Smart Supply Chain and its role in transforming business interventions

A Smart Supply Chain changes how businesses operate by introducing real-time data, automation, and digital tools. Companies now respond faster to risks, improve resource use, and share information better with partners.
Digital supply chains help firms recover quickly after disruptions and absorb shocks by using big data and AI.
IoT and real-time location systems uncover hidden problems and help managers make better decisions.
Blockchain and automation increase speed and trust in every step.
Company / Case | Technology Used | Competitive Advantage |
|---|---|---|
General Companies (McKinsey Study) | Advanced Data Analytics | |
Global Electronics Manufacturer | AI Inventory + Vendor-Managed Inventory | 18% lower costs; better on-time delivery |
Retail Chain | Real-time Analytics + Streamlined Logistics | 12% increase in same-store sales |
Firms that adopt a Smart Supply Chain gain stronger resilience, lower costs, and better customer service.
Key Takeaways
Smart Supply Chains use real-time data, automation, and digital tools to make businesses faster, more flexible, and cost-efficient.
Technologies like IoT, AI, blockchain, and robotics improve tracking, decision-making, and trust across the supply chain.
Companies adopting Smart Supply Chains reduce costs, cut waste, boost customer satisfaction, and recover quickly from disruptions.
Challenges include integrating old systems, ensuring data security, managing costs, and addressing talent shortages with training and partnerships.
Planning phased implementation, investing in skills, and strengthening supplier collaboration help businesses succeed with Smart Supply Chains.
Smart Supply Chain: Definition and Distinction
What Defines a Smart Supply Chain
A Smart Supply Chain uses advanced technology and data to manage goods, information, and relationships. Companies build these systems to improve speed, accuracy, and flexibility. Several key components set this approach apart:
Technology integration connects IoT devices, sensors, and blockchain for real-time tracking and transparency.
Data analytics turns raw information into insights, helping managers predict demand and optimize routes.
Supplier collaboration shifts from competition to partnership, leading to cost savings and new ideas.
Sustainability practices focus on reducing waste and using resources wisely.
Customer-centric strategies aim for faster delivery and ethical sourcing.
Description | |
|---|---|
Data Integration and Sharing | Real-time information from IoT, sensors, and RFID tags tracks goods and status. |
Analytics and Insights | Advanced analytics and machine learning support better decisions and demand forecasts. |
Automation and Robotics | Robots and automated systems handle repetitive tasks and transport. |
Predictive and Prescriptive Analysis | Data helps predict problems and suggest solutions before issues arise. |
Blockchain Technology | Secure records track product origins and movements. |
Supplier Collaboration | Digital platforms enable quick, clear communication with partners. |
Real-time Visibility | Live tracking monitors goods and conditions. |
Risk Management | Data-driven tools spot and reduce risks. |
Environmental Sustainability | Optimized routes and processes cut waste and emissions. |
Smart Supply Chains act as cohesive systems, improving competitiveness and responsiveness to market changes.
Smart Supply Chain vs. Traditional Supply Chain
Smart Supply Chains differ from traditional models in several important ways. Traditional supply chains often use manual processes and basic software. They rely on large inventories and slow, step-by-step workflows. These systems struggle to adapt when markets shift or disruptions occur.
Smart Supply Chains, on the other hand, use automation, real-time data, and advanced analytics. They respond quickly to changes and reduce errors. The table below highlights the main differences:
Feature | Traditional Supply Chain Management | |
|---|---|---|
Process Management | Linear, slow to adapt | Agile, flexible, dynamic |
Inventory | Large stockpiles, risk of overstocking | Optimized with real-time data |
Visibility | Limited, manual tracking | Real-time monitoring and tracking |
Efficiency | Manual, error-prone, slow | Automated, data-driven, fast |
Technology Use | Minimal automation, basic tools | AI, IoT, blockchain, advanced software |
Flexibility | Low, struggles with disruptions | High, adapts quickly |
Sustainability | Often inefficient, more waste | Optimized for less waste and emissions |
Smart Supply Chains address the weaknesses of traditional models by increasing visibility, automating decisions, and improving resilience. These features help companies stay profitable, efficient, and adaptable in a changing world.
Technologies Enabling the Smart Supply Chain

Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
IoT technology connects devices, sensors, and machines across the supply chain. These sensors collect real-time data on inventory, shipments, and equipment health. Managers use this information to track goods, monitor warehouse conditions, and prevent equipment failures. IoT sensors and RFID tags help companies automate warehouse management and predict maintenance needs. According to Gartner, 59% of organizations now use IoT in their supply chains. This widespread adoption improves traceability, reduces inventory loss, and increases operational efficiency. Real-time monitoring also helps companies manage shortages and surpluses, making supply chains more agile and resilient.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) play a major role in modern supply chains. AI-driven platforms connect with IoT devices and blockchain to provide real-time tracking and transparency. These systems use predictive analytics to forecast demand, manage risks, and select suppliers. AI-controlled inventory systems reorder stock automatically based on real-time data, which lowers costs and reduces errors. Companies use AI to optimize transportation routes, improve delivery speed, and cut fuel use. Collaborative robots, or cobots, powered by AI, work with humans to handle repetitive tasks, boosting safety and productivity. AI also helps companies meet sustainability goals by reducing waste and emissions.
Data Analytics and Predictive Insights
Data analytics turns raw information into useful insights. Supply chain managers use advanced analytics to predict demand, spot risks, and make better decisions. Predictive analytics helps companies prepare for disruptions like supplier bankruptcy or natural disasters. These tools also support proactive management by suggesting solutions before problems grow. Digital technologies such as blockchain, IoT, and AI work together to improve transparency and efficiency. Cloud computing and ERP systems integrate data from across the supply chain, making it easier to track products and manage operations. This digital transformation leads to faster, more accurate, and more responsive supply chains.
Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain technology brings a new level of trust and visibility to supply chains. Companies use blockchain to create secure, unchangeable records of every transaction. Each step, from raw material sourcing to final delivery, gets logged on a shared digital ledger. This process helps all partners see the same information at the same time.
Note: Blockchain reduces fraud and errors by making records permanent and easy to verify.
Key benefits of blockchain in supply chains include:
Traceability: Companies track products back to their origin. This helps prove authenticity and quality.
Transparency: All parties see the same data. This builds trust between suppliers, manufacturers, and customers.
Faster Audits: Auditors check records quickly because data stays organized and secure.
Reduced Disputes: Clear records help solve disagreements about shipments or payments.
A food company, for example, can use blockchain to trace a product from farm to table. If a problem occurs, they find the source quickly and take action. Blockchain also helps companies meet regulations by providing proof of compliance.
Automation and Robotics in Operations
Automation and robotics change how supply chains work. Companies use robots to move goods, pack boxes, and sort items in warehouses. Automated systems handle repetitive tasks faster and with fewer mistakes than people.
Speed: Robots work around the clock. They do not need breaks or rest.
Accuracy: Machines follow instructions exactly. This reduces errors in picking and packing.
Safety: Robots take on dangerous jobs. Workers stay safe and focus on tasks that need human skills.
Companies that use automation often see lower costs and higher productivity.
Some warehouses use automated guided vehicles (AGVs) to transport goods. Others use robotic arms to load and unload trucks. These tools help companies respond quickly to changes in demand. Automation also supports better inventory control by updating stock levels in real time.
A table below shows examples of automation in supply chain operations:
Automation Tool | Main Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Robotic Arms | Picking and Packing | Faster order handling |
AGVs | Moving Goods | Reduced labor costs |
Automated Sorters | Sorting Packages | Fewer shipping errors |
Automation and robotics help companies build supply chains that are fast, reliable, and ready for the future.
Business Interventions Transformed by Smart Supply Chain
Operational Efficiency and Process Optimization
Companies that adopt advanced supply chain technologies see major improvements in how they operate. Smart platforms powered by artificial intelligence help businesses plan better and reduce extra inventory. For example, Lenovo uses an AI-based demand sensing platform. This system improves planning accuracy and cuts surplus inventory by 20%. Forecast accuracy also rises by 25%. Amazon uses AI-driven warehouse automation and predictive routing. These tools speed up picking and packing, reduce shipping delays, and boost customer satisfaction. As a result, Amazon saves billions in operational costs and delivers more orders on time.
Company | AI Intervention | Operational Efficiency Improvements | Quantitative Outcomes / ROI |
|---|---|---|---|
Lenovo | AI-based demand sensing platform | Improved planning accuracy, reduced excess inventory | 20% reduction in surplus inventory; 25% improvement in forecast accuracy |
Amazon | AI-driven warehouse automation & predictive routing | Reduced shipping delays, improved customer satisfaction, faster picking and packing | Billions saved in operational costs; enhanced on-time delivery and productivity |
Many companies also use smart tools to optimize warehouse processing, fleet fuel use, and delivery routes. These changes lead to faster order processing, better inventory management, and less time spent on the road. For example, warehouse processing optimization can cut order processing time by 15%. Fleet fuel consumption analysis shows a 10% annual savings on fuel costs. Route efficiency improvements reduce delivery times by 12%. These results come from real-world case studies and statistical analysis.
Case Study Focus | Key Operational Improvements | Statistical Evidence / Metrics |
|---|---|---|
Warehouse Processing Optimization | 15% reduction in order processing time, increased throughput | Reduced standard deviation in processing times; significant F-statistic values indicating shift impact |
Fleet Fuel Consumption Analysis | 10% annual fuel cost savings | Statistically significant differences in fuel consumption across vehicle types confirmed by ANOVA |
Route Efficiency and Delivery Times | 12% reduction in delivery times | Significant variance between routes identified, enabling route optimization |
Inventory Turnover and Stock Management | Improved inventory accuracy, reduced stock holding costs | Enhanced F-statistic validating differences between product categories |
Packaging and Material Handling | 8% reduction in handling time, less material wastage | Statistically significant differences between packaging types and efficiency metrics |
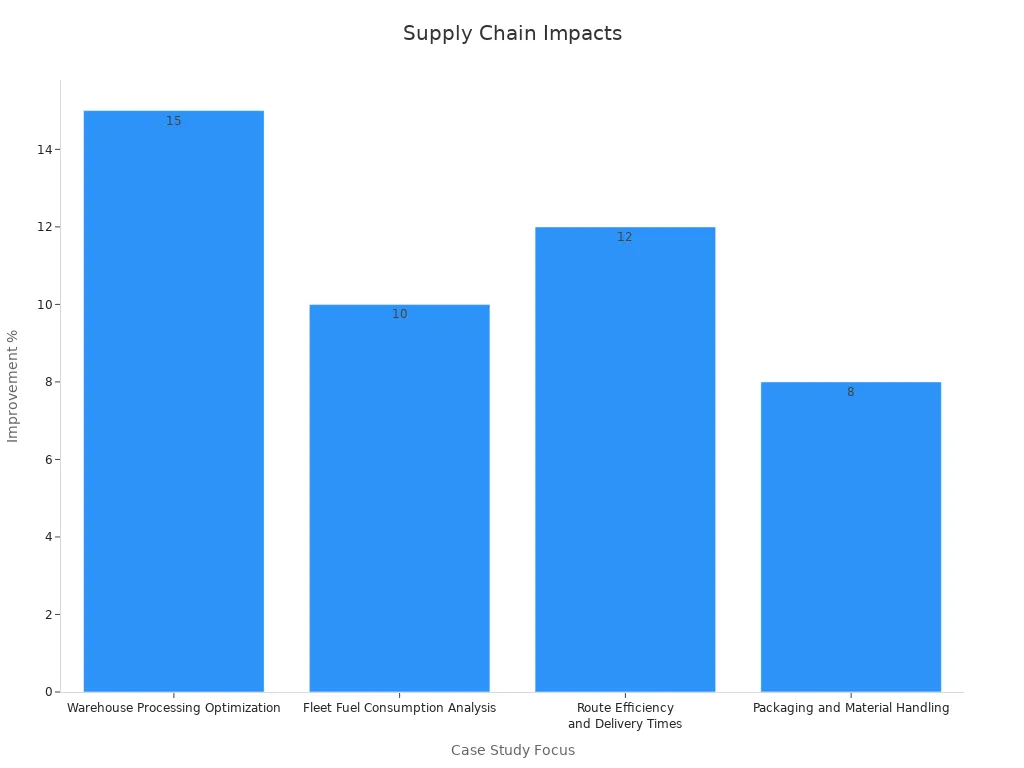
These examples show that Smart Supply Chain interventions help companies work faster, use fewer resources, and make better decisions.
Cost Reduction and Waste Minimization
Smart technologies help companies save money and reduce waste. Digital tools and sensors track fuel use, driver wages, and delivery times. For example, companies save about £1,876 per year on diesel fuel and £1,207 per year on driver wages. Each delivery takes less time, saving 0.09 hours per trip. Over a year, this adds up to 76.79 hours saved. The payback time for investing in sensor technology is about 4.2 years, making it a smart financial choice.
Metric | Value | Unit | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
Diesel Savings | 1876.15 | GBP/year | Annual savings on diesel fuel costs |
Driver Wages Savings | 1207.84 | GBP/year | Annual savings on driver wages |
Driving Time Saved per Delivery | 0.09 | hours | Reduction in driving time per successful delivery |
Total Time Saved per Year | 76.79 | hours/year | Aggregate time saved annually |
Payback Time for Sensorisation | ~4.2 | years | Time to recover investment costs on sensorisation |
In urban waste management, companies use smart bins and real-time data analytics to cut costs. For example, a circular supply chain model for spent coffee grounds uses data from 1,000 coffee shops. By placing pre-drying technology in the right spots, companies lower transportation and processing costs. Smart logistics also improve network efficiency and sustainability. These strategies show that digitalization and collaboration can reduce both costs and waste.
Enhanced Customer Experience and Responsiveness
Smart Supply Chain strategies improve how companies serve their customers. IoT and Big Data make supply chains more agile, productive, and transparent. These technologies help companies forecast demand, manage routes, and track products. As a result, shipping times get faster, and customers receive products more quickly.
IoT sensors and GPS data help companies choose the best delivery routes. This reduces delays and lowers environmental impact.
Big Data analytics allow companies to use customer feedback in product development. This leads to better products and higher satisfaction.
Temperature control in cold supply chains keeps products fresh. IoT time–temperature indicators help companies monitor conditions and reduce spoilage.
RFID tracking improves product traceability. Customers can see where their products come from and trust the supply chain.
Industry 4.0 technologies make it easier for customers and suppliers to share information. This builds trust and speeds up problem-solving.
Smart Supply Chain solutions support sustainable development by cutting carbon emissions and hazardous waste. Scenario analysis tools help managers plan for the future and keep supply chains resilient.
These improvements mean customers get better service, higher quality products, and more reliable deliveries.
Building Resilience and Agility
Companies face many risks in today’s global market. Disruptions can come from natural disasters, political changes, or sudden shifts in demand. Businesses need supply chains that can recover quickly and adapt to new situations. A Smart Supply Chain helps organizations build this kind of resilience and agility.
Smart Supply Chains use real-time data to spot problems early. Managers can see where goods are at any moment. They can react fast if a shipment gets delayed or a supplier has trouble. This quick response keeps products moving and customers happy.
Key ways Smart Supply Chains build resilience and agility:
Real-Time Monitoring: Sensors and tracking tools give instant updates on shipments and inventory. Managers can make quick decisions when issues arise.
Scenario Planning: Data analytics help companies test different “what-if” situations. They can prepare for events like strikes or weather problems.
Flexible Sourcing: Digital platforms connect businesses with many suppliers. If one supplier cannot deliver, companies can switch to another quickly.
Automated Alerts: Systems send warnings when something goes wrong. Teams can act before small problems grow bigger.
Companies that use Smart Supply Chains recover faster from disruptions. They also adjust more easily to changes in customer demand.
A table below shows how resilience and agility improve with Smart Supply Chain features:
Feature | Impact on Resilience | Impact on Agility |
|---|---|---|
Real-Time Data | Faster problem detection | Quick response to changes |
Multiple Suppliers | Less risk from disruptions | Easier to shift resources |
Predictive Analytics | Early warning for risks | Better planning for demand |
Automated Workflows | Fewer manual errors | Faster process adjustments |
Smart Supply Chains help companies stay strong and flexible, even when the market changes quickly.
Advancing Sustainability Initiatives
Sustainability has become a top priority for many organizations. Companies want to reduce waste, lower emissions, and use resources wisely. A Smart Supply Chain supports these goals by making operations more efficient and transparent.
Smart Supply Chains use technology to track energy use, carbon emissions, and material waste. Managers can see where resources get wasted and find ways to improve. For example, route optimization tools help delivery trucks use less fuel. Automated systems reduce packaging waste by using the right amount of materials for each order.
Ways Smart Supply Chains advance sustainability:
Energy Monitoring: IoT sensors track how much energy warehouses and vehicles use. Companies can spot high usage and make changes to save power.
Waste Reduction: Data analytics show where waste happens in the supply chain. Teams can adjust processes to cut down on scrap and unused materials.
Eco-Friendly Sourcing: Digital platforms help companies choose suppliers who follow green practices. This supports ethical sourcing and reduces environmental impact.
Transparent Reporting: Blockchain technology records every step in the supply chain. Companies can prove their products meet sustainability standards.
Smart Supply Chains make it easier for companies to meet government rules and customer expectations for sustainability.
A list of benefits from sustainable supply chain practices:
Lower operating costs from reduced energy and material use
Improved brand reputation with eco-conscious customers
Easier compliance with environmental regulations
Stronger relationships with responsible suppliers
Smart Supply Chains help businesses protect the planet while staying competitive in the market.
Smart Supply Chain in Action: Real-World Impact
Retail Industry Success Stories
Retailers have seen remarkable improvements by adopting advanced supply chain technologies. These changes help companies serve customers better and grow their businesses.
A $1 billion health food and supplement retailer used AI-driven marketing campaigns. By integrating data and using machine learning, the company increased customer re-engagement.
An international hardware retailer boosted revenue by 40%. This success came after launching a data-driven platform that enabled bulk sales and connected multiple systems.
Retailers now collect and use many types of data, such as demand, supply, inventory, logistics, and production data. They gather this information through ERP systems, IoT devices, RFID/barcode scanning, CRM systems, and supplier portals.
AI and data management tools allow real-time inventory tracking. These tools reduce stockouts and overstocks, improve turnover rates, and make replenishment more efficient.
AI-driven customer service features, such as personalized recommendations and optimized returns, increase sales and build customer loyalty.
Companies also use AI to find ways to cut waste and optimize transportation. These efforts save money and help the environment.
Retail shrinkage drops when companies use AI-powered predictive analytics, real-time theft monitoring, smart surveillance, automated auditing, and shelf-life optimization.
These examples show how technology-driven supply chains help retailers achieve higher sales, better customer experiences, and more sustainable operations.
Manufacturing Process Optimization
Manufacturers use smart supply chain tools to improve every step of production.
Companies leverage data from ERP systems, IoT sensors, and supplier portals to monitor supply, inventory, and production in real time.
AI and machine learning models help predict demand and adjust production schedules quickly.
Real-time inventory management reduces both shortages and excess stock, which improves turnover rates and lowers costs.
Automated auditing and smart surveillance systems help prevent losses and ensure quality.
AI identifies waste reduction opportunities and suggests ways to optimize transportation and resource use.
These strategies lead to faster production, fewer errors, and better use of resources. Manufacturers become more flexible and can respond quickly to changes in demand or supply.
Logistics and Distribution Innovations
Recent studies highlight how digital transformation in supply chains drives major improvements in logistics and distribution. In a multi-case study of 379 manufacturing companies in China, researchers found that smart supply chain adoption led to better operational performance. Companies improved delivery, manufacturing, and sourcing flexibility. When customer needs changed quickly, businesses used IoT, cloud computing, big data, AI, and blockchain to boost delivery flexibility. In times of supplier uncertainty, they turned to robotics, 3D printing, simulation, and augmented reality to enhance sourcing flexibility. These innovations helped companies deliver products faster, manage risks, and adapt to market changes.
Challenges in Smart Supply Chain Implementation
Integrating with Legacy Systems
Many companies struggle to connect new digital tools with old supply chain systems. Outdated ERP software often contains messy code and hidden weaknesses. These problems make it hard to share real-time data and increase the risk of cyberattacks. Siloed and manual processes slow down operations and reduce efficiency. To address these issues, experts recommend starting with small, modular AI solutions. Cloud-based platforms offer flexibility and work well with existing infrastructure. This approach allows companies to grow and adapt over time.
Tip: Begin with focused projects that solve specific problems. Expand as teams gain experience and confidence.
Data Security and Privacy Risks
Supply chains now connect many partners and systems. This connection increases the risk of cyber threats. A breach in one supplier’s system can affect many companies. Attackers may use malware, steal passwords, or exploit insider threats. Third-party suppliers also create risks, as hackers can use their systems to reach larger targets. Companies must protect their data by using strong authentication, encrypting information, and setting role-based access controls. Regular vulnerability checks help find and fix weak spots. Executive leaders now see supply chain security as a top priority.
A list of best practices for data security:
Authenticate and encrypt all data transmissions.
Apply role-based access controls.
Conduct regular vulnerability assessments.
Investment and Return on Investment (ROI)
Investing in new supply chain technology brings both risks and rewards. Many leaders worry about high costs and uncertain returns. Reports show that 62% of companies rate supply chain risks as high or very high. Disruptions can cost an average of $1.5 million per day. External threats, such as geopolitical instability and cyberattacks, cause even greater losses. However, AI adoption can reduce transportation costs by 5-10%. Companies also face pressure from investors to improve sustainability and transparency.
Aspect | Statistic / Data Point | Implication for Supply Chain Practices |
|---|---|---|
Workforce Shortages | 76% report significant shortages | Talent scarcity impacts operations |
Talent Gaps | 64% experience talent gaps | Hard to recruit skilled staff |
Investment Risks | 62% rate risks as high or very high | High risk awareness affects decisions |
Cost of Disruptions | $1.5 million loss per day | Shows financial impact of interruptions |
ROI via AI | 5-10% reduction in transportation costs | Indicates potential gains from technology investments |
Note: Careful planning and clear goals help companies measure ROI and reduce investment risks.
Addressing Skills and Talent Shortages
Many companies face a shortage of skilled workers in supply chain management. As smart supply chains use more advanced technology, the need for employees with digital skills grows. Companies must find ways to close this gap and build a workforce ready for the future.
Key strategies to address talent shortages:
Upskilling and Reskilling:
Companies invest in training programs to teach current employees new digital skills. These programs cover topics like data analytics, robotics, and artificial intelligence. Employees learn how to use new tools and systems, which helps them adapt to changing job roles.Partnerships with Educational Institutions:
Businesses work with universities and technical schools to create courses focused on supply chain technology. These partnerships help students gain real-world experience and prepare for jobs in the industry.Attracting New Talent:
Companies use internships, apprenticeships, and outreach programs to attract young people. They highlight career growth, innovation, and the impact of smart supply chains on society.
Tip: Companies that offer clear career paths and continuous learning attract and keep top talent.
A table below shows common skill gaps and solutions:
Skill Gap | Solution |
|---|---|
In-house training, online courses | |
Robotics Operation | Vendor-led workshops |
AI and Machine Learning | Certification programs |
Cybersecurity Awareness | Regular security training |
Smart supply chains need people who can solve problems, think critically, and use technology. Companies that invest in their workforce build stronger, more flexible supply chains. They also create a culture of learning and innovation. This approach helps businesses stay competitive in a fast-changing world.
Overcoming Smart Supply Chain Challenges
Phased Implementation Strategies
Organizations often face obstacles when adopting new supply chain technologies. A phased approach helps manage these challenges and reduces risk. Companies can start with pilot projects to show value before expanding. This method spreads costs over time and allows teams to learn from early results.
Pilot projects demonstrate return on investment and build confidence.
Middleware solutions connect new tools with existing systems, limiting disruptions.
Early stakeholder engagement and clear communication reduce resistance from staff.
Choosing vendors with strong support agreements ensures quick problem-solving.
Modular, scalable technologies allow for future growth without costly replacements.
Rigorous cost-benefit analysis justifies investments and highlights efficiency gains.
Open-source tools can lower expenses and provide flexibility.
By following these steps, companies can balance innovation with stability.
Workforce Upskilling and Training
Building a skilled workforce is essential for successful supply chain transformation. Companies invest in industry-specific training for technology, logistics, and data analytics. Internal learning programs, digital courses, and partnerships with educational institutions help employees gain new skills. Ford’s experience shows that targeted training, measured by skill assessments and productivity metrics, leads to real business improvements.
Continuous evaluation tracks progress, identifies barriers, and measures the impact on performance. Key performance indicators include skill acquisition rates, employee retention, and productivity. Companies also assess cost savings from reduced hiring and improvements in customer satisfaction. Long-term benefits, such as adaptability and morale, support ongoing business success.
Continuous learning and standardized metrics help organizations maximize the value of upskilling.
Ensuring Data Security and Compliance
Protecting data remains a top priority in digital supply chains. Companies use strong authentication, encryption, and role-based access controls to keep information safe. Regular vulnerability assessments help find and fix weak spots.
Compliance with data security regulations builds trust with partners and customers.
Proactive cybersecurity practices reduce the risk of breaches.
Unified data architectures limit data silos and improve oversight.
A secure and compliant supply chain supports business growth and protects valuable assets.
Measuring and Demonstrating ROI
Companies need to prove the value of smart supply chain investments. Measuring ROI helps leaders justify spending and guide future decisions. Clear metrics show how technology improves business outcomes.
Key Metrics for ROI in Smart Supply Chains:
Cost Savings: Track reductions in labor, transportation, and inventory costs.
Process Efficiency: Measure faster order processing, shorter delivery times, and fewer errors.
Revenue Growth: Monitor increases in sales due to better product availability and customer satisfaction.
Inventory Turnover: Calculate how often inventory sells and gets replaced.
Waste Reduction: Record decreases in material waste and energy use.
Tip: Use baseline data from before implementation. Compare it with results after deploying smart technologies.
A simple table can help teams organize ROI data:
Metric | Before Smart Supply Chain | After Smart Supply Chain | Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
Order Processing Time | 48 hours | 24 hours | 50% |
Inventory Costs | $500,000 | $400,000 | 20% |
Delivery Accuracy | 92% | 98% | 6% |
Waste Generated | 10 tons/month | 7 tons/month | 30% |
Companies often use dashboards to track these metrics in real time. Visual reports make it easier for managers to spot trends and share results with stakeholders.
Best Practices for Demonstrating ROI:
Set clear goals before starting any project.
Involve finance and operations teams in tracking results.
Share success stories with leadership and staff.
Review and update ROI calculations regularly.
Measuring ROI builds trust in new technology and supports ongoing investment in smart supply chains.
The Future of Smart Supply Chain
Emerging Trends and Innovations
Supply chains are changing quickly as new technologies appear. By 2025, companies will use more automation, machine learning, blockchain, and augmented reality. These tools help businesses make and deliver products in smarter ways. Procurement leaders now use advanced risk prediction tools. They also add sustainability goals to their supply chain plans. This shift helps companies become more agile and innovative.
Recent research shows several important trends:
Advanced automation and artificial intelligence improve logistics and inventory management. Companies that use AI see better results.
Automation and AI streamline inventory, manufacturing, and real-time logistics control.
Cloud-based supply chain technology is growing fast. Experts expect this market to reach over $40 billion by 2027.
Digital transformation can increase revenue by 20% and cut costs by half.
Resilient supply chains can expand output capacity by 25% or more.
Machine learning, blockchain, and augmented reality help companies predict risks and work better with suppliers.
These trends point to a future where supply chains are more transparent, data-driven, and able to handle risks. Companies will work closely with suppliers and use data to make better decisions.
Preparing for Continuous Transformation
Businesses must get ready for constant change. They need to build supply chains that can adapt quickly. Leaders should focus on three main areas:
Invest in Technology: Companies should choose flexible tools that can grow with their needs. Cloud solutions and automation help teams respond to changes faster.
Develop Skills: Employees need training in digital tools and data analysis. Ongoing learning helps teams stay ahead as technology evolves.
Strengthen Partnerships: Working closely with suppliers and partners builds trust. Sharing data and goals leads to better results for everyone.
Companies that plan for change will stay strong and competitive. They will meet customer needs and handle new challenges with confidence.
Smart Supply Chain solutions drive business transformation by enabling real-time visibility, predictive analytics, and automation. Companies gain efficiency, resilience, and customer satisfaction through data-driven decision-making and rapid response to disruptions.
Predictive analytics reduce costs and stockouts.
Automation increases productivity and accuracy.
Collaboration and visionary leadership foster ongoing innovation.
Businesses that embrace these strategies scale efficiently and adapt to changing markets. Leaders should prioritize digital integration and continuous improvement to stay competitive.
FAQ
What is a Smart Supply Chain?
A Smart Supply Chain uses digital tools, real-time data, and automation. Companies use these systems to track goods, predict demand, and improve efficiency. Smart Supply Chains help businesses respond quickly to changes and reduce errors.
How does a Smart Supply Chain improve customer experience?
Smart Supply Chains give customers faster deliveries and better product tracking. Companies use real-time data to avoid delays and keep products fresh. Customers see where their orders are at every step.
Which industries benefit most from Smart Supply Chains?
Retail, manufacturing, and logistics companies gain the most. These industries need fast, accurate deliveries and strong inventory control. Smart Supply Chains help them save money and serve customers better.
What challenges do companies face when adopting Smart Supply Chains?
Companies often struggle with old systems, high costs, and a lack of skilled workers. Data security also poses a risk. Many businesses start with small projects to manage these challenges.
Are Smart Supply Chains environmentally friendly?
Yes. Smart Supply Chains use less energy and create less waste. Companies track their carbon footprint and choose eco-friendly suppliers. These actions support sustainability goals.
See Also
The Journey From Automation To Intelligent Supply Chains
Using Consumer Insights To Drive Effective Business Actions
Multi-Layered Design For AI-Powered International Supply Networks
Incorporating Social Media Strategies Into Business Solutions
How Artificial Intelligence Is Revolutionizing Retail Shopping

