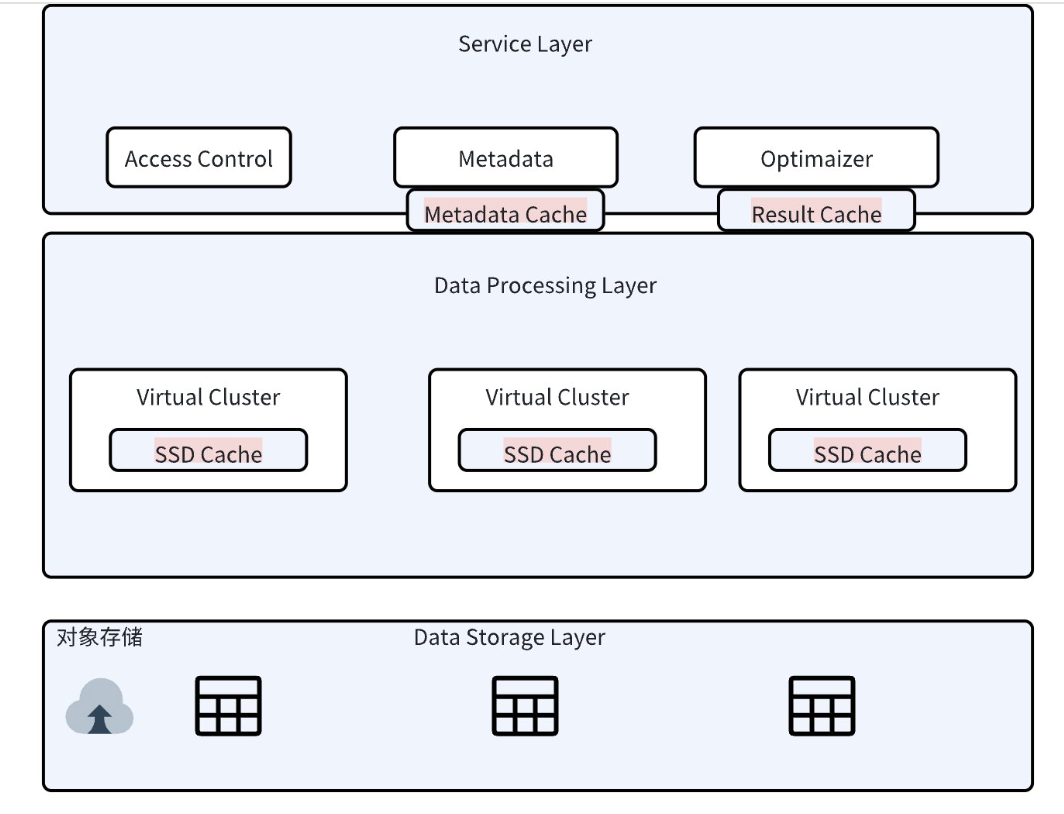
Among them:
Metadata Cache and Query Result Cache services belong to the service layer and can be shared within the workspace.
Compute Cluster Local Disk Cache is stored on the local nodes of the cluster and can only be used when using the specified virtual cluster.
In the storage-compute separation architecture of Lakehouse, data is stored in object storage. To address network request latency and improve response speed in analytical scenarios, we adopt caching strategies. Compute Cluster Cache stores frequently accessed data on local nodes, thereby accelerating queries.
Compute Cluster Cache is divided into two types:
- Active Cache: Manually cache tables to the compute cluster through commands. Each time the compute cluster starts, these pre-cached tables will be automatically loaded. Currently, only AP type clusters are supported. Suitable scenarios include BI report queries, which can significantly reduce query latency and improve data processing speed.
- Passive Cache: During the first query, Lakehouse automatically caches the read files to the compute cluster. Subsequent queries involving the same table files will directly utilize the cache, speeding up the query process. Supports both GP and AP type clusters. For the second and subsequent queries, if they involve the initially cached tables, the cache will be directly hit.
Usage
-
Proactive Caching Table Method:
If you need to add a new table to the cache:
Viewing Cache Status:
When tables are loaded into the compute cluster using the ALTER..PRELOAD_TABLES command, there may be a delay in the update of the cache status displayed by SHOW PRELOAD. However, the cached tables are actually effective. Under normal circumstances, this delay is about 10 minutes.
- Active Cache Table Method:
- Display the preload table/partition status of the current virtual cluster:
- Display the preload table/partition status of the specified virtual cluster:
- Filter preload status information by table name:
- Display the preloaded cache summary information of the virtual cluster:
Precautions
- The cluster supports automatic start and stop. When the cluster stops, the cached tables will be automatically released. In AP type clusters, the pre-cached tables will be automatically loaded upon restart.
- After executing the cache command, only newly written data will be cached.
