Lakehouse Architecture
Lakehouse Architecture represents a modern approach to data management. This architecture combines the strengths of data lakes and data warehouses. The design supports efficient data storage and retrieval. Lakehouse Architecture enables seamless integration with various data environments. Singdata Lakehouse enhances this concept by offering an open and flexible platform. The architecture eliminates both "cloud lock-in" and "data lock-in." Singdata Lakehouse leverages open-source technologies for improved data management. The architecture ensures robust security measures for data protection.
Understanding Lakehouse Architecture
Definition and Origin
Lakehouse Architecture represents a modern data management approach. This architecture combines the flexibility of data lakes with the performance of data warehouses. The concept emerged to address limitations in traditional data storage solutions. Data lakes offer scalability, while data warehouses provide structured query capabilities. Lakehouse Architecture integrates these benefits into a unified platform.
What is a Lakehouse?
A Lakehouse serves as a hybrid data platform. It merges the strengths of data lakes and data warehouses. The platform supports both structured and unstructured data. A Lakehouse enables efficient data processing and analytics. Users can perform machine learning and business intelligence tasks seamlessly.
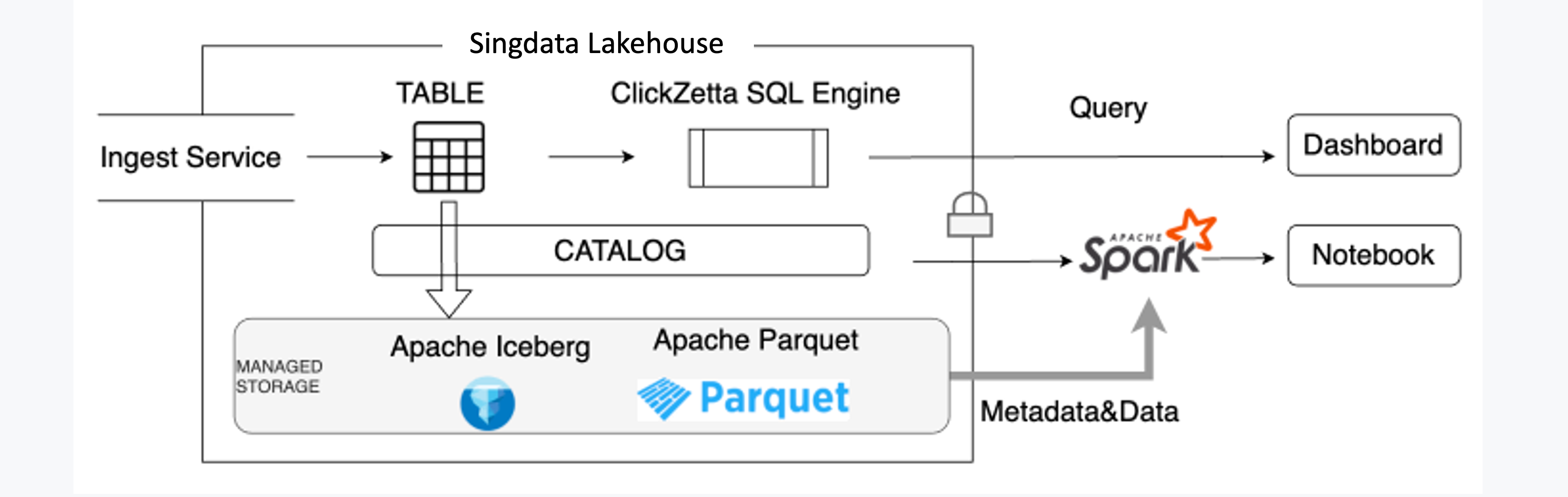
Key Features
Unified Storage & Open Data Format
Unified Storage forms the backbone of Lakehouse Architecture. This feature allows seamless data integration from various sources. Users can store raw data and processed data in a single location. Unified Storage enhances data accessibility and management. The architecture supports diverse data formats and types.
Real-time Processing
Real-time Processing stands as a crucial aspect of Lakehouse Architecture. This capability enables immediate data analysis and insights. Users can process streaming data without delays. Real-time Processing supports time-sensitive applications and decision-making. The architecture ensures efficient handling of continuous data flows.
Core Features of Lakehouse Architecture
Scalability
Scalability stands as a fundamental characteristic of Lakehouse Architecture. The architecture supports the growth of data and user demands without compromising performance.
Horizontal Scaling
Horizontal scaling allows Lakehouse Architecture to expand by adding more nodes. This method enhances the system's capacity to handle increased workloads. Each node contributes additional resources, such as storage and processing power. Horizontal scaling ensures that the architecture remains efficient as data volumes grow.
Cost Efficiency
Cost efficiency is a significant advantage of Lakehouse Architecture. The architecture optimizes resource usage, reducing unnecessary expenses. Users can store large volumes of data at a lower cost compared to traditional systems. Cost efficiency makes Lakehouse Architecture an attractive option for businesses seeking budget-friendly solutions.
Flexibility
Flexibility is a key feature that sets Lakehouse Architecture apart. The architecture adapts to changing data requirements and diverse workloads.
Schema Evolution
Schema evolution in Lakehouse Architecture allows for changes in data structure over time. Users can modify schemas without disrupting existing processes. This capability supports the integration of new data sources and formats. Schema evolution ensures that the architecture remains relevant and adaptable.
Support for Diverse Workloads
Support for diverse workloads enables Lakehouse Architecture to handle various data processing tasks. The architecture accommodates both batch and real-time processing needs. Users can perform analytics, machine learning, and reporting within the same platform. Support for diverse workloads enhances the versatility of Lakehouse Architecture.
Components of a Lakehouse
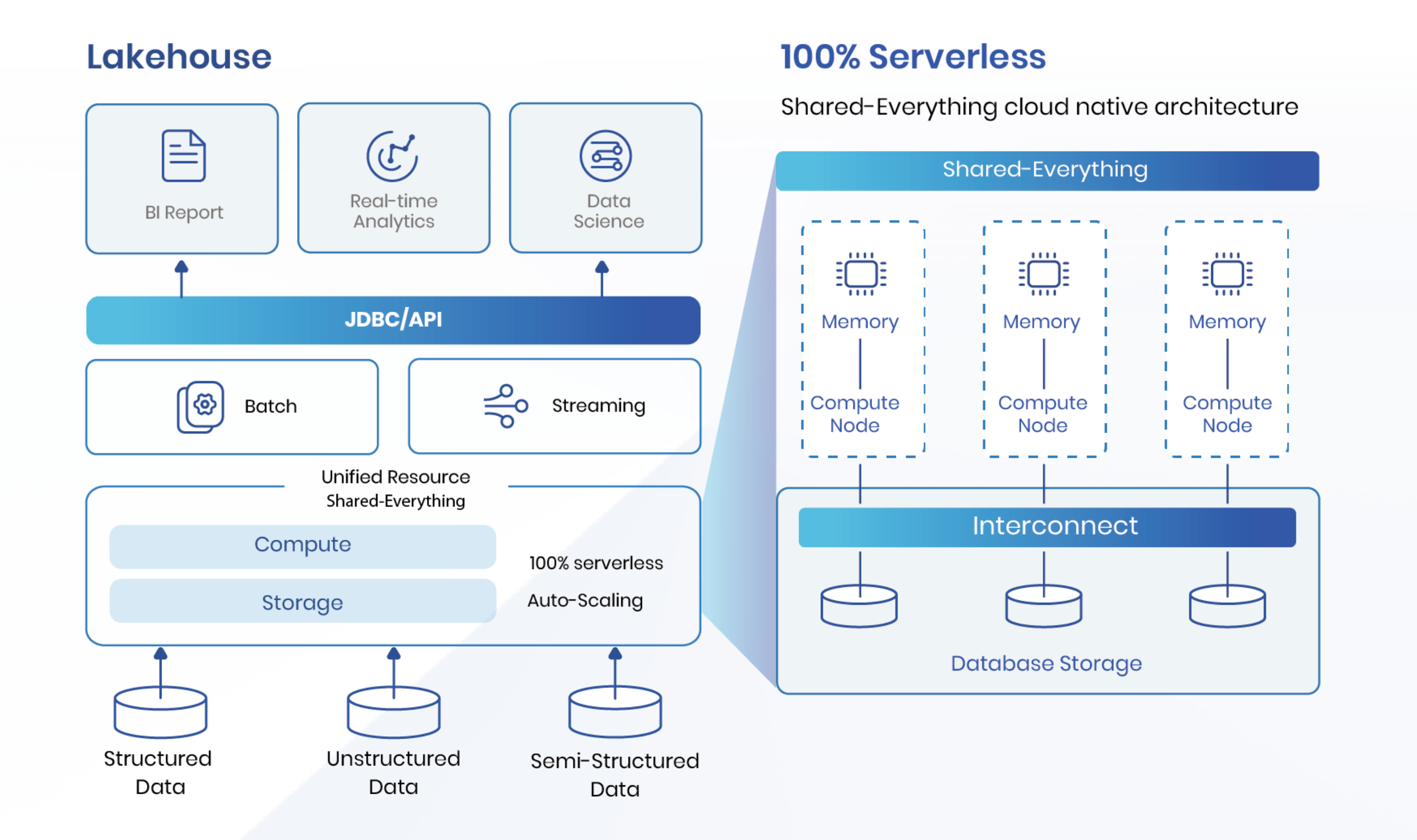
Storage Layer
Data Lake Integration
Data Lake Integration plays a crucial role in Lakehouse Architecture. This integration allows seamless access to vast amounts of raw data. Users can store structured and unstructured data together. Data Lake Integration supports efficient data retrieval and management. The architecture ensures compatibility with various data sources.
Metadata Management
Metadata Management enhances the functionality of Lakehouse Architecture. This component organizes and catalogs data efficiently. Metadata provides essential information about data assets. Users can easily discover and access data through metadata. Metadata Management improves data governance and quality.
Processing Layer
Batch Processing
Batch Processing is a key feature of Lakehouse Architecture. This process handles large volumes of data at scheduled intervals. Users can perform complex computations on historical data. Batch Processing supports data analytics and reporting tasks. The architecture ensures reliable and consistent data processing.
Stream Processing
Stream Processing enables real-time data handling in Lakehouse Architecture. This capability processes data as it arrives. Users can gain immediate insights from continuous data streams. Stream Processing supports applications requiring instant decision-making. The architecture maintains high performance and low latency.
Benefits of Lakehouse Architecture

Improved Data Accessibility
Simplified Data Access
Lakehouse Architecture enhances data accessibility. Users find data access straightforward and efficient. The architecture supports a unified platform for diverse data types. This integration allows users to retrieve information quickly. Simplified access reduces time spent searching for data.
Enhanced Collaboration
Lakehouse Architecture fosters collaboration among teams. Shared data environments enable seamless teamwork. Users can access and analyze data collectively. This approach promotes consistent insights across departments. Collaborative efforts lead to more informed decision-making.
Cost-effectiveness
Reduced Data Duplication
Lakehouse Architecture minimizes data duplication. Centralized storage eliminates redundant copies. Users store data once and access it as needed. This method reduces storage costs significantly. Efficient data management leads to financial savings.
Optimized Resource Usage
Lakehouse Architecture optimizes resource usage. The architecture allocates resources based on demand. Users experience improved performance without waste. Efficient resource management enhances operational efficiency. Businesses benefit from reduced operational expenses.
Lakehouse Architecture revolutionizes data management. Lakehouse Architecture revolutionizes data management. The architecture combines the best features of data lakes and data warehouses. Businesses benefit from improved data accessibility and cost-effectiveness. Lakehouse Architecture supports diverse workloads with flexibility. Scalability ensures that data growth does not hinder performance. Unified storage and real-time processing enhance data handling. Lakehouse Architecture provides a secure and open platform. Organizations can achieve seamless integration with various data environments. Lakehouse Architecture represents a significant advancement in modern data solutions.
See Also
Essential Information About Single-Engine Lakehouses
Evaluation of Singdata Lakehouse's Single-Engine Performance
Factors Behind Cost Savings in Contemporary Data Infrastructure

