Inventory Structure Adjustment and its role in business interventions

Inventory Structure Adjustment drives measurable improvements in business performance. Companies see gains through key metrics such as inventory turnover rate, fill rate, and order accuracy.
Inventory turnover rate tracks how quickly stock moves.
Fill rate measures the percentage of customer orders fulfilled without backorders.
Order accuracy ensures correct products reach customers.
These adjustments help businesses lower costs, improve operational efficiency, and respond faster to market shifts. Strategic inventory positioning and advanced forecasting further boost responsiveness and cost savings.
Key Takeaways
Changing how companies manage inventory saves money and time.
It helps them work better and make more money.
Using tools like robots, smart computers, and online systems helps a lot.
These tools make counting items easier and faster.
They also help companies react quickly when things change.
Flexible plans, like Just-in-Time, help companies adjust fast.
These plans stop them from having too much or too little stock.
Checking inventory often and teaching workers is important.
Good training helps everyone use new systems well.
This keeps the company doing well for a long time.
When inventory is managed well, customers are happier.
Products are in stock, orders are right, and deliveries are on time.
Inventory Structure Adjustment: Definition and Relevance
What is Inventory Structure Adjustment?
Inventory Structure Adjustment refers to the process of changing how a business organizes, tracks, and manages its inventory. Companies use different systems and methods to fit their needs. Some use periodic systems, counting inventory at set times. Others use perpetual systems, tracking inventory in real time with software and barcodes. Businesses often choose their system based on cost, accuracy, and industry needs.
Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Ordering, storing, using, and selling inventory, including raw materials and finished goods. | |
Scope of Adjustment | Optimizing tracking and control using industry-specific strategies. |
Management Methods | JIT, MRP, EOQ, DSI—each method fits different business goals. |
Control Systems | Periodic (interval counts) or Perpetual (real-time tracking). |
Technology Use | Software, barcoding, and automation improve accuracy and decision-making. |
Industry Considerations | Perishable goods need tight timing; durable goods allow longer storage. |
Tip: Companies that use barcoding and automation reduce errors, speed up updates, and track inventory across many locations.
Why Inventory Structure Adjustment Matters for Business Interventions
Inventory Structure Adjustment helps businesses respond quickly to changes. Real-time tracking and modern technology, such as RFID, raise inventory accuracy rates to 98-99%. This improvement reduces labor costs and errors. Companies see fewer stockouts and smoother workflows. For example, cycle counting with automation keeps accuracy above 95%, while traditional counts only reach 80%.
Metric | Target/Benchmark | Impact on Effectiveness and Profitability |
|---|---|---|
Retailers: 4-6; Manufacturers: 10-12 | Higher turnover brings 10% higher profits. | |
Stock Days | 30-45 days | Cutting stock days by 10% can boost profits by 5%. |
Out-of-Stock Rate | Below 5% | A 1% drop in stockouts can raise sales by 2-4%. |
Fill Rate | Above 98% | Incorrect orders cost $13 per order on average. |
Lead Time | Reduce as much as possible | A 10% shorter lead time can lift profit by 7%. |
Inventory Accuracy | Above 95% | A 10% gain in accuracy can cut costs by 5%. |
These results show that adjusting inventory structure supports better business interventions. Companies gain higher profits, lower costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
Immediate Impact of Inventory Structure Adjustment
Operational Efficiency Gains
Companies that implement Inventory Structure Adjustment see immediate improvements in how they manage daily operations. They move products faster, reduce mistakes, and keep better track of stock. These changes help teams work smarter and avoid wasted time.
A recent case study highlights several key metrics that improve after adjusting inventory structures:
Metric / Aspect | Description / Outcome |
|---|---|
Inventory Turnover | Improved turnover rates after inventory adjustments |
Inventory Accuracy | Increased accuracy in stock records |
Stock Holding Costs | Reduced costs due to better inventory management |
Statistical Validation | ANOVA analysis with enhanced F-statistic confirming significant differences between product categories |
Inventory Turnover Ratio: Shows how often inventory is sold and replaced, reflecting better stock management.
Operating Expense Ratio: Measures expenses compared to revenue, helping spot cost reduction opportunities.
Profit Margins by Operational Unit: Reveals which departments gain the most from inventory changes.
Companies that track these metrics see faster order processing, fewer errors, and better use of warehouse space.
Enhanced Cost Control
Inventory Structure Adjustment leads to lower costs right away. Businesses spend less on storing extra stock and avoid tying up money in unsold goods. Lean inventory practices and smarter ordering policies help companies save money without hurting customer service.
Inventory leanness improvements can save between 32.87% and 60.90% on raw material management costs, depending on buffer levels.
Optimized procurement strategies cut total inventory management costs over two years, while keeping customer service levels near 99.99%.
Weekly Ordering Policies outperform other models, making cost control even stronger.
Some companies report savings of over 55% in inventory management investments by reducing holding costs.
Demand forecasting using causal methods matches industry patterns, supporting more accurate inventory adjustments.
KPI / Benefit | Description | Immediate Benefit After Inventory Structure Adjustment |
|---|---|---|
Percentage cost of holding inventory in storage | Reduced costs due to optimized stock levels | |
Total Inventory Value | Overall valuation of inventory held | Optimized inventory value reflecting better stock management |
Operational Cost Reduction | Lowered expenses from inventory optimization strategies | Decreased operational costs via reduced overstocking and liquidation of slow items |
Cash Flow Management | Working capital optimization through inventory reduction | Improved cash flow by reducing excess inventory |
Smart inventory adjustments help companies keep more cash on hand and spend less on storage and waste.
Improved Responsiveness to Market Changes
Firms that adjust their inventory structures respond faster to changes in demand. They can quickly increase or decrease stock levels when the market shifts. This agility helps them avoid lost sales during spikes and prevents overstock during slow periods.
An empirical study of 1,263 U.S. manufacturing firms during the 2008 financial crisis found that companies with strong inventory agility adapted better to sudden demand shocks. These firms showed higher awareness of market trends, strong motivation to act, and the capability to adjust resources quickly. The study linked inventory agility to better financial performance, showing that firms with flexible inventory structures avoided losses from both overages and shortages. This flexibility improved profitability and market standing, even during tough economic times.
Companies that stay agile with their inventory can meet customer needs faster and keep up with changing markets.
Core Benefits of Inventory Structure Adjustment
Cost Reduction and Profitability
Inventory Structure Adjustment helps companies lower costs and increase profits. Real-world examples show that Toyota used multi-echelon inventory optimization to reduce inventory levels while keeping production steady. Zara’s just-in-time approach cut holding costs and markdowns. Data analytics tools track inventory in real time, forecast demand, and analyze supplier performance. These tools improve turnover rates and reduce costs. Companies use formulas to measure savings, such as Total Savings = Σ (Reduction in Holding Cost_i - Implementation Cost_i). Lean practices like Just-In-Time reduce waste and holding costs. Data-driven strategies using ERP and predictive analytics can boost supply chain performance by up to 15%. Analytical methods, such as cost-volume-profit and break-even analysis, help companies find the best inventory levels for profit. These approaches show that smart inventory management leads to measurable cost savings and higher profit margins.
Risk Mitigation and Supply Chain Resilience
Adjusting inventory structures strengthens a company’s ability to handle risks and disruptions. Network data envelopment analysis (NDEA) measures the cost and benefits of risk strategies, including stockpiling and multi-sourcing. This method shows how inventory changes affect disruption costs, service levels, and recovery times. Companies that use these strategies see better resilience across their supply chains. Technologies like IoT sensors and blockchain also help by providing real-time tracking and transparency. These tools reduce risks such as counterfeiting and supply chain delays. As a result, businesses recover faster from disruptions and maintain steady operations.
Customer Satisfaction and Service Quality
Inventory Structure Adjustment directly improves customer satisfaction and service quality. Real-time inventory management software allows accurate stock tracking and demand forecasting. Just-In-Time practices keep products fresh and reduce excess stock. Customer feedback helps companies spot and fix fulfillment issues. Predictive analytics use sales history and feedback to forecast demand and ensure timely deliveries. Integration with sales and supply chain systems reduces errors and boosts order accuracy. Companies that train staff and work closely with suppliers see fewer delays and better fulfillment.
Companies that use these strategies report higher customer satisfaction and more reliable service.
Real-time tracking and demand sensing optimize inventory and reduce stockouts.
Cycle counting improves inventory accuracy and prevents errors.
Accurate product availability and delivery information increase customer trust.
Operational Agility and Flexibility
Operational agility and flexibility allow businesses to adapt quickly to changing market conditions. Companies that adjust their inventory structures can respond faster to customer needs and unexpected disruptions. This adaptability leads to better performance and stronger competitiveness.
Key performance metrics highlight how inventory adjustments improve agility and flexibility:
Inventory levels show how well a company maintains stock to meet sudden demand.
Sales trends help teams spot shifts in customer preferences and act quickly.
Order fulfillment rates measure how fast and accurately companies deliver products.
Real-time dashboards give managers instant insights for quick decisions.
Unified order management systems streamline processes, ensuring timely and accurate deliveries.
These metrics help companies allocate resources efficiently and keep customers satisfied. When teams monitor these indicators, they can react to demand spikes or drops without delay.
Other important measures include:
Changeover efficiency, which tracks how quickly teams switch between products or processes.
Capacity utilization, showing how well a company uses its resources.
Configuration adaptability, reflecting the ability to modify operations for new requirements.
Cost impact, which evaluates the financial results of flexible practices.
Customer response speed, measuring how fast a business adapts to market changes.
Volume adaptation rate and process variation, both part of the Flexibility Performance Index (FPI), which quantify how well a company manages change.
Companies that focus on these metrics build a flexible operation. They can shift production, adjust inventory, and meet customer needs with minimal delay.
Operational agility and flexibility reduce risks from supply chain disruptions. They also help businesses seize new opportunities as soon as they arise. By tracking the right metrics and making smart inventory adjustments, companies stay ahead in dynamic markets.
Strategies for Effective Inventory Structure Adjustment
Demand Planning and Forecasting
Demand planning and forecasting form the backbone of effective inventory management. Companies use these strategies to predict customer needs and align stock levels with actual demand. Predictive analytics plays a key role by analyzing historical sales, real-time market signals, and external factors such as weather or economic trends. Businesses that use predictive analytics for demand forecasting often see a 10-20% reduction in forecast errors and a 10-15% increase in revenue. These improvements help companies avoid both stockouts and excess inventory.
AI and machine learning models adapt quickly to changes in demand. They refine forecasts continuously, ensuring inventory matches real-world needs. Teams that collaborate across departments can optimize inventory levels, reducing the risk of overstock or shortages. Real-time demand sensing allows companies to adjust orders when actual demand exceeds forecasts, preventing missed sales opportunities.
Note: Accurate demand forecasting not only improves product availability but also reduces delivery times and boosts customer satisfaction.
Key benefits of demand planning and forecasting include:
Lower inventory costs by minimizing excess stock.
Better cash flow management through reduced overstock.
Enhanced supply chain resilience by adapting to market changes.
Improved customer service due to higher product availability.
Strategy | Description | Benefits | Challenges/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
Demand Planning | Forecasting future customer demand to optimize inventory levels. | Minimizes stock-outs, reduces excess inventory, improves turnover, enhances satisfaction. | Requires accurate forecasts; risk of errors. |
Safety Stock Optimization
Safety stock acts as a buffer against unexpected demand spikes or supply chain delays. Companies optimize safety stock by using statistical methods that consider demand variability, lead time uncertainty, and service level targets. For example, a 95% service level uses a Z-score of 1.65 in the safety stock formula. Regular reviews and updates ensure that safety stock levels remain aligned with current market conditions.
AI-driven demand forecasting and real-time tracking systems help prevent stockouts. Multi-echelon inventory optimization reduces total safety stock while maintaining high service levels. A fashion retailer, for instance, cut stockouts by 50% and minimized overstocking costs by applying machine learning tools. An electronics store increased sales by 20% through dynamic safety stock adjustments during peak seasons.
Statistic / Metric | Description / Impact | Example / Result |
|---|---|---|
Safety Stock Formula | Safety Stock = Z-Score × Std Dev of Demand × √(Average Lead Time) | For 95% service level (Z=1.65), demand std dev=20, lead time=7 days, safety stock = 231 units |
Stockout Reduction | Adjusting safety stock reduces stockouts | Fashion retailer reduced stockouts by 50% |
Sales Increase | Optimized safety stock can boost sales | Electronics store increased sales by 20% |
Cost-Benefit Analysis | Balances carrying costs against service levels to optimize inventory | Avoids overstocking and stockouts |
Tip: Cross-functional collaboration ensures safety stock decisions align with company-wide goals and market realities.
Companies that optimize safety stock achieve smoother operations, higher customer satisfaction, and reduced supply chain risks.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory
Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory focuses on receiving goods only as they are needed in the production process. This method reduces inventory holding costs and waste. Companies that implement JIT see significant improvements in efficiency and cost savings.
Performance Metric | Quantifiable Improvement | Source/Study Reference |
|---|---|---|
Inventory Reduction | Kumar & Suresh, 2020 | |
Inventory Carrying Cost Savings | 42% reduction, $3.2 million annual savings | Deloitte, 2021 |
Lead Time Reduction | 20-50% reduction in lead times | Association for Manufacturing Excellence, 2022 |
Defect Rate Reduction | 25-30% reduction in defect rates | American Society for Quality, 2022 |
Supplier Disruptions Reduction | 40% reduction in supplier-related disruptions | Chen & Paulraj, 2021 |
Waste Reduction | 20-40% reduction in scrap material | Environmental Protection Agency, 2021 |
JIT inventory methods also improve energy efficiency and speed up new product introductions. Companies report an 18-24% reduction in energy use per unit output and a 30-60% decrease in time to market for new products. These gains make JIT a powerful tool for Inventory Structure Adjustment.
Companies that use JIT inventory can respond quickly to changes in demand, reduce waste, and maintain high product quality.
Hybrid Inventory Models
Hybrid inventory models combine different inventory management strategies to address complex business needs. These models use multiple criteria, such as demand variability, parts criticality, and cost, to optimize inventory levels. Companies often blend forecasting methods and control systems to achieve better results than single-method approaches.
A hybrid model might use just-in-time practices for fast-moving items and safety stock optimization for slow-moving or critical parts. This flexibility helps businesses adapt to changing market conditions and product lifecycles. By integrating several forecasting techniques, companies can improve accuracy and reduce the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
Researchers have compared various hybrid models to traditional approaches. The table below highlights key studies and their findings:
Model/Author | Classification Criteria | Forecasting Method | Multi-Criteria Usage | Case Study Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Dolgui & Pashkevich | Parts Criticality, Demand Variability | Hybrid Model (Beta-binomial) | Yes | No |
Hua et al. | Demand Volume | Integrated Forecasting Method | Yes | Yes |
Makridakis et al. | Parts Cost, Parts Criticality, Demand Variability | Moving Average, Exponential Smoothing, EWMA | Yes | Yes |
These studies show that hybrid and multi-criteria models improve forecasting accuracy and inventory control. Companies using these models manage critical items more effectively, maintain higher turnover rates, and optimize inventory levels. Although most research provides qualitative insights, the benefits include better alignment with business goals and more responsive supply chains.
Tip: Businesses that adopt hybrid inventory models can tailor their approach to fit unique product lines, customer demands, and supply chain risks.
Hybrid models also support scalability. As companies grow or diversify, these models adjust to new challenges without requiring a complete overhaul of existing systems. This adaptability makes hybrid inventory models a strong choice for organizations seeking both stability and flexibility.
Technology Integration and Automation
Technology plays a vital role in modern inventory structure adjustment. Automation and integration streamline processes, reduce errors, and provide real-time visibility across the supply chain. Companies that invest in advanced technologies see faster, more accurate inventory adjustments and improved decision-making.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): These machines transport goods within warehouses, reducing manual labor and increasing efficiency.
Blockchain: This technology secures inventory transactions, enhances transparency, and prevents counterfeit products.
Predictive Analytics: By analyzing historical data, predictive analytics forecast demand and help avoid both stockouts and excess inventory.
Augmented Reality (AR): AR guides warehouse workers, improving picking accuracy and reducing mistakes.
Third-Party Integration: APIs automatically synchronize inventory data with external systems, ensuring accuracy and timely updates.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI optimizes reorder processes and improves supply chain efficiency through advanced forecasting.
Automated Replenishment: Systems reorder stock based on sales patterns, minimizing overstock and shortages.
Robotics and Automation: Robots handle sorting, picking, and packing, which reduces human error and speeds up operations.
IoT Integration: Smart shelves and sensors monitor inventory in real time, triggering automatic reorders when needed.
Cloud-Based Solutions: These platforms provide synchronized, real-time access to inventory data across multiple locations.
The impact of these technologies can be seen in measurable improvements:
Technological Benchmark | Impact on Inventory Adjustments |
|---|---|
Reduction in operational errors | Up to 70% decrease due to automated data entry eliminating manual input errors |
Real-time inventory adjustments | Automated systems enable instant stock level updates responding to demand fluctuations |
Predictive analytics for demand forecasting | Enables proactive strategy adjustments, reducing stockouts and overstocking |
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) | Increase picking efficiency by up to 300%, reducing manual labor and errors |
IoT sensor integration | Continuous monitoring reduces downtime by 50%, improves inventory tracking accuracy |
Cost reductions | Up to 30% savings from minimized manual errors and optimized resource allocation |
Faster response times | 50% reduction in customer response times through real-time data analytics |
Improved accuracy | 35% improvement in inventory data precision via automated updates and error-checking |
Cloud-based solutions | Synchronize data across locations for unified inventory management and real-time alerts |
Blockchain technology | Enhances security and transparency in inventory transactions, preventing counterfeit products |
Note: Companies that use automation and integration respond to market changes faster, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
Technology integration also supports scalability. As businesses expand, cloud-based and automated systems grow with them, maintaining efficiency and accuracy. By leveraging these tools, companies build resilient, agile inventory structures that support long-term success.
Tools and Technologies Supporting Inventory Structure Adjustment

Inventory Management Software Solutions
Modern inventory management software transforms how companies control stock and streamline operations. These solutions track inventory in real time, automate data collection, and centralize information for better decision-making. Companies use dashboards to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) like inventory turnover, fill rate, and lead times. Automation reduces human error and speeds up order processing.
Operational Performance Metric | Impact of Inventory Management Software | Resulting Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Inventory Turnover | Real-time tracking and automation improve turnover rates | Enhanced cash flow and reduced holding costs |
Demand Forecast Accuracy | Accurate data and forecasting tools reduce excess stock | Optimized inventory levels and cost savings |
Perfect Order Rate | Automation reduces errors in order fulfillment | Increased customer satisfaction and reliability |
Fill Rate | Improved stock availability through centralized control | Higher customer loyalty and fewer backorders |
Lead Times | Faster processing and better coordination shorten lead times | Timely deliveries and improved customer experience |
Companies that use inventory management software see ongoing improvements by regularly updating forecasting parameters and safety stock levels.
Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence
Data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) help businesses predict demand and optimize inventory. AI models analyze sales history, market trends, and customer behavior to improve forecasting. Retailers like Walmart have used machine learning to reduce out-of-stocks by 16%. Real-time data collection and neural networks allow quick responses to changes in demand. Automated replenishment systems use AI to reorder stock, keeping inventory at the right level and reducing waste.
AI and machine learning improve demand prediction and inventory allocation.
Real-time monitoring technologies like RFID and IoT devices increase inventory accuracy to 95-99%.
Data science tools help companies understand inventory data, reduce excess, and avoid stockouts.
AI-driven platforms also convert unstructured supplier data into clear, usable information. This process supports better decision-making and faster inventory adjustments.
Cloud-Based Inventory Systems
Cloud-based inventory systems give companies flexibility and scalability. These systems allow instant updates and real-time synchronization across locations. Businesses can add users or features quickly without large IT projects. During busy seasons, cloud systems scale up to handle more orders without extra hardware.
Order processing time drops by up to 82%.
Inventory accuracy rises from 80% to 98%.
Inventory carrying costs fall by 10-30%.
Companies manage multiple locations with one system, improving control and fulfillment.
Cloud platforms connect easily with e-commerce, ERP, and accounting tools. This integration ensures accurate, up-to-date inventory data everywhere. As companies grow, cloud-based systems support continuous improvement and efficient operations.
Real-World Examples of Inventory Structure Adjustment

Manufacturing Industry Applications
Manufacturers use inventory structure adjustment to improve efficiency and reduce waste. Toyota set the standard with its Just-in-Time (JIT) system, which keeps inventory low and adapts quickly to changes in demand. Apple manages a global supply chain with JIT and a centralized warehouse, holding most inventory in retail stores to cut costs and avoid overstock. These companies track key metrics to measure success:
Defect Rate: Shows the percentage of faulty products, helping spot quality issues.
Inventory Turnover: Measures how often inventory sells and gets replaced, improving cash flow.
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE): Tracks how well machines run, pointing out areas for improvement.
Lead Time: Measures how long it takes to produce and deliver products.
Company | Industry | Inventory Strategy | Quantitative Outcome / Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
Toyota | Automotive Manufacturing | Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory since 1970 | Minimizes inventory levels and costs; adapts quickly to demand |
Apple | Consumer Electronics | JIT with 150 global suppliers and centralized U.S. warehouse | Reduces costs and overstock; most inventory held in retail stores |
Retail and E-commerce Success Stories
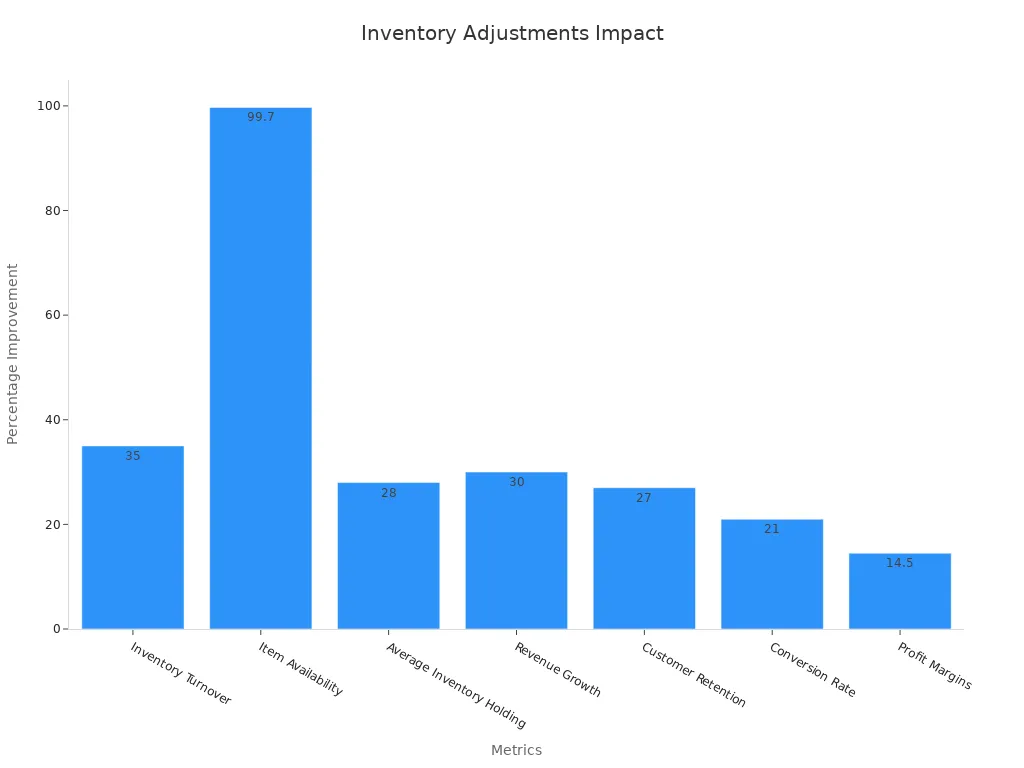
Retailers and e-commerce brands rely on inventory adjustments to boost sales and keep customers happy. IKEA uses real-time POS data and min/max reorder points to optimize stock. Glossier, a direct-to-consumer beauty brand, uses expert forecasting to avoid stockouts and support rapid growth. Effective inventory management helps retailers reduce costs, speed up fulfillment, and improve customer satisfaction. For example, one retailer cut average inventory by 28% while keeping item availability at 99.7%. This led to higher sales, better profit margins, and improved customer loyalty.
Metric | Improvement Statistic | Impact Description |
|---|---|---|
Inventory Turnover | Faster turnover improves cash flow and reduces carrying costs. | |
Item Availability | 99.7% availability | High availability with lower inventory boosts customer satisfaction. |
Revenue Growth | 30% higher | Data-driven inventory management increases revenue. |
Customer Retention | 27% improvement | Fewer stockouts and better personalization increase loyalty. |
Service Sector Implementations
Service companies also benefit from inventory structure adjustment. They use operational analytics to track stock movements and demand patterns. This approach prevents overstocking and stockouts, streamlines logistics, and reduces costs. Physical inventory counts improve accuracy and help managers make better decisions about reordering and pricing. These practices lead to faster deliveries, lower holding costs, and better customer service. Accurate inventory records also support compliance and financial reporting. Service providers who adjust inventory structures see improved efficiency, resource allocation, and supply chain responsiveness.
Physical counts verify stock levels and uncover inconsistencies.
Accurate data supports better resource allocation and pricing.
Lower holding costs result from identifying slow-moving items.
Improved customer service comes from reliable order fulfillment.
Overcoming Challenges in Inventory Structure Adjustment
Managing Demand Variability
Businesses often struggle to predict customer demand accurately. Demand can change quickly due to trends, seasons, or unexpected events. Companies use metrics like demand variability, lead time variability, and demand forecast accuracy to track these changes. The coefficient of variation (CV) helps measure how unpredictable demand is. A lower CV means more stable demand, while a higher CV signals more risk.
To manage these fluctuations, companies use several strategies:
Maintain safety stock as a buffer for sudden spikes.
Collaborate with suppliers and customers to improve forecast accuracy.
Apply demand smoothing techniques, such as targeted promotions, to stabilize sales.
Monitor and update forecasting processes regularly.
Scenario planning prepares teams for different demand outcomes, helping them respond quickly and avoid stockouts or overstocking.
Addressing Supplier and Supply Chain Risks
Supply chain disruptions can halt production and delay deliveries. Companies face risks from supplier failures, transportation issues, and even cyberattacks. Real-world incidents, like the Colonial Pipeline cyberattack, show the importance of strong risk management.
Key risk management practices include:
Use third-party data sources to monitor supplier health and compliance.
Set up key risk indicators (KRIs) to track potential problems.
Automate risk detection with AI tools for faster response.
Continuously monitor suppliers with real-time data feeds.
These steps improve operational continuity, support better decisions, and strengthen supplier relationships. Structured onboarding and regular communication also help reduce risks.
Technology Adoption and Integration
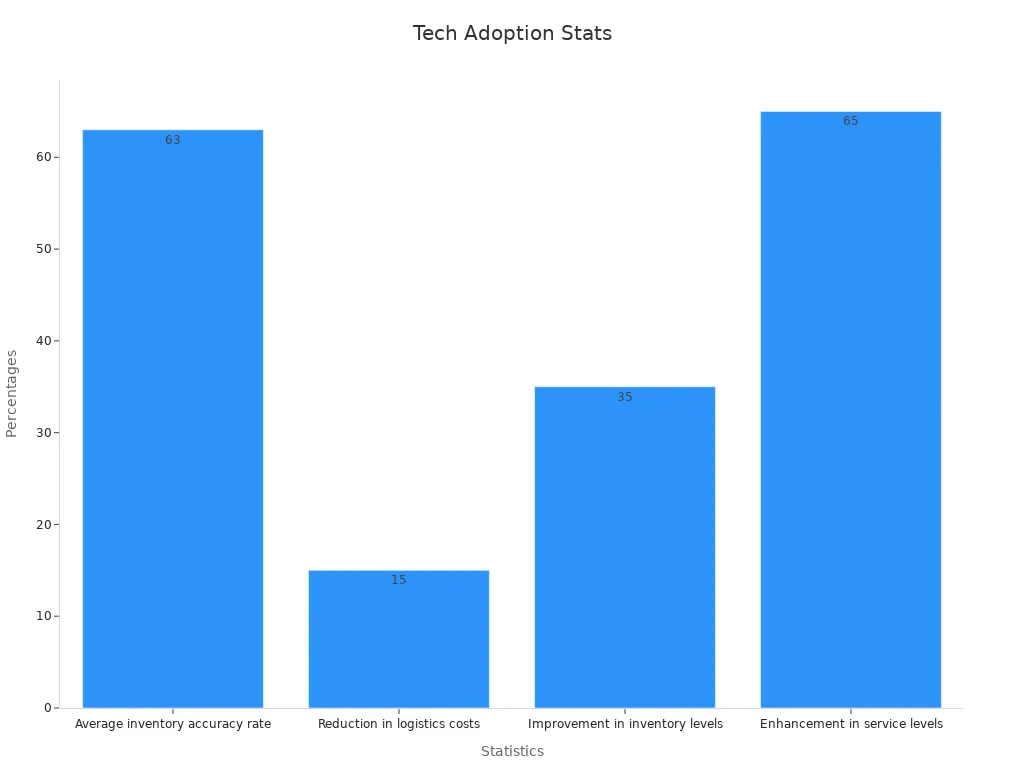
Adopting new technology in inventory management brings both opportunities and challenges. Many companies struggle with system integration, high costs, and data security. In the US, the average inventory accuracy rate stands at only 63%, showing the need for better technology.
Statistic | Description | Implication |
|---|---|---|
63% | Average inventory accuracy rate in US retail operations | Low accuracy leads to stockouts and poor customer experience |
15% | Reduction in logistics costs possible with technology | Cost savings require overcoming adoption barriers |
35% | Improvement in inventory levels after tech adoption | Highlights the gap before integration |
65% | Service level enhancement with technology | Shows potential gains after successful adoption |
Common challenges include siloed systems, poor data quality, and resistance to change. Companies address these by investing in training, improving data validation, and choosing scalable, cloud-based solutions. Strong cybersecurity measures protect sensitive inventory data. Overcoming these barriers unlocks the full benefits of technology, leading to higher accuracy and better service.
Change Management and Staff Training
Change management and staff training play a vital role in successful inventory structure adjustment. Employees often resist new systems or processes. Leaders must guide teams through transitions and provide the right support. Effective change management starts with clear communication. Managers explain the reasons for change and set expectations. They also identify change champions who encourage others and model positive behaviors.
Staff training ensures employees understand new inventory systems and procedures. Training programs use hands-on workshops, online modules, and coaching sessions. These methods help staff build confidence and competence. Companies measure training effectiveness using several metrics. Participant feedback and satisfaction, collected through surveys and interviews, show if the training meets employee needs. High satisfaction rates indicate that staff feel engaged and ready to apply new skills.
Behavior change metrics track how well employees use new knowledge on the job. Supervisors observe staff, review self-assessment questionnaires, and evaluate job performance. These metrics reveal if training leads to better inventory management and fewer errors. Companies also monitor user adoption rates and proficiency levels to ensure everyone uses the new system correctly.
Metric Category | Examples of Metrics and KPIs |
|---|---|
Training Effectiveness | Test scores, course completion, certification, supervisor feedback |
Post-Training Impact | Self-assessment, on-the-job observation, job performance KPIs, customer feedback |
Change Management Coaching | Coaching success scoring, experience level, enthusiasm, coaching availability |
Change Champion Network | Experience, training required, availability, performance in champion activities |
Sponsor Engagement | Influence, visible support, enthusiasm, availability for change activities |
Change Adoption and Engagement | User adoption rates, proficiency KPIs, awareness KPIs |
Tip: Companies that invest in ongoing training and strong change management see smoother transitions, higher employee engagement, and better inventory outcomes.
A well-trained team adapts quickly to new inventory structures. This agility leads to fewer mistakes, faster order processing, and improved customer satisfaction.
Actionable Recommendations for Inventory Structure Adjustment
Steps for Proactive Inventory Structure Adjustment
Companies achieve strong results when they follow a clear process for Inventory Structure Adjustment. Teams start by setting up regular KPI review meetings with key stakeholders. These meetings help everyone stay focused on important goals. When a metric falls below target, managers develop action plans to address the issue. Sharing best practices across locations ensures that improvements spread quickly.
A step-by-step approach helps organizations benchmark their progress:
Select a process to benchmark, focusing on areas that impact performance.
Choose organizations or industries for comparison, including top competitors.
Document current processes to spot improvement opportunities.
Gather data from interviews and research to understand best practices.
Measure performance against benchmarks to find gaps.
Create a plan to close those gaps with clear, actionable goals.
Implement changes and provide training for employees.
Repeat the benchmarking process to drive continuous improvement.
Teams also use A/B testing to evaluate new ideas and create feedback loops between operations and analytics. This cycle helps refine strategies and keeps the business agile.
Best Practices for Sustained Inventory Success
Long-term success depends on consistent best practices. Companies develop strong audit strategies, including cycle counts and regular supply chain audits, to catch errors early. Calculating Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) helps balance ordering and holding costs, preventing both overstocking and stockouts. Accurate reorder points, based on lead times and safety stock, keep supply steady.
Other proven methods include:
Applying ABC analysis to focus on high-value inventory items.
Conducting capital expenditures and total quality maintenance to avoid breakdowns.
Reviewing stock levels weekly and coordinating with suppliers for timely deliveries.
Performing monthly audits and analyzing sales trends for better planning.
Completing yearly system reviews and adjusting strategies for new technologies.
Companies that follow these practices maintain efficient operations and adapt to market changes with confidence.
Proactive Inventory Structure Adjustment gives companies a strong advantage in business interventions. Regular reviews of inventory strategies help teams lower costs, reduce risks, and improve daily operations. Companies that focus on these adjustments respond faster to market changes. They also build a foundation for long-term growth and success.
Businesses that adapt their inventory structures stay ahead in dynamic markets.
FAQ
What is the main goal of inventory structure adjustment?
The main goal focuses on aligning inventory with business needs. Companies want to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and respond quickly to market changes. This adjustment helps businesses stay competitive and meet customer demands.
How often should a company review its inventory structure?
Experts recommend reviewing inventory structure at least once every quarter. Regular reviews help companies spot problems early and adjust strategies before issues grow. Some fast-moving industries may need monthly checks.
Which technology helps most with inventory structure adjustment?
Inventory management software provides the biggest impact. These tools track stock in real time, automate orders, and give managers clear data. Companies also benefit from AI, IoT sensors, and cloud-based systems for better accuracy and speed.
Can small businesses benefit from inventory structure adjustment?
Yes, small businesses gain many advantages. They can lower storage costs, avoid stockouts, and improve customer service. Even simple changes, like better tracking or regular audits, make a big difference for smaller operations.
See Also
Transforming Consumer Insights Into Effective Business Strategies
A Data-Based Approach To SKU Rationalization And Metrics
Effective Weekly Retail Demand Forecasting Techniques Explained
Key Basket Analysis Methods For Retail Analytics Teams
Four Algorithms To Streamline Large-Scale Daily Replenishment

