Configure Access Control
This document introduces how to configure access control policies for accounts and metadata objects in Singdata Lakehouse. By properly configuring access control, you can ensure that data and object access is limited to authorized users and roles, adhering to the principle of least privilege, and enhancing system security.
Service Instance Level Management
Assign Additional Administrator Users to Service Instances
In Singdata Lakehouse, the user who creates a service instance is by default assigned the "instance_admin" role. To ensure that at least one user can perform instance-level management tasks (such as creating workspaces and managing instance-level roles), you must retain at least one user when removing a user granted the "instance_admin" role, otherwise, you will receive an error message. It is recommended to assign at least one more user as an instance administrator to avoid impacts due to user unavailability or other special circumstances.
Grant Instance-Level Roles
Instance-level roles can only be granted through the web interface. Only users with the "instance_admin" role can perform this operation.
In the service instance, open the "Management" - "Security" menu in sequence, click to enter, and switch to the "Roles" page.
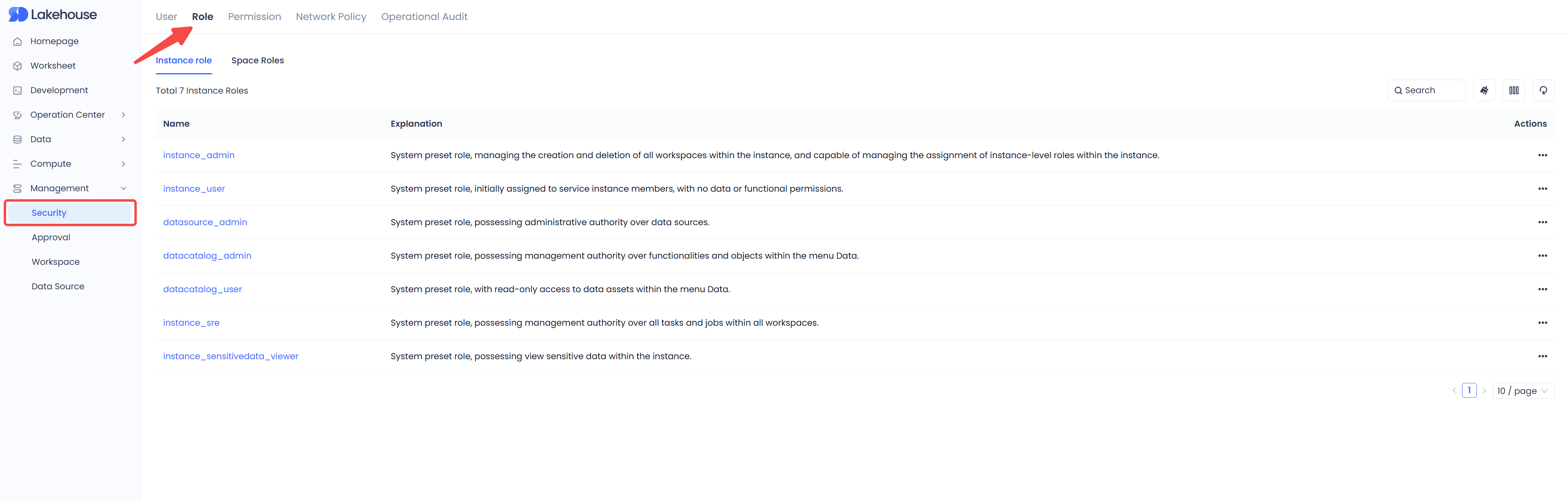
Click the service instance role you want to grant, enter the details page of that role, and click "Grant Users":
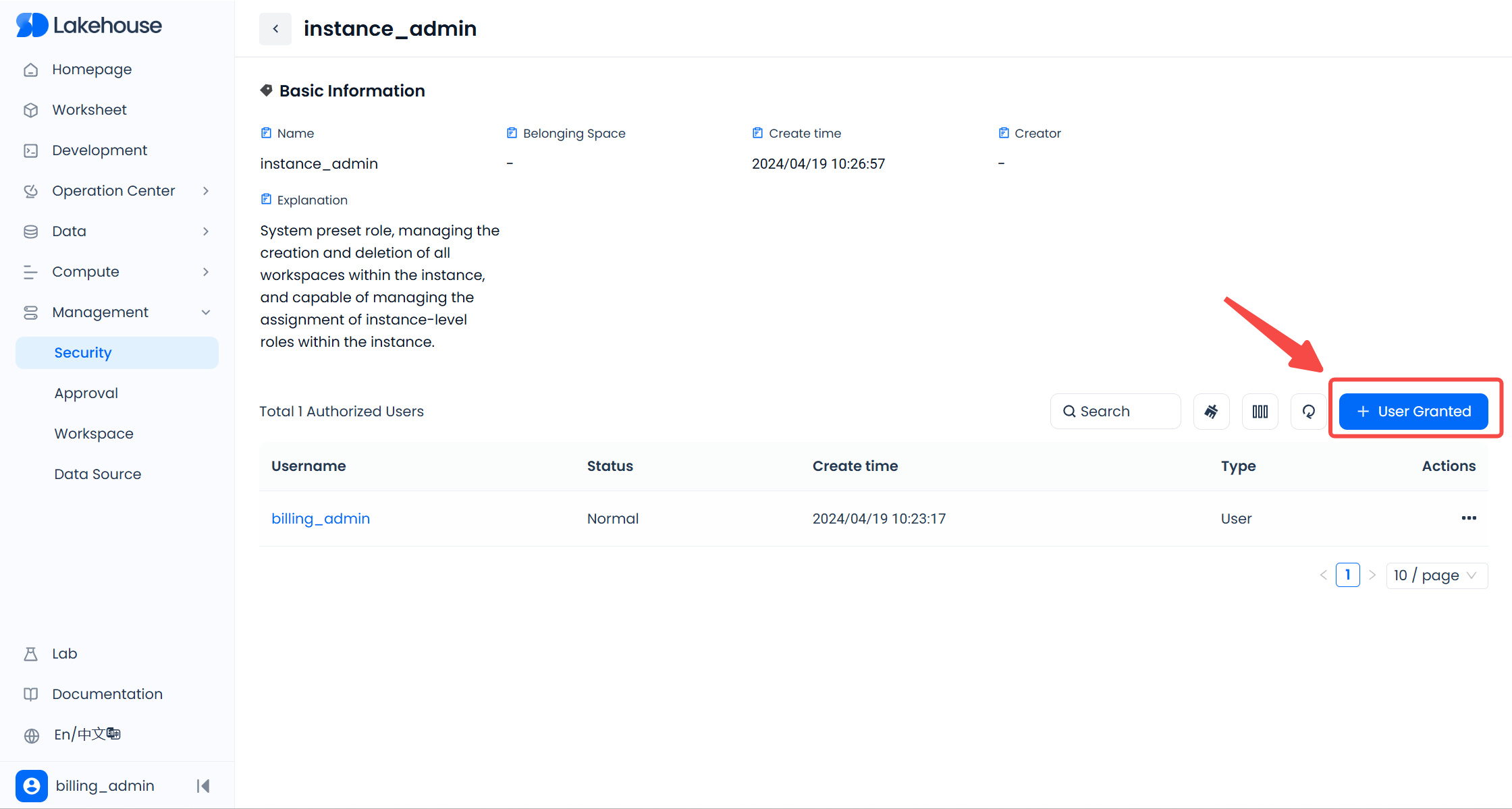
In the pop-up window, check the users you want to grant, and click the "Authorize" button to complete the granting of the instance role.
Workspace Level Management
Assign Workspace Administrators
The user who creates a workspace is by default assigned the "workspace_admin" role for that workspace, which has all permissions within the workspace. At least one user must be granted the workspace administrator role in each workspace, and multiple users can be granted simultaneously.
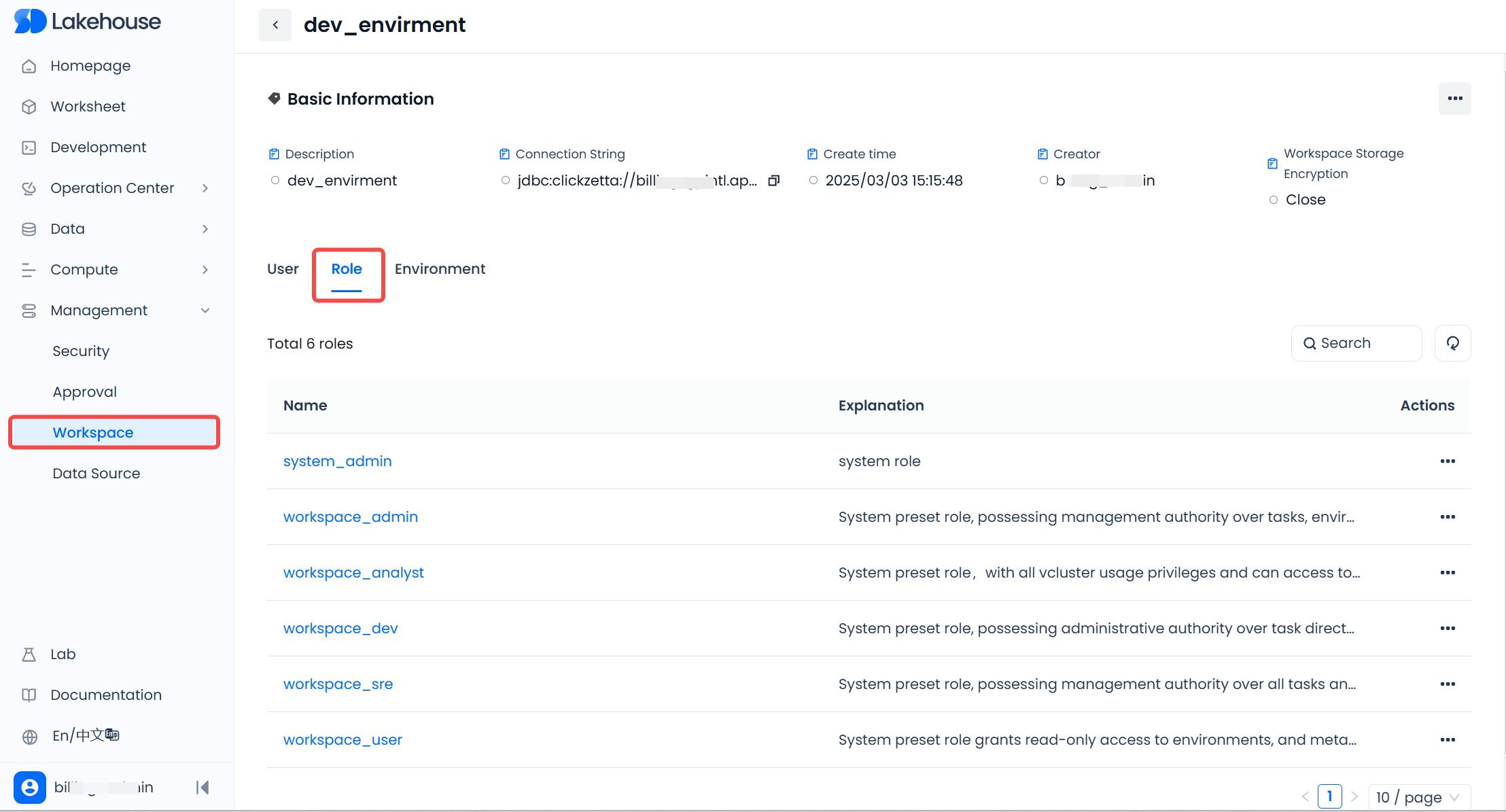
Manage Roles and Members within a Workspace
Roles and members within each workspace are independent of other workspaces and need to be granted separately. Only a workspace administrator (workspace_admin) can manage role grants, creation, deletion, and the addition or removal of members within that workspace.
Manage Workspace Members
A user needs to join a specified workspace to use the Virtual cluster (Vcluster) and execute SQL within that workspace. Workspace administrators can add specified users to the workspace in the following two ways:
Web Interface Operation
After entering the service instance, click "Management" - "Workspace" in the menu in sequence to enter the workspace list. Click the workspace name to enter the workspace details where you need to add members.
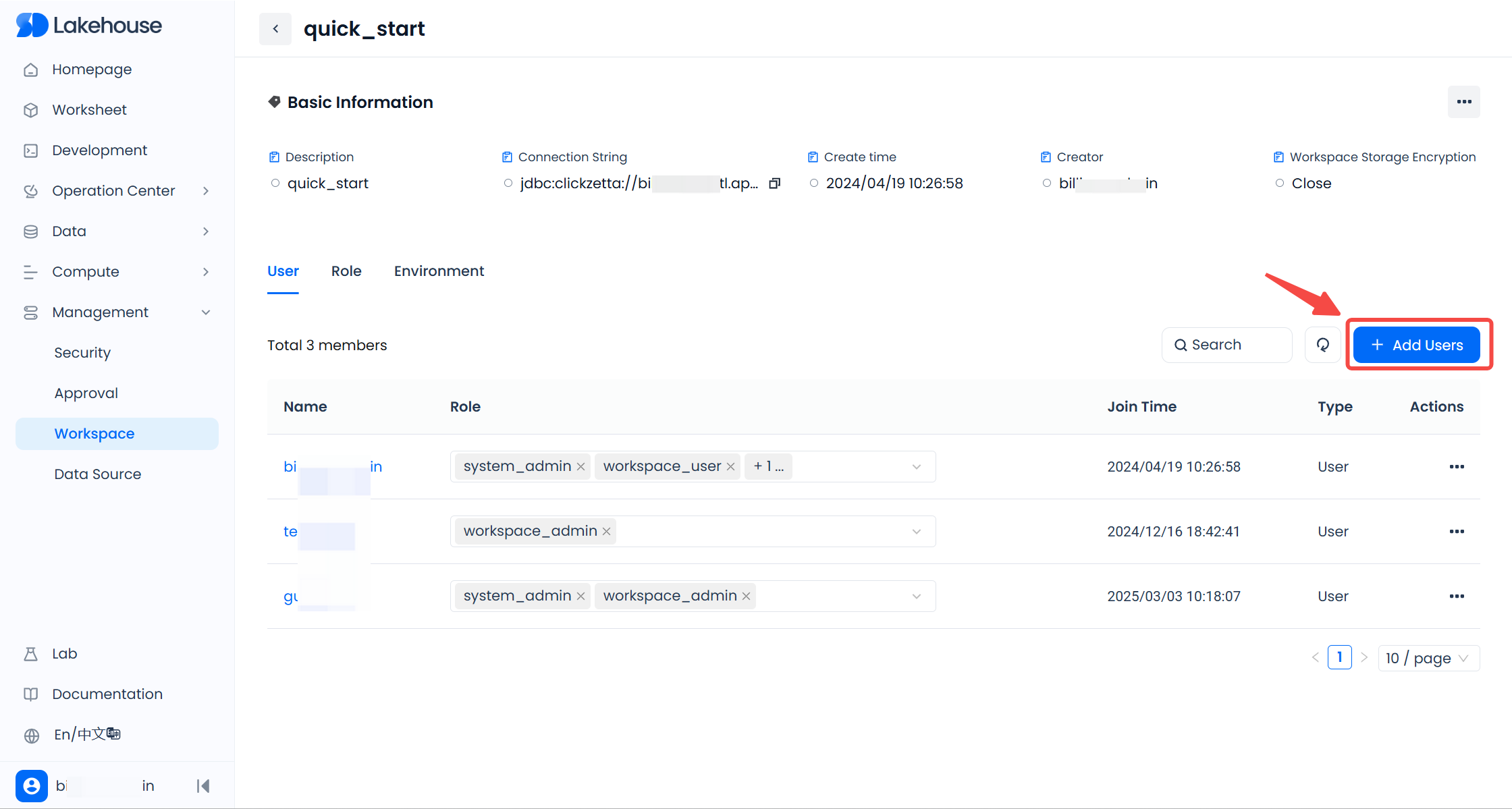
In the workspace details page, click the "+ Add User" button, and select the users you need to add in the pop-up window. Only users who already exist in the service instance and are not currently in this workspace will be listed. Check one or more users, then click the "Add User" or "Add User and Grant Role" button to add the selected users to the workspace. After successfully adding, you can find the newly added users in the "Users" list of the workspace.
In the "Users" list of the workspace, click the "..." in the operation column on the right side of a user, and select "Remove User" to remove the user from the workspace. The removed user will immediately lose the granted workspace roles and the permissions to use the Virtual cluster (Vcluster) and execute SQL within that workspace.
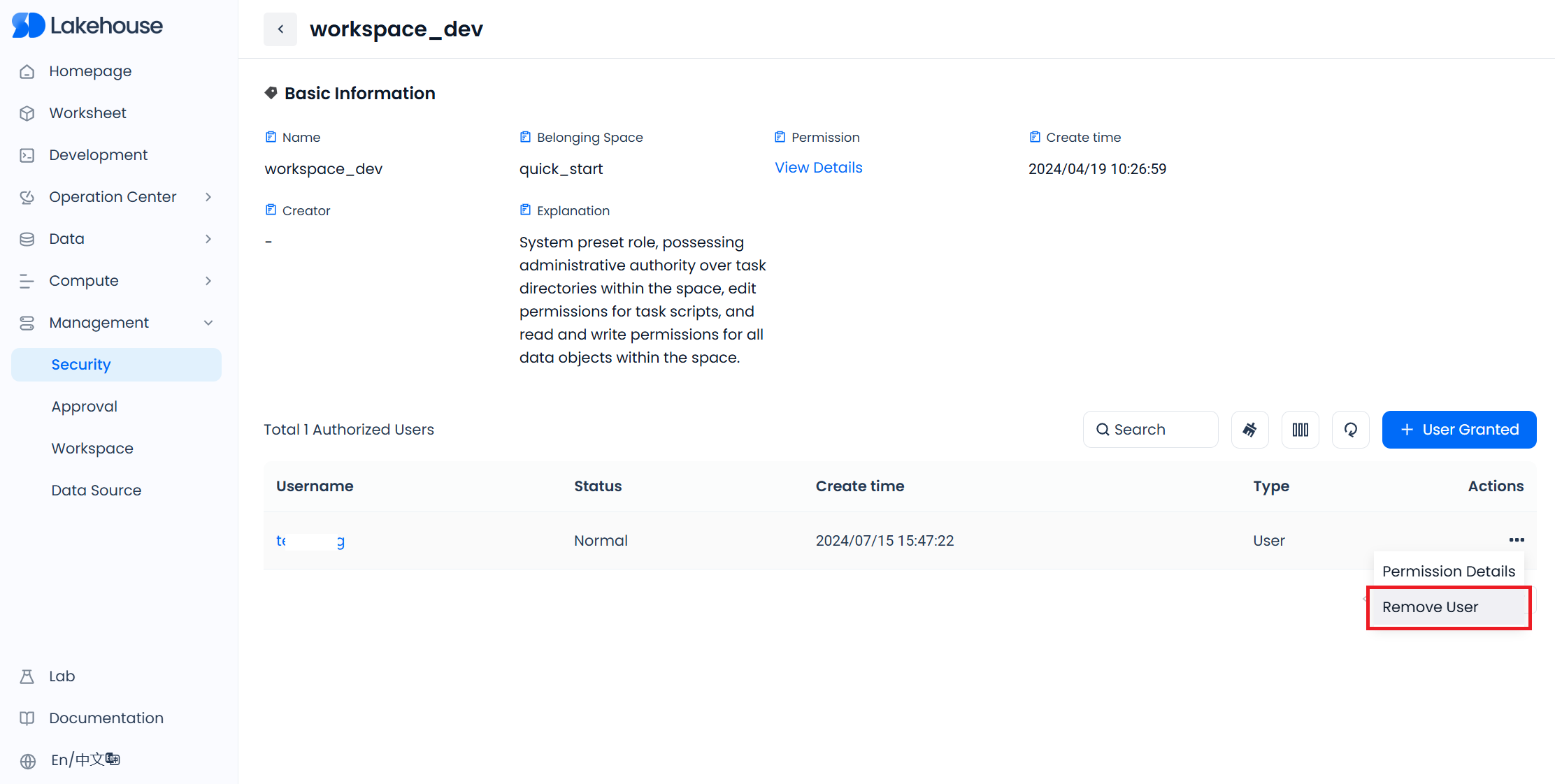
Please note that users removed from the workspace will still retain data permissions directly granted to them, meaning they can exercise the granted data permissions in other workspaces to query or modify data. Therefore, it is recommended to manage permissions by granting roles to reduce the difficulty of permission management in such scenarios.
SQL Operation
When adding users to a workspace via JDBC connection, execute the following statement:
<user_name> Replace with the username that needs to be added to the workspace. Only users who already exist in the service instance and are not currently part of this workspace can be added.
To remove a user from the workspace, execute the following statement:
<user_name> is replaced with the username that needs to be removed from the workspace. This operation will not delete the user's identity, it will only remove the user from the current workspace.
Using Workspace-Level Roles
Developing within the Workspace
Developing within the workspace requires: permission to execute SQL within the workspace (granted upon becoming a workspace member); permission to use computational resources within the workspace; and permission to operate on the required data objects.
The following roles are pre-configured in each workspace with one or more of the above permissions by default. These roles can be granted to users to quickly start data development.
Workspace Developer (workspace_dev) Role
The workspace_dev role by default has read and write permissions for all data objects (table, view, dynamic table, etc., see 'Metadata Objects') within the workspace, and has permission to use all computational clusters within the workspace.
Once a user is granted the workspace_dev role, they can directly perform data development on the Web page's "Development" feature or use the JDBC protocol.
Note that the read and write permissions for data objects granted by default to the workspace_dev role do not support secondary authorization. To grant other roles read or write permissions for data objects, use a user with the workspace_admin role.
Data Analyst (workspace_analyst) Role
The workspace_analyst role by default has permission to use all computational clusters within the workspace and has read metadata permissions for all data objects (table, view, dynamic table, etc.) within the workspace. However, it does not have select permissions for data objects, meaning it cannot execute select queries on any table or view. When using the workspace_analyst role for data query analysis, the select permission for the data objects to be queried must be granted to the workspace_analyst role to perform data query operations.
For data authorization operations for the workspace_analyst role, refer to the "GRANT" statement operation documentation.
Using Custom Roles or Users
Custom roles and users can also execute SQL statements for development or data query analysis within the workspace through authorization, but they cannot use the Web-based "Development" feature. Authorization for custom roles and users needs to be performed by a user with the workspace_admin role. Refer to the following statements for authorization:
Replace TO ROLE <CUSTOME_ROLE_NAME> with TO USER <USER_NAME> when authorizing users.
Submit and Operate Workspace Scheduling Tasks
Submitting scheduling tasks in the workspace can only be done through the "Development" feature on the web. The roles workspace_admin (workspace administrator) and workspace_dev (workspace developer) have the permission to "submit" job scripts as scheduling tasks.
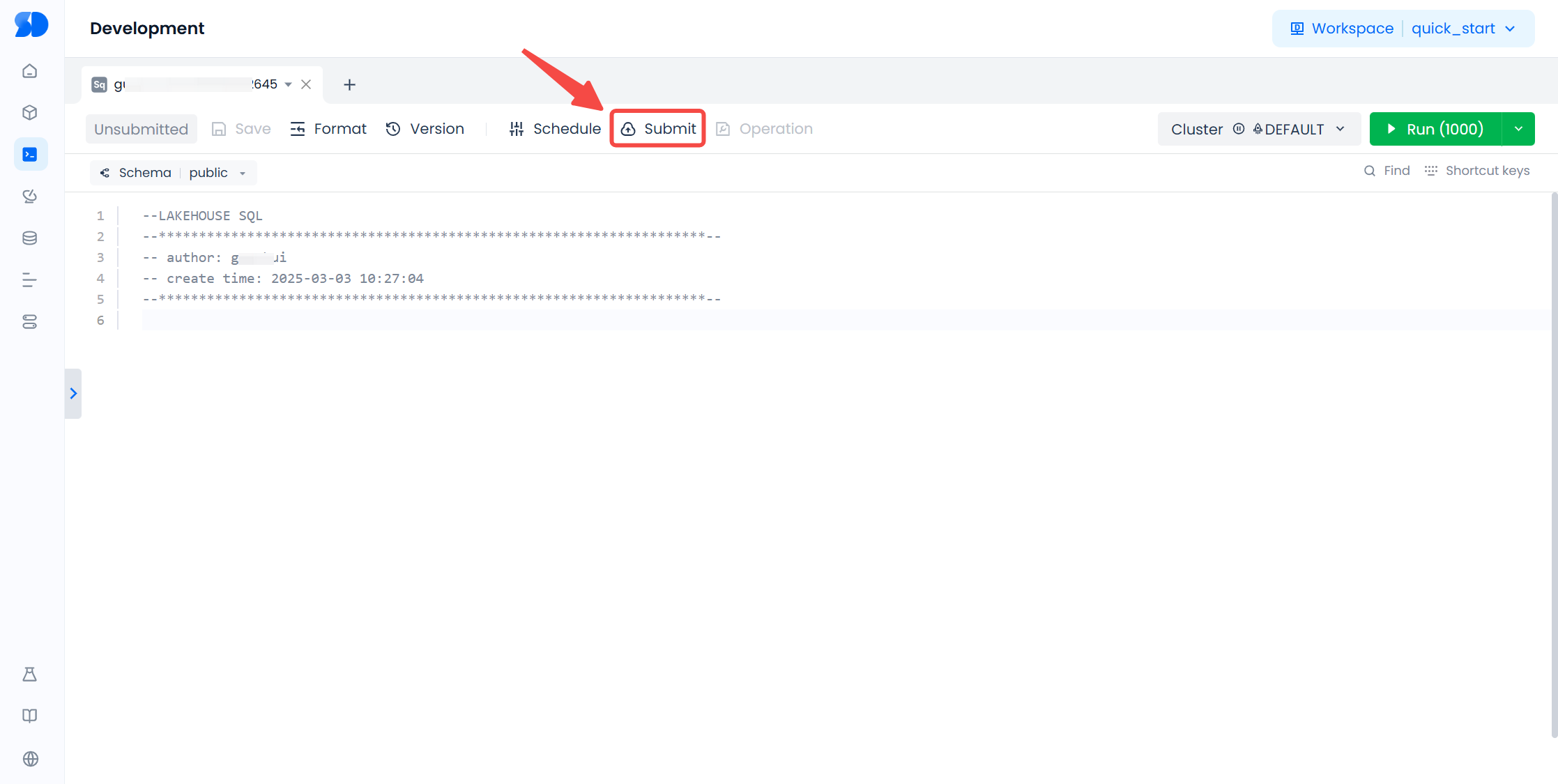
The system role for operating scheduling tasks in the workspace is: workspace_sre (workspace operations). Users with this role can manage scheduling tasks in their workspace through the "Task Operations" and "Monitoring and Alerts" features under the "Operations Monitoring" menu, as well as the "Data Quality" feature under the "Data" menu.
The workspace_sre (workspace operations) role has the permission to manage all scheduling tasks in the workspace but does not have the permission to use computing resources or query data objects in the workspace.
To manage scheduling tasks across all workspaces within a service instance, you can grant users the instance-level role: instance_sre (instance operations). This role's permissions are the union of the default permissions of all workspace_sre roles within the service instance.
Create Custom Roles
To practice the "principle of least privilege," it is recommended to create custom roles based on your organization's business functions and assign permissions for specific objects and operations to them. This way, you can precisely control users' access to specific data or objects.
General process for creating custom roles:
- Create a custom role (CREATE ROLE statement).
- Grant the necessary permissions to the role (GRANT statement).
- Grant the role to users who need the relevant permissions (GRANT ROLE statement or web operation).
Note: In Singdata Lakehouse, roles cannot be granted to other roles, meaning role hierarchy is not supported. All roles are ultimately granted directly to users, avoiding the complexity of determining specific user permissions due to hierarchical role inheritance.
Grant or Remove User Roles
You can grant or remove roles for users using the web or by executing authorization SQL statements. Only users with the service instance administrator (instance_admin) or workspace administrator (workspace_admin) roles can grant or remove roles for users. The service instance administrator (instance_admin) has the permission to grant instance-level roles to all users within the service instance; the workspace administrator (workspace_admin) has the permission to grant workspace roles to members within the workspace.
Web Operation
On the "Security" - "Roles" page, you can view the service instance-level roles and workspace-level roles under the current instance.
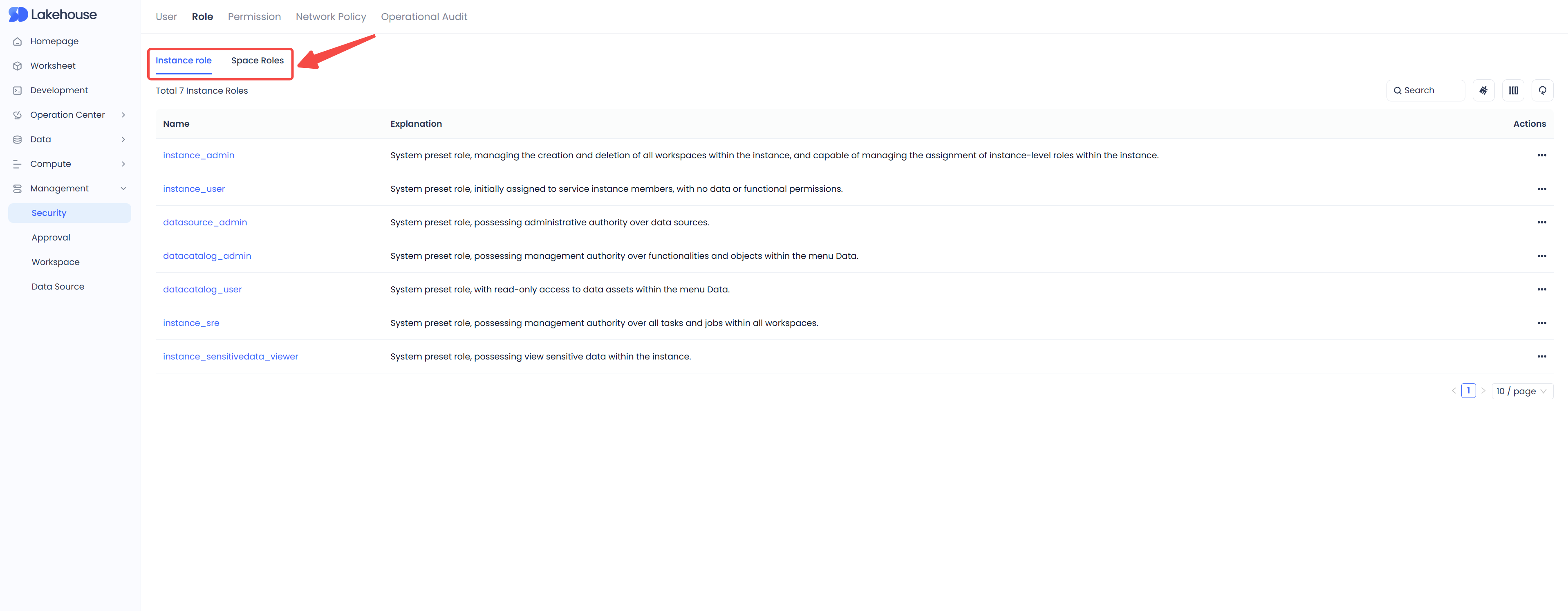
The service instance administrator (instance_admin) role can view all instance-level roles and all workspace-level roles and manage the authorization of all instance-level roles;
The workspace administrator (workspace_admin) role can view all workspace roles within the workspace and manage the authorization of these roles. If a user has the workspace administrator (workspace_admin) role for multiple workspaces, they can manage role authorizations across multiple workspaces.
To authorize any role, click the role name to enter the role details page, where you can view all users who have been granted the role. Click "+User Grant," select the users to be added in the pop-up window, and click "Authorize" to grant the role to the users.
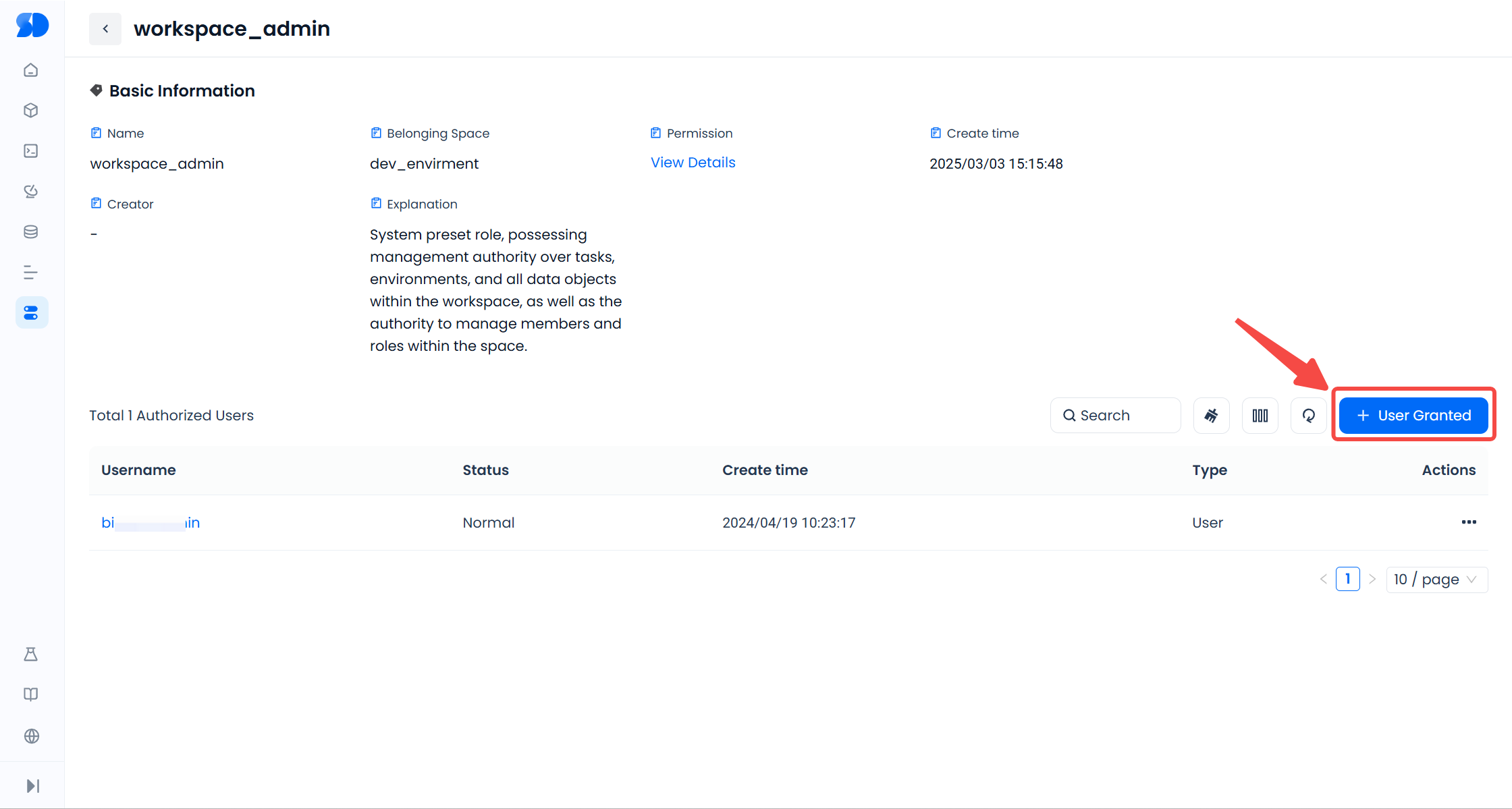
To remove a user from a role, click the "..." next to the username and select "Remove User" to revoke the user's permission to use the role.
In the "Management" - "Workspace" list, enter the workspace details page, and on the "Roles" tab, you can also view the list of roles in the workspace and grant or revoke roles for users through the above operations.
SQL Operation
Only workspace-level users support using SQL operations for authorization. Execute the following statements within the workspace to grant workspace roles to specified users.
To remove a specified user from a role, execute the following statement;
Example: Create a Custom Role and Grant Permissions
Note: Currently, creating custom roles and granting permissions to custom roles is not supported on the web. You need to use SQL to create custom roles.
Suppose you want to create a space-level role r1 to manage a specific table t1 under a schema s1. To do this, you need to grant r1:
- Usage permission (USAGE) for the virtual cluster (assume the name is v1).
- [Optional] Read metadata permission for the virtual cluster (assume the name is v1), so that this virtual cluster is visible on the virtual cluster page or in the show vclusters results.
- ALL permissions on the table s1.t1, to perform operations such as select, insert, update, alter, etc., on the table.
Create a Custom Role
Grant Permissions to Roles
Granting Roles to Users
Example: Creating a Read-Only Role
If you need a role that can only query (read-only access) all tables in a certain schema, you can follow the same process as creating a custom role. The difference in this scenario is that only the SELECT and READ METADATA permissions for the tables are granted, without any permissions for writing, modifying, or deleting. Additionally, the use of all tables in schema s1 is employed to express all current and future table objects under s1, simplifying the authorization expression.
For example, grant the read_only role the SELECT and READ METADATA permissions for all tables under schema s1:
Please note that if the read_only role does not have permission to use the virtual cluster, it will not be able to execute queries on the table using compute resources. Therefore, you also need to grant this role permission to use at least one virtual cluster (vcluster).
For example, grant the read_only role permission to use the virtual cluster named demo_vcluster.
View Granted Permissions
Use the SHOW GRANTS command to view the current permissions of an object or role. For example:
