Roles
Role Definition
In Lakehouse, a role is a tool for authorization management that groups several permission points together, and then grants this role to one or more users.
- When a user is granted a role, the user has all the permissions included in that role.
- Roles can also be granted more permission points, allowing for flexible expansion and management of permissions.
Compared to granting permissions to users one by one (ACL mode), assigning permissions through "roles" can significantly simplify the management process and is easier to maintain and audit. Therefore, it is recommended to fully use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) in daily permission management.
Role Types
Roles in Lakehouse are divided into two types: predefined roles and custom roles.
-
Predefined Roles
- Predefined roles are roles automatically configured by the platform when a service instance is created. Their permissions cannot be modified or deleted, but predefined roles can be directly granted to users.
- The platform provides multiple predefined roles, covering management from the instance level to the workspace level, helping users quickly complete basic authorization and use product features. For all system predefined roles and their default permissions, see Permissions of Built-in Workspace-Level Roles.
-
Custom Roles
- Users can create custom roles within the workspace scope according to their business needs, and flexibly configure and maintain the permissions of these roles.
- The permissions of custom roles can be modified or deleted at any time to adapt to changing business scenarios.
- Note: Currently, custom roles can only be created within a workspace and not at the instance level. The operation of creating custom roles is only supported through SQL execution and is not supported via the web interface.
Role Levels
The big data platform distinguishes metadata objects into "instance-level" and "workspace-level" categories, and roles are correspondingly divided into "instance roles" and "workspace roles":
Instance Role: Instance-level roles have two usage scenarios: 1) for global control of instance-level resources and operations; 2) for granting permissions across multiple workspaces.
Workspace Role: Applies to objects within a specific workspace (such as schema, table, virtual cluster, etc.). Workspace roles are bounded by the workspace and do not affect each other.
Management and Use of Roles
Viewing Roles
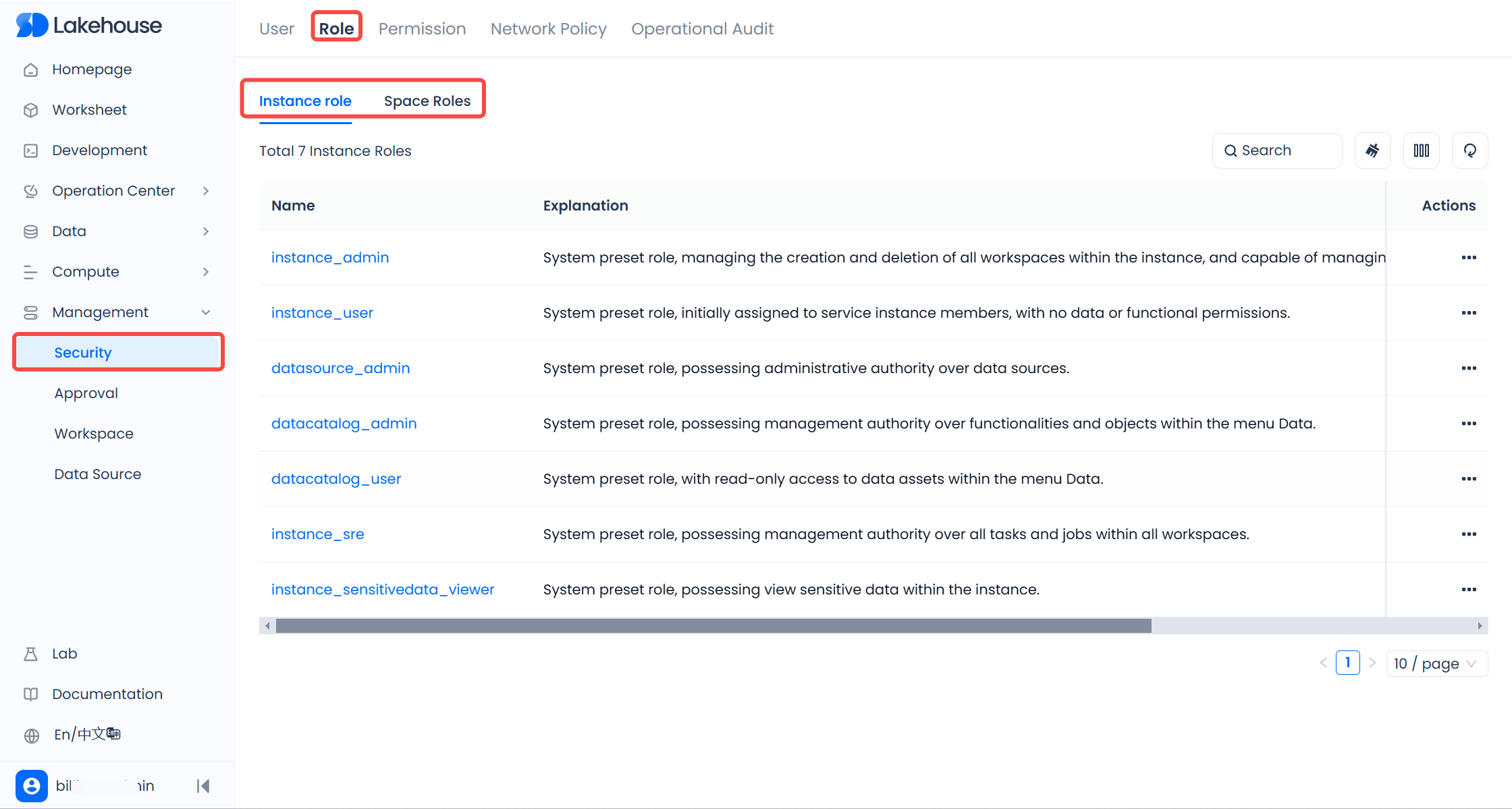
You can view the roles in the current instance and workspace in the "Management" - "Security" - "Roles" list.
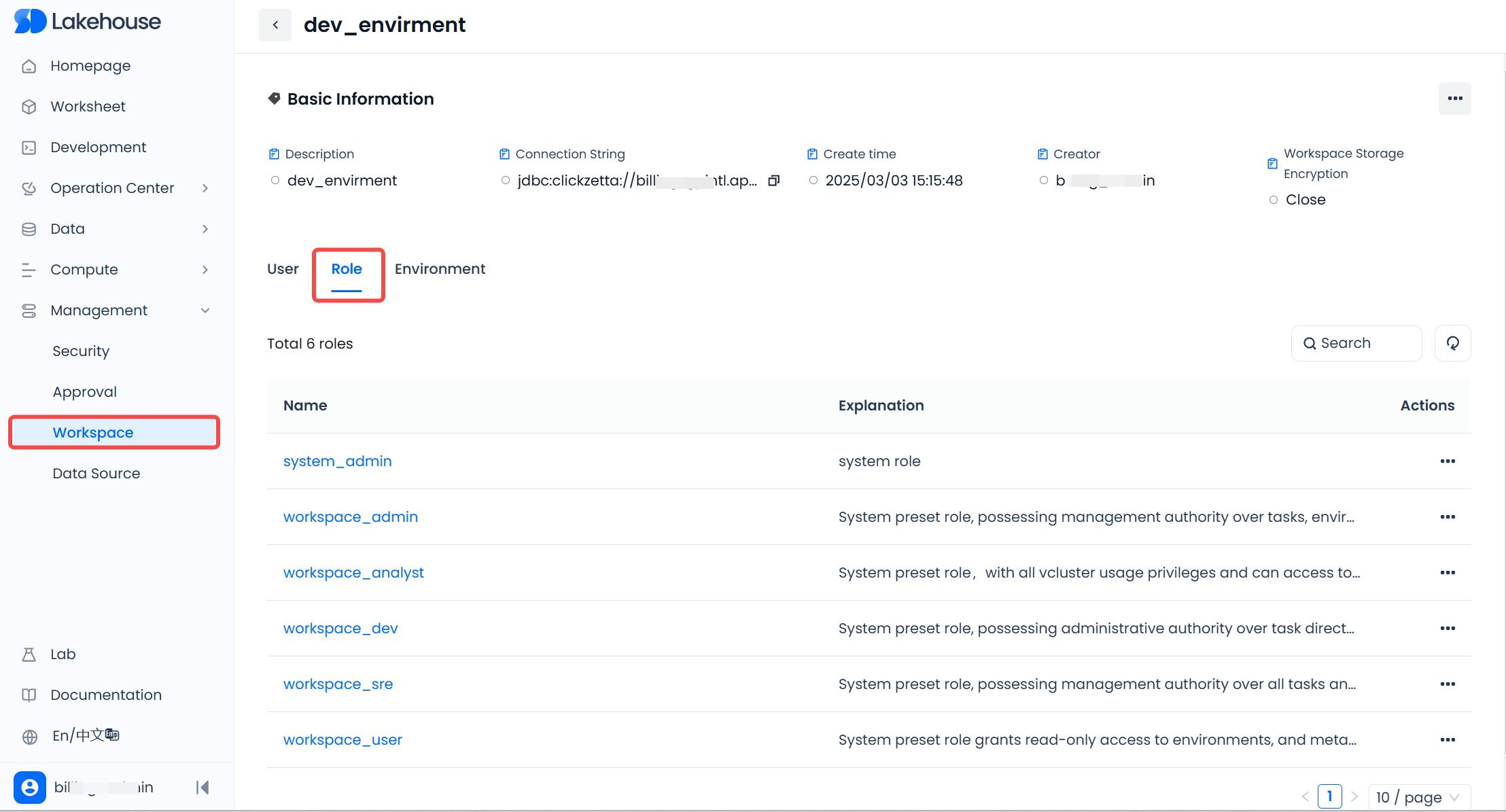
Or click into the workspace details page in the "Management" - "Workspace" list, switch to the "Roles" tab, and view all roles under the workspace.
Or execute the following statement in SQL to query all workspace-level roles in the currently connected workspace:
Granting Roles to Users
When a custom role is created and has the corresponding permissions, it needs to be granted to users so that they can actually use the permissions included in the role.
Roles can be granted to users via the Web interface or SQL.
Web Interface Operation
On the "Security" - "Roles" page, you can view the service instance-level roles and workspace-level roles under the current instance.
When authorizing any role, click the role name to enter the role details page, where you can view all users who have been granted this role. Click "+User Grant", check the users to be added in the pop-up window, and click "Authorize" to grant the role to the users.
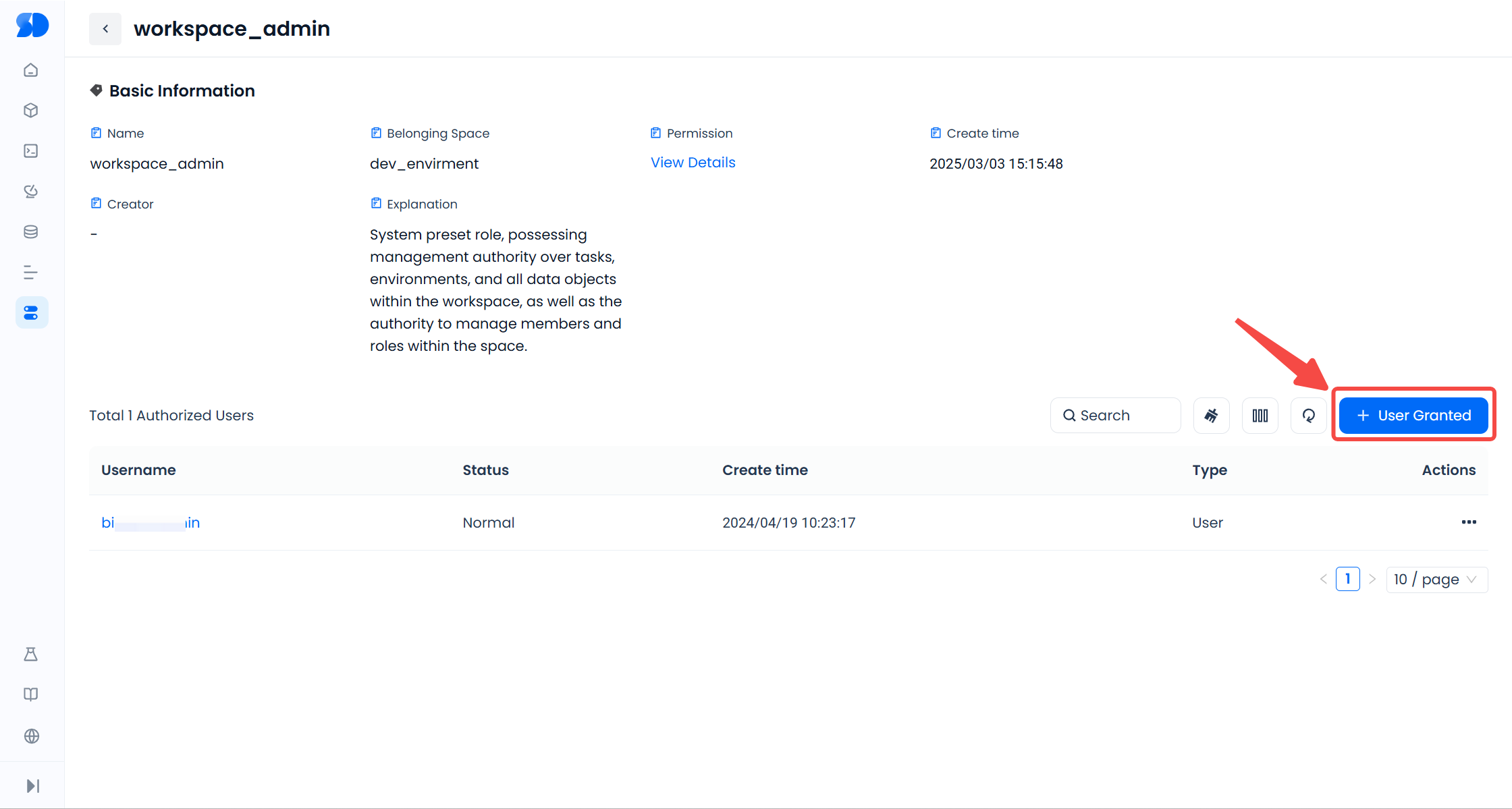
To remove a user from a role, click the "..." on the right side of the username and select "Remove User" to revoke the user's permission to use this role.
In the "Management" - "Workspace" list, enter the workspace details page, and in the "Roles" tab, you can also view the list of roles in the space and grant or revoke the role to users through the above operations.
SQL Operation
Only workspace-level users support using SQL operations for authorization. Execute the following statement in the workspace to grant the role in the space to the specified user.
To remove a specified user from a role, execute the following statement;
Create Custom User Roles
Currently, only workspace-level custom roles are supported, and the operation needs to be performed by a user with the workspace administrator (workspace_admin) role. Custom roles can only be created using SQL.
Example of creation syntax:
Add Permissions to Custom Roles
In the workspace, you can add permissions to custom roles using the GRANT statement. Example:
FAQ
-
What is the difference between roles and ACL (Access Control List)?
- ACL directly grants permissions to users; roles "package" permissions before granting them to users.
- For scenarios with frequent personnel changes or complex permission configurations, it is recommended to use roles to reduce repetitive operations.
-
Does it support multi-role overlapping permissions?
- Yes. A user can be granted multiple roles, and the final effective permissions are the union of the permissions of each role.
-
Can instance roles access the workspace?
- No. Instance roles and workspace roles do not affect each other. Instance roles do not have and cannot obtain permissions for workspace-level objects.
-
Can preset roles be modified or deleted?
- No. Preset roles are system-built and immutable roles, and you can only choose whether to grant them to users.
