Support Multiple Concurrent Queries with Horizontal Elastic Scaling
Overview
Through this tutorial, you will learn how to use the horizontal elastic scaling capability of the Lakehouse virtual compute cluster to support dynamically changing multiple concurrent queries from clients.
Import Scripts
Open the "Lakehouse Tutorial" on the console's Tutorial page and select the "Support Multiple Concurrent Queries with Horizontal Elastic Scaling" course. Follow the prompts on the page to import the script files needed for this course.
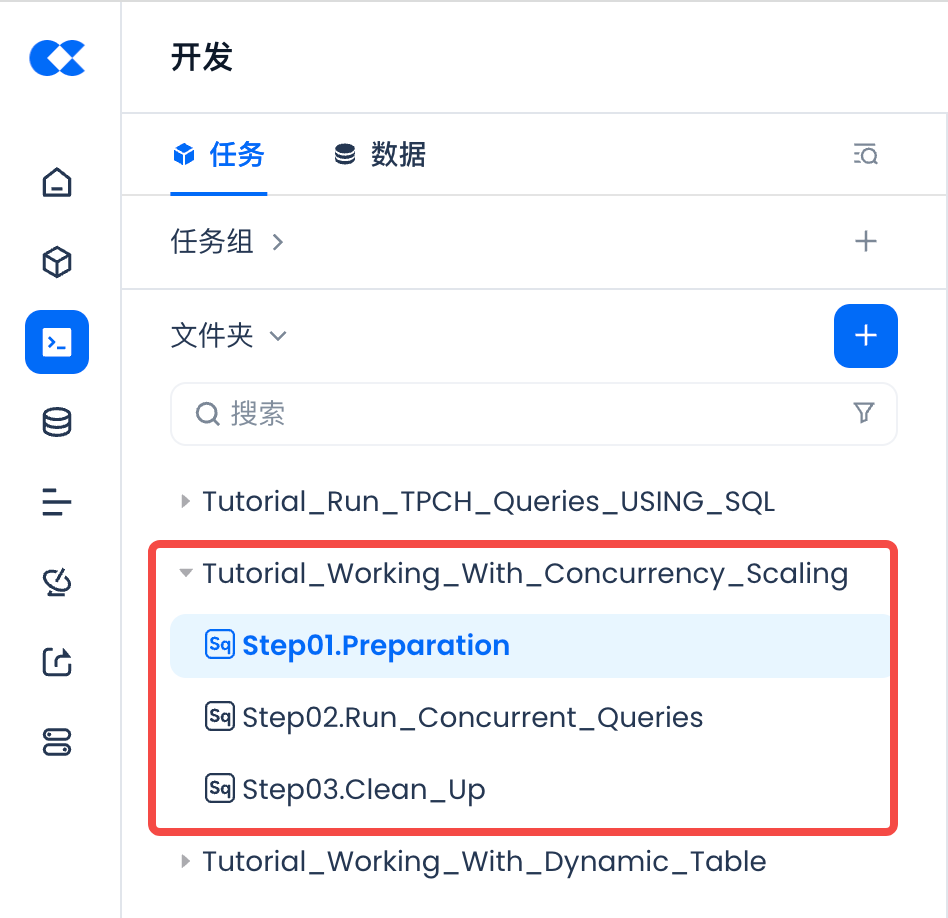
View the "Tutorial_Working_With_Concurrency_Scaling" directory in the "Development Module".
Basic Knowledge
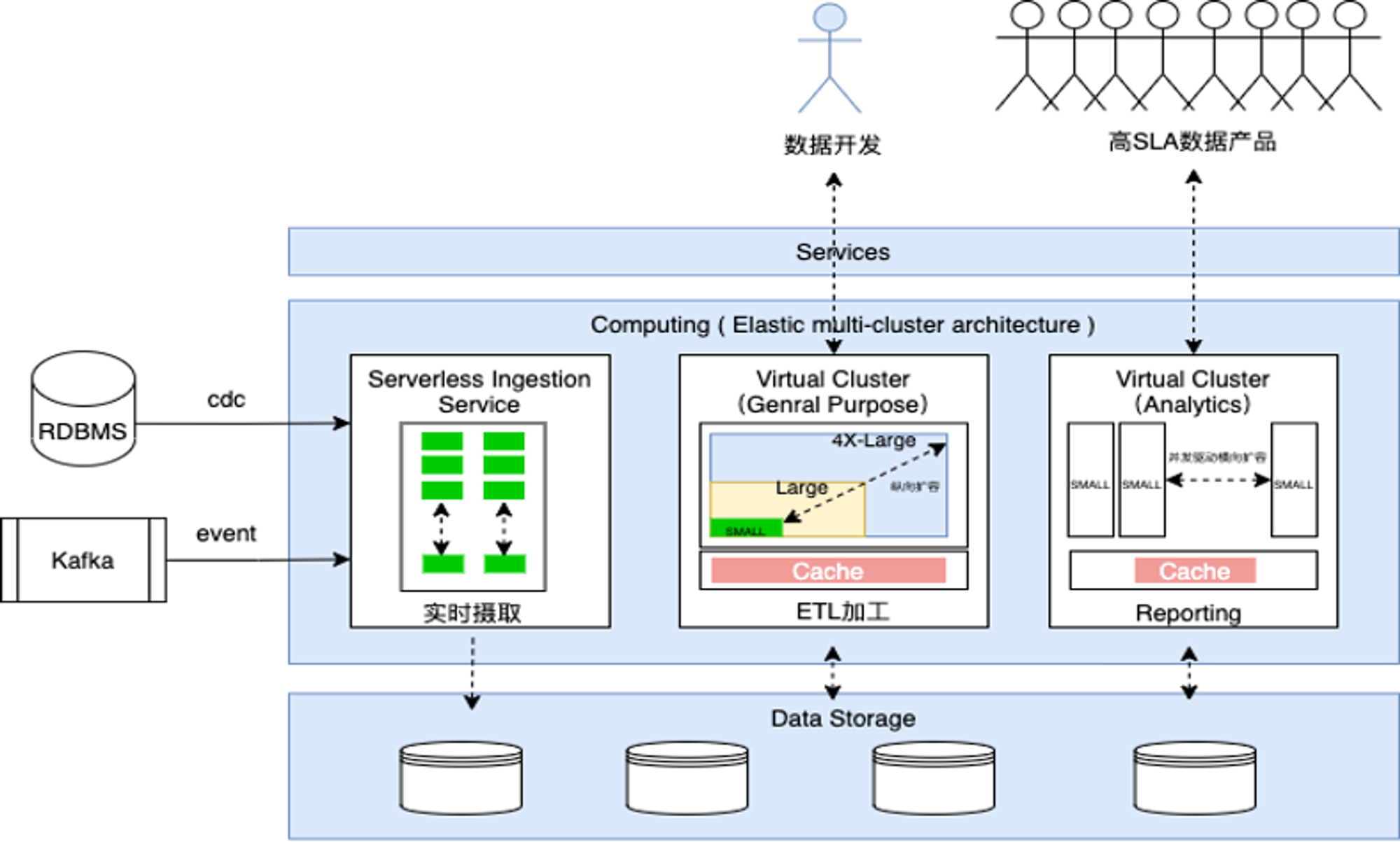
A virtual compute cluster (Virtual Cluster, abbreviated as VC or cluster) is a computing resource object provided by Singdata Lakehouse for data processing and analysis. Virtual compute clusters provide the CPU, memory, and local temporary storage (SSD medium) resources needed to execute SQL jobs in Lakehouse. Clusters feature rapid creation/destruction, scaling up/down, pausing/resuming, and are charged based on resource specifications and usage duration, with no charges incurred after pausing or deletion. Virtual compute clusters offer two types of clusters, general-purpose and analytical, to meet the isolation and optimization needs of different workloads for ETL and analysis scenarios.
Tutorial Steps
- Environment Preparation: Create a compute cluster for testing.
- Initiate Queries: Use the Studio Web environment to create Python tasks to perform continuous queries on Lakehouse with different concurrency levels, and observe the execution log results of the Python tasks to understand the cluster's rapid scaling capabilities under different concurrent requests.
- Clean Up Environment: Delete the compute cluster used for testing.
Through the above steps, you will be able to understand how to configure and use the elastic concurrency feature of virtual clusters and understand the performance of elastic concurrency.
Preparation
First, create an analytical compute cluster and enable and set the elastic concurrency feature through SQL commands.
This tutorial creates a cluster and sets the elastic scaling policy by running the [Tutorial_Working_With_Concurrency_Scaling->Step01.Preparation] SQL script task in the "Development" module.
Initiate Concurrent Queries Using Python Program
Open the [Tutorial_Working_With_Concurrency_Scaling->Step02.Run_Concurrent_Queries] Python concurrent task template in the [Development] module. You need to modify the connect connection configuration parameters before you can connect to Lakehouse and execute queries.

After modifying the connection information, please click to run the task and view the task execution log.

While executing the task, you can also view the cluster's concurrent requests and elastic scaling status through the cluster monitoring page.

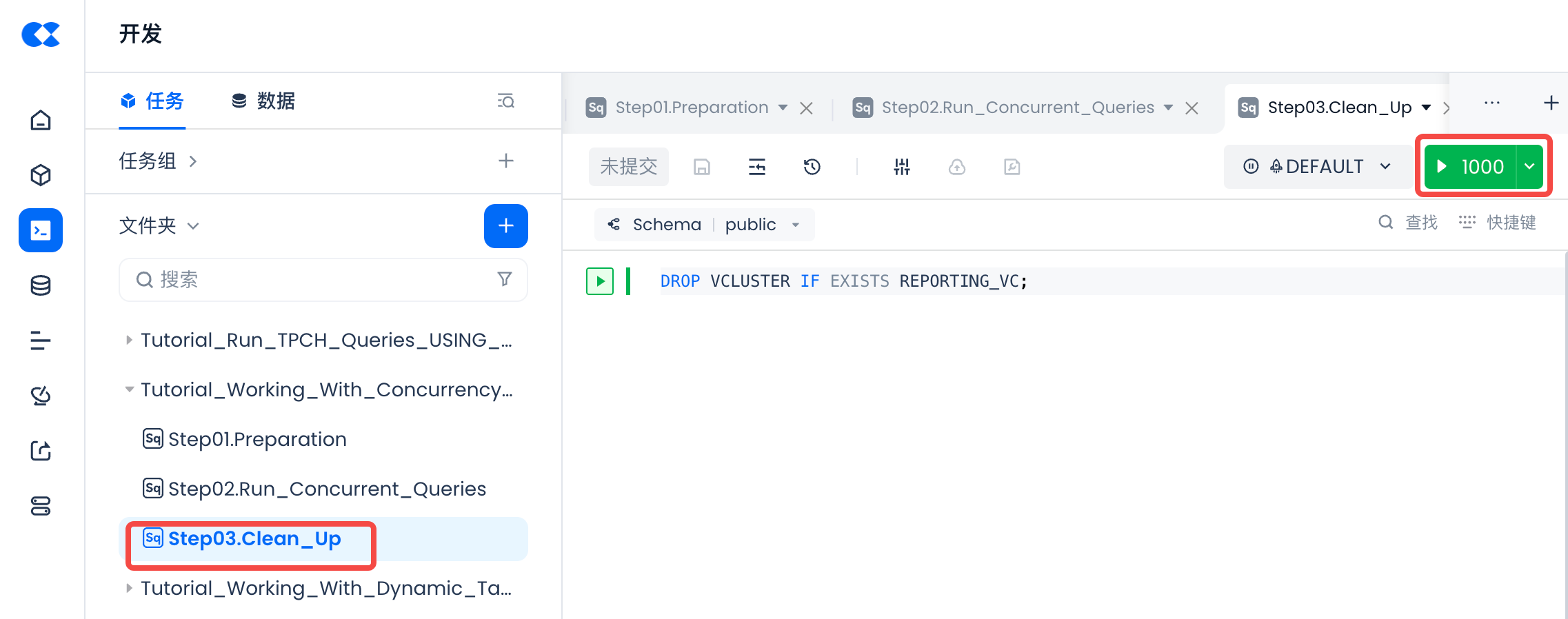
Environment Cleanup
Open the "Development" module [Tutorial_Working_With_Concurrency_Scaling->Step03.Clean_Up] SQL script file, execute the script to delete the test cluster for this tutorial.