Understanding the Key Differences Between Application and Data Integration

When you hear the term "integration," it’s easy to think of combining things into one. In the world of technology, integration takes two distinct forms: application and data integration. Application integration focuses on connecting multiple software systems so they can share processes and workflows. Data integration, on the other hand, revolves around consolidating data from different sources into a unified view.
The key difference lies in their goals. Application and data integration ensures systems work together seamlessly, while data integration organizes and harmonizes information for better decision-making. Understanding these distinctions helps you choose the right approach for your needs.
Key Takeaways
Application integration links software systems to make tasks easier. It saves time and reduces mistakes by sharing data automatically.
Data integration combines information from different places into one view. This helps businesses make better choices using complete information.
Pick application integration for quick tasks and data integration for deep data study. Match your choice to what your business needs.
Use new tools like easy-to-use platforms for app integration and smart data tools for fast data work. These make integration simpler.
Check your current setup and costs before choosing. Knowing what you need helps you pick the best integration plan.
What is Application Integration?
Definition of Application Integration
Application integration refers to the process of enabling different software applications to work together seamlessly. It ensures that data, processes, and workflows can flow across systems without manual intervention. By connecting various tools and platforms, application integration allows you to create a unified ecosystem where information moves efficiently between applications.
This approach is essential for modern businesses that rely on multiple software solutions. For example, integrating your customer relationship management (CRM) system with your email marketing platform ensures that customer data updates automatically across both systems. This eliminates the need for repetitive data entry and reduces errors.
Purpose and How It Works
The primary purpose of application integration is to improve operational efficiency by connecting disparate systems. It ensures that your applications communicate effectively, enabling real-time data sharing and streamlined workflows. This connectivity supports better decision-making and enhances the overall user experience.
Application integration works through various methods, such as APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), middleware, and event-driven architectures. APIs act as bridges, allowing applications to exchange data. Middleware serves as a central hub that facilitates communication between systems. Event-driven architectures trigger actions in one application based on events in another.
Recent trends highlight the growing adoption of low-code/no-code platforms, which simplify the integration process. These platforms empower non-technical users to create integrations without extensive coding knowledge. Additionally, the integration of AI and machine learning enhances automation, making data analysis faster and more accurate.
Common Use Cases for Application Integration
Application integration plays a critical role in various industries. Here are some common use cases:
Customer Experience: Integrating CRM systems with marketing tools helps you deliver personalized campaigns and improve customer satisfaction.
E-commerce: Connecting inventory management systems with online stores ensures accurate stock levels and faster order fulfillment.
Healthcare: Integration between electronic health records (EHR) and laboratory systems reduces duplicate tests and improves care coordination.
Finance: Enterprise application integration enables banks to launch new services faster and collaborate with fintech companies seamlessly.
The global application integration market reflects its importance. Valued at $14.5 billion in 2024, it is projected to grow to $74.82 billion by 2033, driven by digital transformation and cloud adoption. This growth underscores the increasing reliance on integration solutions to enhance business operations.
What is Data Integration?
Definition of Data Integration
Data integration is the process of combining data from multiple sources into a unified and consistent view. It ensures that information from various systems, databases, or applications is accessible and usable in one place. This process eliminates data silos, enabling you to analyze and act on information more effectively. Whether you’re working with structured data from spreadsheets or unstructured data from social media, integration helps you bring it all together.
At its core, data integration focuses on creating a seamless flow of information. This allows businesses to make informed decisions based on a complete and accurate dataset. For example, integrating sales data with customer feedback can help you identify trends and improve your offerings.
Purpose and How It Works
The primary purpose of data integration is to provide a holistic view of information. This enables better decision-making, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced customer experiences. By consolidating data, you can uncover insights that would otherwise remain hidden in isolated systems.
Data integration typically involves several steps:
Data Extraction: Retrieving data from various sources, such as databases, APIs, or cloud storage.
Data Transformation: Standardizing and cleaning the data to ensure consistency.
Data Loading: Storing the processed data in a central repository, such as a data warehouse or lakehouse.
Modern tools like Singdata Lakehouse simplify this process by offering real-time data processing and advanced computing capabilities. These tools handle massive data volumes efficiently, making them ideal for organizations embracing big data technologies.
Common Use Cases for Data Integration
Data integration plays a vital role across industries. Here are some examples:
Healthcare: Combines patient records, clinical trial data, and lab results to improve treatment outcomes.
Marketing: Merges survey data and online behavior to create personalized campaigns.
Finance: Integrates risk management and portfolio data for better investment decisions.
E-commerce: Consolidates inventory, sales, and customer data to optimize supply chains.
Recent trends highlight the growing adoption of data integration tools:
Approximately 67% of manufacturers now use Data-as-a-Service (DaaS) solutions, with adoption rates reaching 78% in the automotive sector.
Organizations increasingly invest in advanced integration technologies to manage the rapid growth of data sources and eliminate silos.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) like data quality scores, query performance, and data pipeline latency measure the success of integration projects. For instance, faster query performance allows analysts to generate insights quickly, while high data quality ensures reliable decision-making.
Key Differences Between Application and Data Integration

Goals: Connecting Systems vs. Consolidating Data
The primary goal of application integration is to connect different software systems so they can work together. It ensures that processes and workflows flow smoothly across applications. For example, when you integrate a CRM system with an email marketing tool, customer data updates automatically in both systems. This eliminates manual updates and reduces errors. Application integration focuses on creating a seamless ecosystem where systems communicate in real time.
On the other hand, data integration aims to consolidate data from multiple sources into a single, unified view. Its purpose is to eliminate data silos and provide you with a complete dataset for analysis. For instance, combining sales data with customer feedback allows you to identify trends and make informed decisions. While application integration connects systems, data integration organizes information for better insights.
Tip: If your goal is to streamline workflows, application integration is the right choice. If you need a comprehensive view of your data, focus on data integration.
Methods, Tools, and Technologies
Application integration relies on technologies like APIs, middleware, and event-driven architectures. APIs act as bridges, enabling systems to exchange data. Middleware serves as a central hub that facilitates communication between applications. Event-driven architectures trigger actions in one system based on events in another. Real-time integration is a key feature of modern application integration, ensuring instant data sharing and improved efficiency.
Data integration, however, uses methods like ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform). These processes retrieve data from various sources, clean and standardize it, and store it in a central repository like a data warehouse or lakehouse. Advanced tools like Singdata Lakehouse simplify this process by offering real-time integration and high-performance data processing. These tools handle massive data volumes, making them ideal for organizations managing big data.
Aspect | Application Integration | Data Integration |
|---|---|---|
Focus | Connecting systems | Consolidating data |
Key Technologies | APIs, middleware, event-driven systems | ETL, ELT, data warehouses/lakehouses |
Real-Time Integration | Essential for workflows | Crucial for live data analysis |
Typical Use Cases
Application integration is widely used in scenarios where systems need to work together. For example:
E-commerce: Syncing inventory management with online stores ensures accurate stock levels.
Healthcare: Connecting EHR systems with lab software improves patient care.
Finance: Integrating banking platforms with fintech apps enables seamless transactions.
Data integration, on the other hand, is essential for creating a unified view of information. Common use cases include:
Marketing: Merging customer behavior data with survey results for personalized campaigns.
Healthcare: Combining patient records and clinical trial data for better treatment plans.
E-commerce: Consolidating sales, inventory, and customer data to optimize supply chains.
Both application and data integration play critical roles in modern businesses. While application integration focuses on real-time workflows, data integration ensures you have the insights needed for strategic decisions.
Benefits and Challenges of Application and Data Integration

Benefits of Application Integration
Application integration offers significant advantages for businesses aiming to streamline operations. By connecting systems, you can automate workflows and reduce manual tasks. This improves efficiency and minimizes errors. For example, integrating your CRM with an email marketing platform ensures customer data updates automatically, saving time and effort.
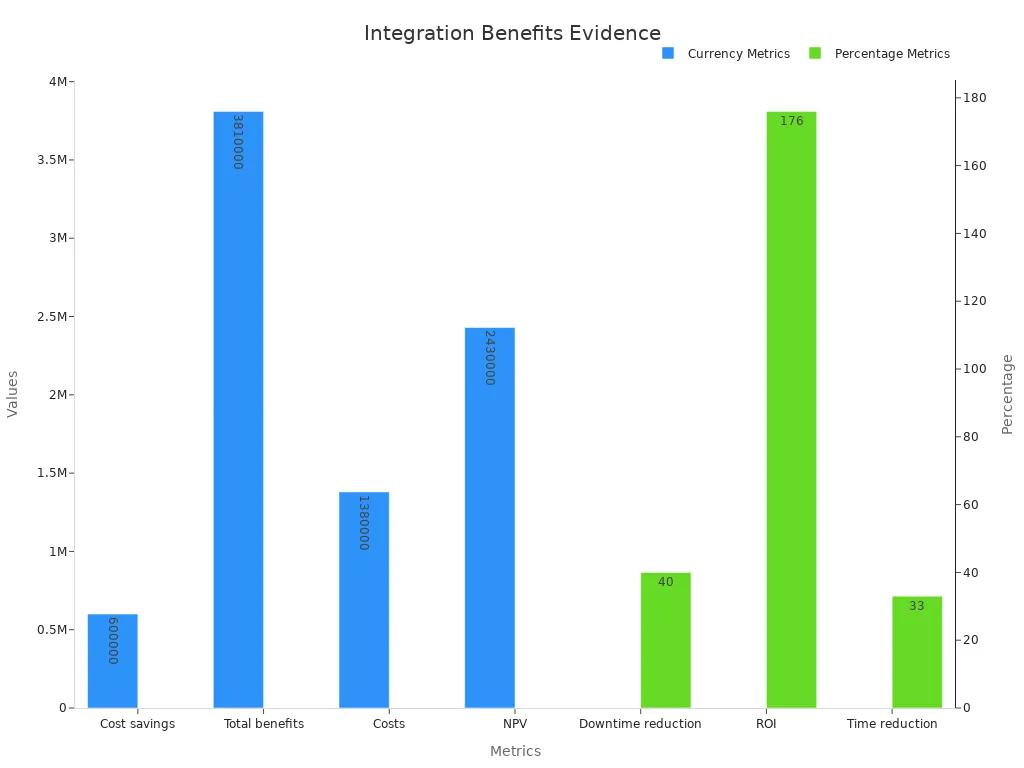
Organizations also experience measurable financial benefits. A study revealed that companies save up to $600,000 annually by consolidating technology and vendors. Additionally, application integration reduces downtime by 40%, leading to smoother operations. Over three years, businesses report total benefits of $3.81 million, with a return on investment (ROI) of 176%.
Benefit Description | Value |
|---|---|
Cost savings from technology consolidation | $600,000/year |
Reduction in application downtime | 40% |
Total benefits over three years | $3.81 million |
Return on investment (ROI) | 176% |
Benefits of Data Integration
Data integration enhances decision-making by providing a unified view of information. It eliminates silos, allowing you to analyze data holistically. This leads to better business intelligence and more reliable insights. For instance, combining sales and customer feedback data helps you identify trends and improve strategies.
Other benefits include improved data quality and increased efficiency. Integration resolves discrepancies, ensuring accurate analysis. Streamlined data collection reduces manual work, speeding up access to information. Many organizations leverage data integration to enhance customer insights. A 360-degree view of customer interactions enables personalized services and better understanding of needs.
Enhanced data quality ensures reliable analysis.
Increased efficiency reduces manual tasks.
Better business intelligence aids decision-making.
Streamlined operations improve collaboration.
Enhanced customer insights enable personalized services.
Challenges of Each Approach
Despite their benefits, both application and data integration come with challenges. Application integration often involves complex setups. Ensuring seamless communication between systems requires expertise and time. Additionally, managing real-time data integration can be difficult, with 44% of organizations citing it as a challenge.
Data integration faces its own hurdles. High infrastructure costs and a lack of skilled professionals can delay projects by up to six months. Data quality issues, such as errors and security concerns, further complicate the process. A survey found that 62.5% of participants struggle with managing data integration processes.
Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
Complexity of application integration | Real-time data integration is challenging for 44% of organizations. |
Skilled professional shortage | Lack of expertise delays data integration projects by up to six months. |
High infrastructure costs | Large-scale data integration requires significant capital and operational expenses. |
Data quality issues | Errors and security concerns hinder the integration process. |
Choosing Between Application and Data Integration
Decision-Making Framework Based on Business Needs
Choosing between application and data integration requires a structured approach. You need to evaluate your business needs and align them with the right integration solution. A decision-making framework can simplify this process by breaking it into manageable steps:
Identify interrelated domains of choice, such as operational efficiency, data accessibility, or customer experience.
Explore potential options for each domain to understand how integration can address specific challenges.
Define and prioritize criteria, such as cost, scalability, or ease of implementation.
Make trade-off-based decisions by weighing the benefits and limitations of each approach.
The Strategy Stack framework offers a practical way to make these decisions. It integrates critical activities, such as assessing current capabilities and setting clear objectives, to guide you toward the best solution. For example, if your goal is to streamline workflows, application integration may be the right choice. On the other hand, if you need a unified view of your data, data integration could be more suitable.
Evidence-based management (EBM) further supports this process. By using empirical data and structured decision-making models, EBM ensures that your choices align with measurable business criteria. For instance, organizations that conduct formal capability assessments are 2.4 times more likely to achieve their data transformation goals. This highlights the importance of evaluating your current systems and identifying gaps before selecting an integration approach.
Practical Tips for Selecting the Right Approach
When deciding between application and data integration, consider these practical tips to ensure you choose the right approach:
Assess Your Business Goals
Start by identifying what you want to achieve. If your focus is on connecting systems for real-time workflows, an application integration strategy is ideal. If your priority is consolidating data for analysis, data integration is the better option.Evaluate Your Current Infrastructure
Analyze your existing systems and data capabilities. Understanding your infrastructure helps you determine whether it supports the integration solution you need. For example, if your systems lack APIs, application integration may require additional tools or middleware.Prioritize Scalability and Flexibility
Choose an integration solution that can grow with your business. Scalable tools like Singdata Lakehouse offer advanced computing capabilities, making them suitable for handling massive data volumes and evolving business needs.Consider Costs and Resources
Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) for each approach. Application integration often involves lower upfront costs but may require ongoing maintenance. Data integration, while more resource-intensive, provides long-term value by eliminating data silos and improving decision-making.Leverage Advanced Technologies
Use modern tools and technologies to simplify the integration process. For example, low-code platforms make application integration accessible to non-technical users. Similarly, advanced data integration tools enable real-time processing and high-performance analytics.
Tip: Always align your integration strategy with your business objectives. This ensures that your investment delivers maximum value.
By following these tips, you can confidently choose the integration approach that best meets your needs. Whether you opt for application integration to streamline workflows or data integration to gain insights, a well-thought-out strategy ensures success.
Understanding the differences between application and data integration helps you make informed decisions. Application integration connects systems to streamline workflows, while data integration consolidates information for better insights. Each approach offers unique benefits tailored to specific needs.
For example, case studies highlight measurable outcomes:
Case Study | Strategy Implemented | Results |
|---|---|---|
Global Tech Giant | Adopted OKRs and implemented KPI dashboards | 15% increase in product development efficiency, improved customer satisfaction, increased market share |
Mid-sized Bank | Used Balanced Scorecard and integrated measures | 12% increase in customer retention, improved cross-selling metrics |
To apply these strategies, assess your goals and infrastructure. Choose tools that align with your objectives and scale with your growth. Whether you aim to optimize workflows or gain actionable insights, selecting the right integration approach ensures success.
FAQ
What is the main difference between application and data integration?
Application integration connects systems to enable seamless workflows and real-time communication. Data integration consolidates information from multiple sources into a unified view for analysis. While application integration focuses on system connectivity, data integration emphasizes organizing data for better decision-making.
Can you use both application and data integration together?
Yes, you can combine both approaches. Application integration ensures systems work together, while data integration organizes the data they generate. Using both helps you streamline workflows and gain actionable insights, creating a more efficient and informed business environment.
What tools are commonly used for application and data integration?
For application integration, tools like APIs, middleware, and event-driven systems are common. Data integration often uses ETL/ELT processes, data warehouses, or lakehouses. Advanced platforms like Singdata Lakehouse handle both real-time processing and large-scale data management efficiently.
How do you decide which integration approach to use?
Start by identifying your goals. If you need to connect systems for real-time workflows, choose application integration. If your priority is consolidating data for analysis, opt for data integration. Evaluate your infrastructure, scalability needs, and budget to make an informed decision.
What industries benefit most from integration solutions?
Industries like e-commerce, healthcare, finance, and logistics benefit greatly. Application integration improves workflows, while data integration enhances decision-making. For example, healthcare uses integration to combine patient records, while e-commerce consolidates sales and inventory data for better supply chain management.
See Also
Comprehensive Data Handling Solutions For All Needs
Real-Time Data Services For Enterprises Made Easy
Integrating Artificial Intelligence With Data Seamlessly

