Singdata Lakehouse Key Concepts
Welcome to Singdata Lakehouse! This chapter will introduce you to the basic concepts of Singdata Lakehouse in detail, helping you better understand and use this product.
Account
A Singdata account represents an organization or individual (usually a corporate account) that has established a business relationship with Singdata, covering actions such as account registration and service activation. The account is the basic entity for using Singdata product services, making payments, and obtaining service support. Upon registration, the system will automatically generate a globally unique account name, which serves as your unique identifier in Singdata products.
- The account is responsible for recharging, billing, payment, and ordering/changing Singdata products;
- All service instances and their resource objects activated on Singdata products by enterprises or individuals belong to a specific account.
Account URL
Each account has a unique account URL for accessing the management center. You need to log in using a valid username and password under that account. The format of the account URL is: <account_name>.accounts.singdata.com. For example, in the following link, 0256c297 is the account name: 0267c297.accounts.singdata.com.
User
After the account is successfully registered, you can create multiple users to share the resources within the same account. Different users can allocate data and resources through permission control.
Lakehouse Instance
A Lakehouse service instance is the carrier of Singdata Lakehouse product services. When activating the Lakehouse service, you need to create a service instance under your account based on the specified cloud service provider and region. An account can create one or more service instances (currently, only a single service instance creation is open by default).
Within the service instance, data objects, computing resources, and job tasks are managed using unified metadata, and tools such as data integration, development scheduling, operation and maintenance monitoring, and data catalog are used for application building and data management under a unified permission system. The service instance has regional attributes, and its computing, data, and other service resources are all within the region of the cloud service provider. Different service instances are isolated from each other by default.
:-: 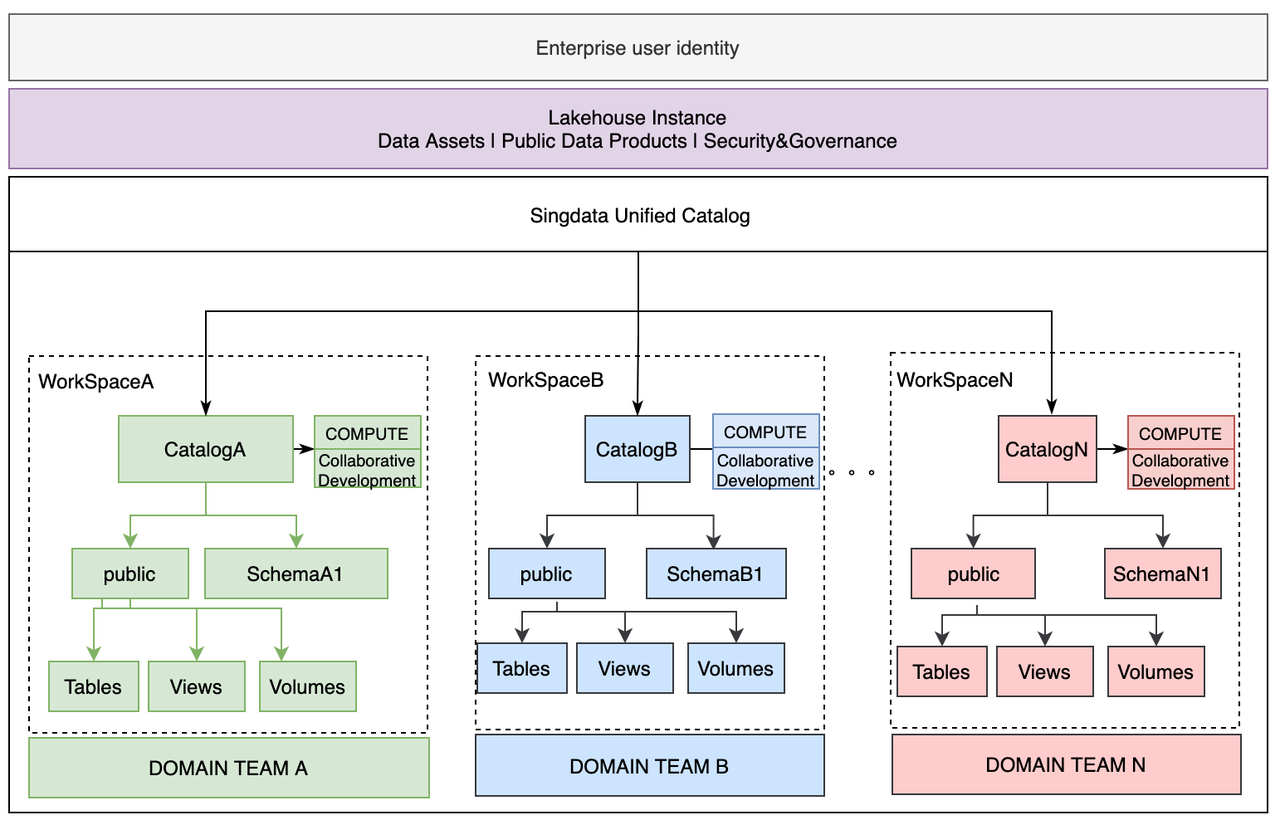
Workspace
A workspace is a logical object used to organize Lakehouse resource objects (data objects, computing resources, users, etc.) and provide supporting data development capabilities (data integration, data development, data operation, and maintenance). You can create multiple workspaces under one service instance. Workspaces are isolated by default, and users need to join a workspace to use the objects within it. Objects within different workspaces under the same instance can be shared through cross-workspace authorization. For how to manage and use workspaces, refer to Workspace Management.
Virtual Cluster
Computing resources consist of multi-instance virtual computing clusters and computing services running in the clusters, providing a computing environment for your jobs, including CPU, memory, and temporary storage. For details, see Compute Cluster.
Data Source
A data source stores the connection string information for data storage, such as the database address, access username, password, etc. Data sources can be used to configure data synchronization tasks or reference and consume data during data analysis. For details, see Data Source Management.
Schema
Within a workspace, a schema is a namespace for a set of database objects, including tables, views, etc. You can include multiple schema objects with different names within a workspace.
Table
A table is a formatted two-dimensional data table.
View
A view is a virtual table that does not actually exist in the database. When used, the view is dynamically generated.
Materialized View
A materialized view is a special type of view that, unlike a regular view, actually exists in the database and occupies storage resources. For details, see Materialized View.
Lakehouse Studio
Lakehouse Studio is a web-based integrated development and management toolset natively provided by Lakehouse, offering a graphical user interface designed to deliver comprehensive one-stop functionalities and an intuitive user experience. After logging into Lakehouse Studio via a browser, users can easily operate various product features on the interface, such as uploading/importing or synchronizing data, developing SQL tasks, scheduling jobs, configuring monitoring alerts, performing task operation, and managing users and permissions. Compared to accessing via JDBC protocol connections or CLI command-line tools, Lakehouse Studio provides richer native features and is more convenient and user-friendly. For details, see Lakehouse Studio.
Task Development
Task development is an integrated big data development environment where you can perform task development, debugging, configuration scheduling, and submission and release operations, completing the key processes of big data aggregation, processing, and analysis. In the left navigation menu, click "Development" to enter the main interface of the Web IDE. For details, see Task Development Overview.
Task Group
A task group is a virtual business management group used to manage a list of tasks within the development section. You can use task groups to organize and orchestrate a series of tasks, including adding/creating task nodes, creating dependencies between task nodes, configuring task group parameters, and performing unified batch submission operations. For details, see Task Group.
Maintenance Center
The maintenance center provides operational management operations for tasks and instances. The tasks managed by the maintenance center include manually triggered tasks and periodically scheduled tasks, and their corresponding instances, for centralized management. For details, see Task and Instance Maintenance.
Data Catalog
The data catalog is a bridge connecting data providers and data consumers. The data catalog builds the directory based on the metadata information of the tables and provides global search and filtering functions, making it easy to quickly find tables and view table details, assisting in the consumption and use of data. For more details, seeData Asset Map.
Workflow
A workflow is a data processing job flow object composed of one or more interdependent tasks. The workflow specifies the running environment and resources for the tasks. Jobs can be executed on-demand, periodically, or triggered by events.
Workflow Instance
When a workflow task is triggered, a workflow instance is generated. The workflow instance includes a timestamp and task status, created by the scheduling system based on the trigger conditions.
Task
A task is an atomic data development task, such as data synchronization tasks, SQL tasks, Python tasks, SHELL tasks, etc. Tasks are created, saved, and organized in a file format.
Lakehouse SQL Task
Refers to SQL query tasks generated in the Lakehouse through web-based data development features or CLI, JDBC connections, etc. For how to develop and schedule a Lakehouse SQL task, refer to Task Development and Scheduling.
Synchronization Task
Refers to data synchronization type tasks. Users generate synchronization tasks by configuring the synchronization data source and target data table. Synchronization tasks also consume computing resources and are metered. Synchronization tasks include two main categories: offline synchronization tasks and real-time synchronization tasks. For more details, see Data Sync.
Python Task
Python tasks refer to tasks that can write and run Python code. For many data analysis and processing scenarios, especially for BI+AI analysis scenarios, combining Python and SQL can greatly improve the efficiency of data analysis and processing. In Singdata Lakehouse, Python code is run by providing a Python script task type. For more details, see Python Task.
JDBC Task
JDBC tasks are an important task node in data development, allowing you to write SQL code to connect to data sources that support the JDBC protocol, enabling operations such as data addition, deletion, modification, and query. For more details, see JDBC Task.
Task Instance
A specific execution instance generated when a data development task is executed manually or scheduled.
More concepts and object model designs can be found in Object Model.
