TABLE STREAM Function Introduction
Overview
Table Stream is an object in the Lakehouse architecture that can record changes in data manipulation language (DML) operations on a table, including insert, update, and delete operations. Table Stream also provides metadata information about each change, allowing users to take corresponding actions based on this information. It can record row-level changes between two transaction time points in a table, similar to the change data capture (CDC) feature of relational databases. Downstream systems can consume Table Stream through SQL statements, and when downstream DML operations include Table Stream, the Table Stream's offset will automatically shift. Table Stream can be created on Table, Dynamic Table, and Materialized View.
TABLE STREAM OFFSET
Table Stream Offset is a mechanism for storing the offset of the stream (i.e., the current transaction version of the source object). The offset determines the range of change records returned by the Table Stream. Here are some characteristics of Table Stream Offset:
- When a Table Stream is created, an initial snapshot of each row of the source object is taken to initialize an offset. Subsequently, Table Stream records information about DML changes that occur after this snapshot.
- Table Stream itself does not contain any table data; it only stores the offset of the source object and uses the version history of the source object to return change records.
- The offset of Table Stream can be specified at creation or updated during consumption. The method to specify the offset uses a timestamp.
- The offset of Table Stream is located between two table versions of the source object. When querying Table Stream, it returns changes caused by transactions committed after the offset and before the current time.
TABLE Version Control
In Lakehouse, whenever an insert, update, or delete operation is performed on a table, a new table version (also known as a snapshot) is generated. These versions are immutable, meaning once created, they cannot be modified. Each version contains a record of all data changes since the previous version. Table Stream is implemented based on TABLE versions. When a Stream is created, it tracks all subsequent versions of the source table and allows users to query changes that have occurred since the Table Stream was created.
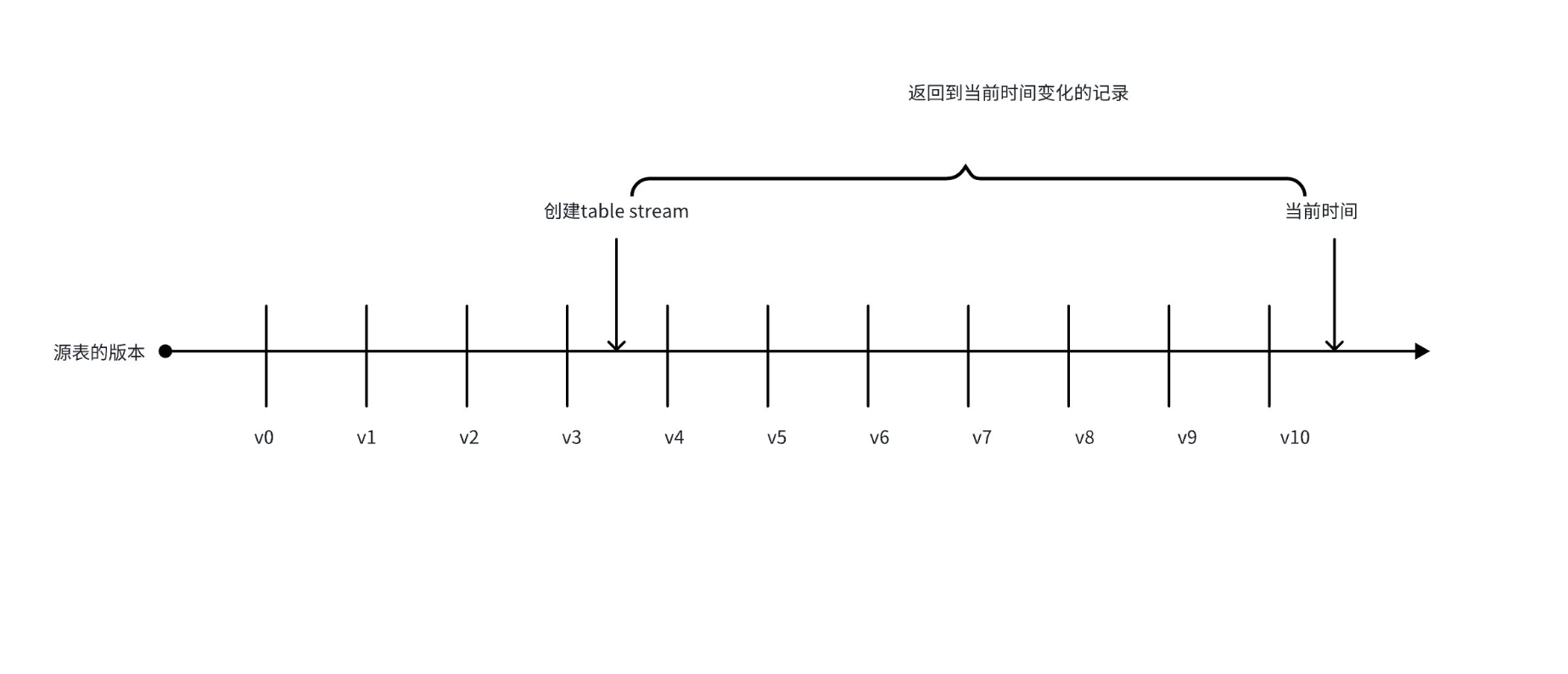
The example above shows a source table with 10 committed versions on the timeline. The offset of the Table Stream is currently between table versions v3 and v4. When querying (or consuming) the stream, the returned records include versions from table version v4, i.e., versions after the stream offset in the table timeline, to v10, i.e., the most recently committed table version in the timeline, including the minimal change set between these two versions.
Types Supported by TABLE STREAM
- STANDARD Mode: In this mode, all DML changes of the source object can be tracked, including insert, update, and delete (including table truncation). This mode provides row-level changes by connecting and processing all delta data changes to provide row-level increments. Delta changes in Table Stream refer to data changes that occur between two transaction time points.
- APPEND_ONLY Mode: Only records the INSERT operation data of the object. UPDATE and DELETE operations are not recorded.
Range of Data Recorded by TABLE STREAM
This time range depends on the data retention period and data extension period (DATA_RETENTION_DAYS) of the source object. The data retention period refers to the length of time the historical data of the source object can be queried through Time Travel.
Consuming TABLE STREAM
Consumers of Table Stream refer to downstream SQL containing DML statements that will consume Table Stream data. When downstream DML operations include Table Stream, the offset of the Table Stream will automatically shift. Executing DQL operations will not shift the offset, such as SELECT statements. A source object can have multiple streams tracking its changes simultaneously. Each Table Stream can have a different offset, i.e., different starting points. Each Table Stream can be used by different consumers, such as different tasks, scripts, or other mechanisms. Consumers can consume the change data in Table Stream by executing DML transactions, thereby updating the offset of the Table Stream.
When querying Table Stream, the result set includes additional metadata columns, including the type of change, the committed version, and the committed time. The specific fields are as follows:
__change_type: Contains DML operations (INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE_BEFORE, UPDATE_AFTER)__commit_version: Data submission version__commit_timestamp: Data submission time
Notes
- Before creating a Table Stream, you must enable change tracking on the base table by executing the following operation:
ALTER TABLE table_name set PROPERTIES ('change_tracking' = 'true');
- Data written through real-time upload can only be read after one minute. Table Stream can only read committed data. Real-time task data needs to wait for 1 minute to be confirmed, so Table Stream also needs to wait 1 minute to see it.
Use Cases
APPEND_ONLY Mode Case
-- Create a test table
CREATE TABLE test_table (id INT, name VARCHAR, age INT);
-- Must be enabled when creating table stream
ALTER table test_table set PROPERTIES ('change_tracking' = 'true');
CREATE TABLE stream test_stream ON TABLE test_table
WITH PROPERTIES ('TABLE_STREAM_MODE' = 'APPEND_ONLY');
-- Create append-only stream
CREATE table stream test_stream ON TABLE test_table
WITH
PROPERTIES ('TABLE_STREAM_MODE' = 'APPEND_ONLY');
-- Insert some data into the test table
INSERT INTO test_table VALUES
(1, 'Alice', 20),
(2, 'Bob', 25),
(3, 'Charlie', 30),
(4, 'David', 35),
(5, 'Eve', 40);
-- Query the test stream, should return the inserted data
SELECT * FROM test_stream;
+---------------+------------------+-------------------------+----+---------+--+
| __change_type | __commit_version | __commit_timestamp | id | name | |
+---------------+------------------+-------------------------+----+---------+--+
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 1 | Alice | |
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 2 | Bob | |
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 3 | Charlie | |
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 4 | David | |
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 5 | Eve | |
+---------------+------------------+-------------------------+----+---------+--+
-- Update some data in the test table
UPDATE test_table SET age = age + 5 WHERE id = 1 OR id = 3;
-- Query the test stream, should return the first appended records, only records the first inserted data, updates are not recorded
SELECT * FROM test_stream;
+---------------+------------------+-------------------------+----+---------+--+
| __change_type | __commit_version | __commit_timestamp | id | name | |
+---------------+------------------+-------------------------+----+---------+--+
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 1 | Alice | |
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 2 | Bob | |
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 3 | Charlie | |
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 4 | David | |
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 5 | Eve | |
+---------------+------------------+-------------------------+----+---------+--+
-- Delete some data from the test table
DELETE FROM test_table WHERE id = 2 OR id = 4;
-- Query the test stream, should return the first appended records, only records the first inserted data, deletes are not recorded
SELECT * FROM test_stream;
+---------------+------------------+-------------------------+----+---------+--+
| __change_type | __commit_version | __commit_timestamp | id | name | |
+---------------+------------------+-------------------------+----+---------+--+
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 1 | Alice | |
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 2 | Bob | |
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 3 | Charlie | |
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 4 | David | |
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 5 | Eve | |
+---------------+------------------+-------------------------+----+---------+--+
-- Delete the original table
DELETE FROM test_table;
-- Query the test stream, should return the first appended records, only records the first inserted data, deletes are not recorded
SELECT * FROM test_stream;
+---------------+------------------+-------------------------+----+---------+--+
| __change_type | __commit_version | __commit_timestamp | id | name | |
+---------------+------------------+-------------------------+----+---------+--+
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 1 | Alice | |
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 2 | Bob | |
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 3 | Charlie | |
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 4 | David | |
| INSERT | 3 | 2023-12-15 20:38:50.768 | 5 | Eve | |
+---------------+------------------+-------------------------+----+---------+--+
Note
To create a Table Stream, it must be executed on the base table.
ALTER TABLE table_name set PROPERTIES ('change_tracking' = 'true');
STANDARD Mode Case Study
-- Create a test table
CREATE TABLE test_table_offset (id INT, name VARCHAR, age INT);
-- Must enable when creating table stream
ALTER TABLE test_table_offset set PROPERTIES ('change_tracking' = 'true');
CREATE table stream test_table_offset_stream ON TABLE test_table_offset
WITH PROPERTIES ('TABLE_STREAM_MODE' = 'STANDARD');
-- Insert some data into the test table
INSERT INTO test_table_offset VALUES
(1, 'Alice', 20),
(2, 'Bob', 25),
(3, 'Charlie', 30),
(4, 'David', 35),
(5, 'Eve', 40);
-- Query the test stream, should return the inserted data
CREATE TABLE test_table_offset_consume (id INT, name VARCHAR, age INT);
-- Synchronize the just inserted data to the target table to keep consistency
INSERT INTO test_table_offset_consume
SELECT id,name,age FROM test_table_offset_stream;
-- Check if the stream has data
SELECT * FROM test_table_offset_stream;
+---------------+------------------+--------------------+----+------+-----+
| __change_type | __commit_version | __commit_timestamp | id | name | age |
+---------------+------------------+--------------------+----+------+-----+
-- Update some data in the test table
UPDATE test_table_offset SET age = age + 5 WHERE id = 1 OR id = 3;
-- Query the test stream, should return the updated data, at this point there will be two rows of data before and after the update
SELECT * FROM test_table_offset_stream;
+---------------+------------------+-------------------------+----+---------+--+
| __change_type | __commit_version | __commit_timestamp | id | name | |
+---------------+------------------+-------------------------+----+---------+--+
| UPDATE_BEFORE | 3 | 2023-12-26 10:47:04.051 | 1 | Alice | |
| UPDATE_AFTER | 4 | 2023-12-26 10:48:43.815 | 1 | Alice | |
| UPDATE_BEFORE | 3 | 2023-12-26 10:47:04.051 | 3 | Charlie | |
| UPDATE_AFTER | 4 | 2023-12-26 10:48:43.815 | 3 | Charlie | |
+---------------+------------------+-------------------------+----+---------+--+
-- Consume the updated data, use the stream data to update the target table
MERGE INTO test_table_offset_consume target USING test_table_offset_stream source_stream ON target.id = source_stream.id WHEN MATCHED
AND source_stream.__change_type = 'UPDATE_AFTER' THEN update set target.age = source_stream.age WHEN MATCHED
AND source_stream.__change_type = 'DELETE' THEN DELETE WHEN NOT MATCHED
AND source_stream.__change_type = 'INSERT' THEN
INSERT VALUES (target.id, target.name, target.age);
-- Check if the data in the updated table test_table_offset_consume is correct
SELECT * FROM test_table_offset_consume;
+----+---------+-----+
| id | name | age |
+----+---------+-----+
| 1 | Alice | 25 |
| 3 | Charlie | 35 |
| 2 | Bob | 25 |
| 4 | David | 35 |
| 5 | Eve | 40 |
+----+---------+-----+
-- Check if there is still data in the table stream, the data in the table stream has been fully consumed
SELECT * FROM test_table_offset_stream;
+---------------+------------------+--------------------+----+------+-----+
| __change_type | __commit_version | __commit_timestamp | id | name | age |
+---------------+------------------+--------------------+----+------+-----+
-- Delete some data from the test table
DELETE FROM test_table_offset WHERE id = 2 OR id = 4;
-- Check the table stream
SELECT * FROM test_table_offset_stream;
+---------------+------------------+-------------------------+----+-------+----+
| __change_type | __commit_version | __commit_timestamp | id | name | ag |
+---------------+------------------+-------------------------+----+-------+----+
| DELETE | 3 | 2023-12-26 10:47:04.051 | 2 | Bob | 25 |
| DELETE | 3 | 2023-12-26 10:47:04.051 | 4 | David | 35 |
+---------------+------------------+-------------------------+----+-------+----+
-- Consume the deleted data, use the table stream data to update the target table
MERGE INTO test_table_offset_consume target USING test_table_offset_stream source_stream ON target.id = source_stream.id WHEN MATCHED
AND source_stream.__change_type = 'UPDATE_AFTER' THEN update set target.age = source_stream.age WHEN MATCHED
AND source_stream.__change_type = 'DELETE' THEN DELETE WHEN NOT MATCHED
AND source_stream.__change_type = 'INSERT' THEN
INSERT VALUES (target.id, target.name, target.age);
---- Check if the data in the updated table test_table_offset_consume is correct
SELECT * FROM test_table_offset_consume;
+----+---------+-----+
| id | name | age |
+----+---------+-----+
| 1 | Alice | 25 |
| 3 | Charlie | 35 |
| 5 | Eve | 40 |
+----+---------+-----+
-- Check if there is still data in the table stream, the data in the table stream has been fully consumed
SELECT * FROM test_table_offset_stream;
+---------------+------------------+--------------------+----+------+-----+
| __change_type | __commit_version | __commit_timestamp | id | name | age |
+---------------+------------------+--------------------+----+------+-----+

