User Identity
Singdata adopts a flexible user and identity management system, allowing differentiation and permission control between different levels and types of users.
This help document will detail:
- User levels: including global account users and service instance users.
- User types: including regular users and service users.
User Levels
Users in Singdata can be divided into two levels based on their scope: global account users and Lakehouse service instance users. These two levels help enterprises manage all users under a global account across multi-cloud and multi-region service instances, while also distinguishing the permission scope of different users based on service instances.
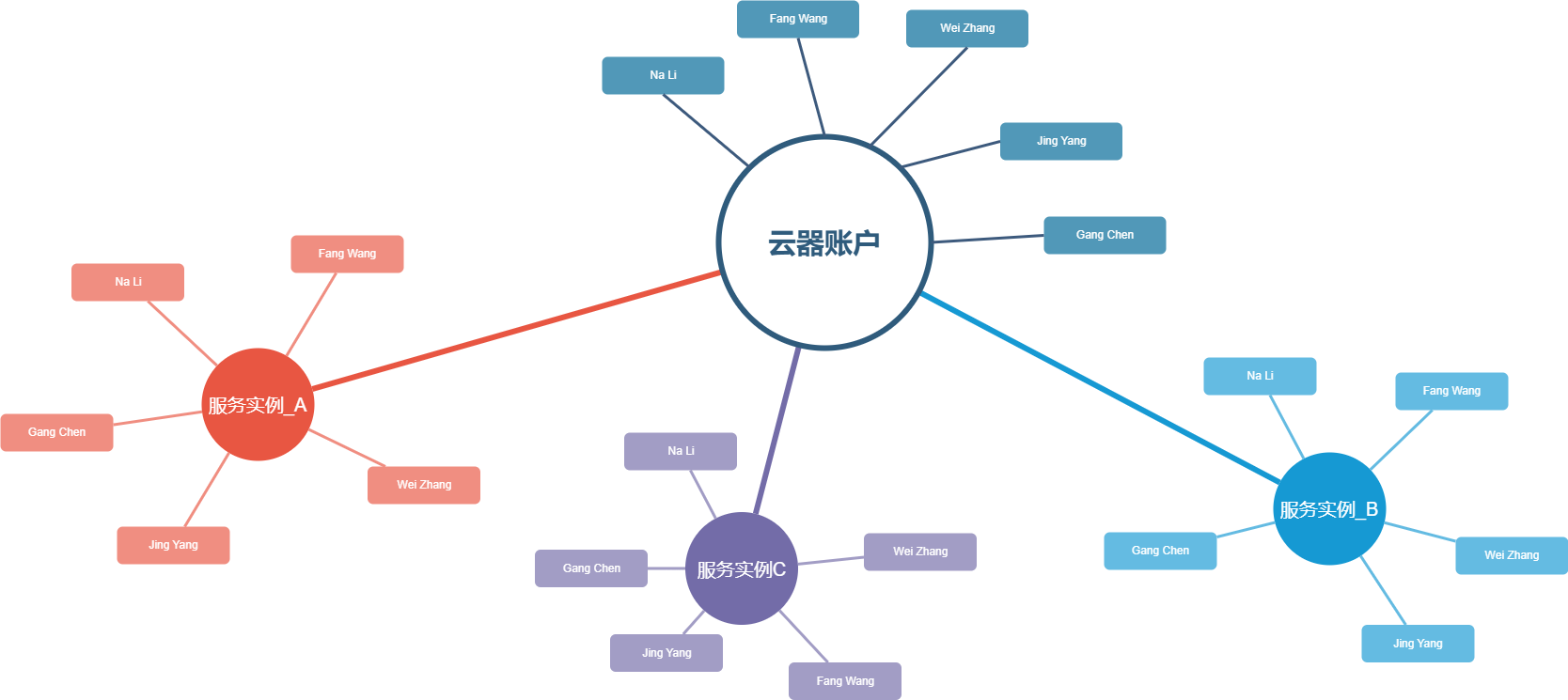
Global Users
Global users are users who perform global management and configuration on the Singdata platform. Each user is an independent identity within the system, with a unique username and password. Within an account, the username (user_name) must be unique to distinguish different user identities. Information such as phone numbers and email addresses can be repeated among different users.
Service Instance Users
Service instance users are users within the scope of a specific service instance (instance). Users can only be granted various roles and permissions within the service instance. Global users are automatically synchronized to each service instance, becoming service instance users. Therefore, the creation, deletion, and management of the enabled status of service instance users are all conducted on the global "User Management" page. The "User" list within the service instance only provides user information query functions.
Service instance users are by default granted the "instance_user" role, with no data or functional permissions. They need to be further granted permissions within the instance or workspace to perform operations.
User Types
Users in Lakehouse are mainly divided into regular users and service users:
Regular users typically represent actual personnel within an enterprise, performing daily data queries, analysis, management, and other operations in the system;
Service users are a special type of user created to meet the needs of automated processes or system-level operations. Service users are not allowed to log in via the Web but can use JDBC connections or be configured and scheduled for tasks, used for scheduling tasks, and programmatic calls to Lakehouse for automation or system-level operations.
In Lakehouse, service users include system service users and custom service users:
System service users are created by default when the Lakehouse account is initialized, used for customer service instance resources to achieve certain system functions;
Custom service users are identities that users can create themselves for their own business applications.
System service users in Lakehouse are disabled by default and will only prompt the user to "enable" them when the functionality used involves system service users, including:
sysservice_singdata——operates temporary system resources and system data in the SYS workspace.
sysservice_auto_mv——enabled when auto_mv is turned on, used to read job_history and manage temporary mv used by auto_mv.
