Spark Connector Overview
Lakehouse Connector for Spark allows using Lakehouse as an Apache Spark data source, similar to other data sources (PostgreSQL, HDFS, S3, etc.).
Interaction between Lakehouse and Spark
This connector supports bidirectional data movement between Lakehouse and Spark clusters. Using the connector, you can:
- Read tables from Lakehouse and convert them into Spark DataFrames
- Write data from Spark DataFrames into tables in Lakehouse.
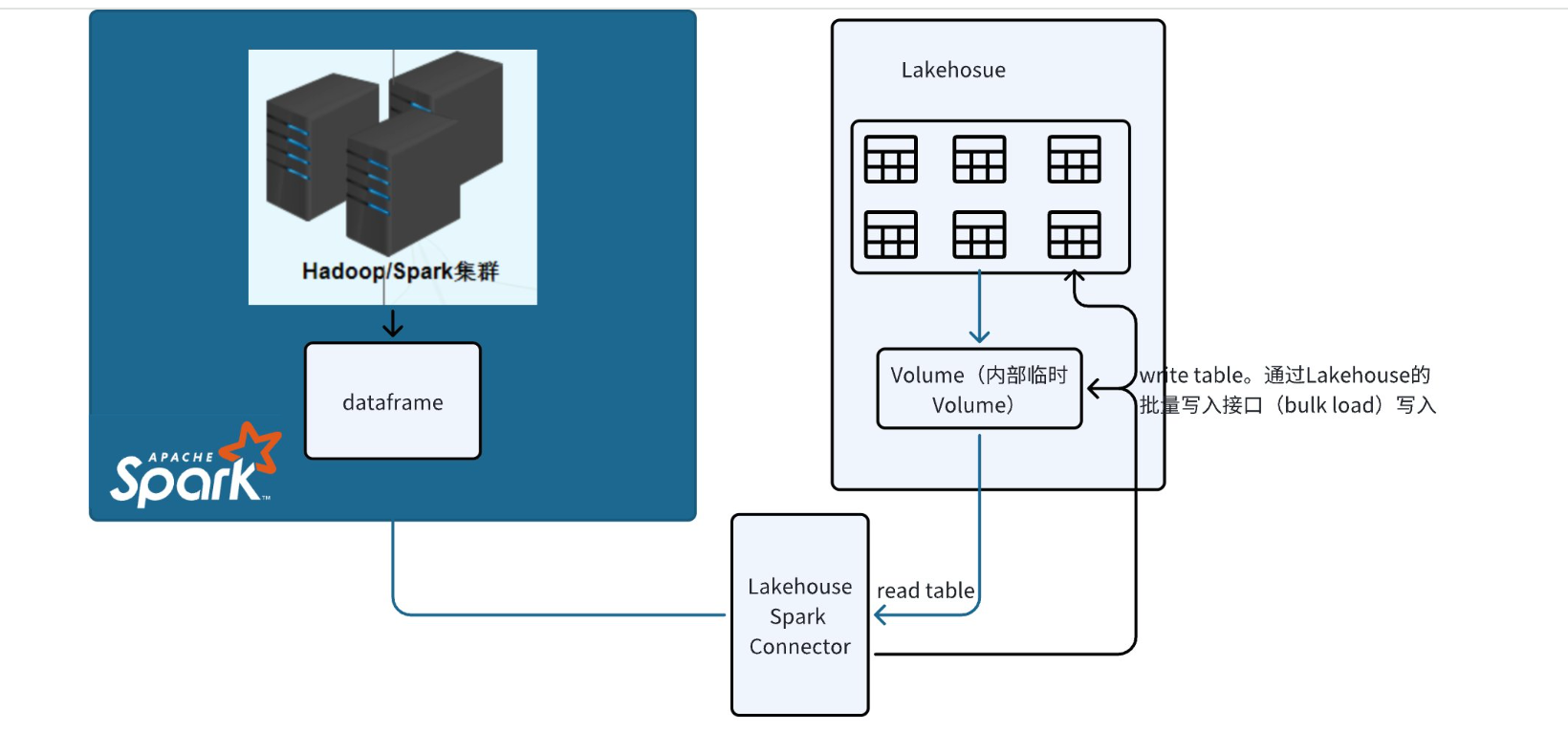
Data Transfer Process
Data transfer between the two systems is achieved through a Lakehouse volume that is automatically created and managed by the connector.
- When connecting to Lakehouse and executing queries, data is loaded into a temporary volume, which the connector uses to store data.
- Writing to Lakehouse is done by calling the bulkload SDK for batch writing.
Connection Parameters
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|
| endpoint | Y | The endpoint address for connecting to Lakehouse, e.g., 6861c888.cn-shanghai-alicloud.api.clickzetta.com. You can find the JDBC connection string in Lakehouse Studio under Management -> Workspace. The domain name in the JDBC connection string is the endpoint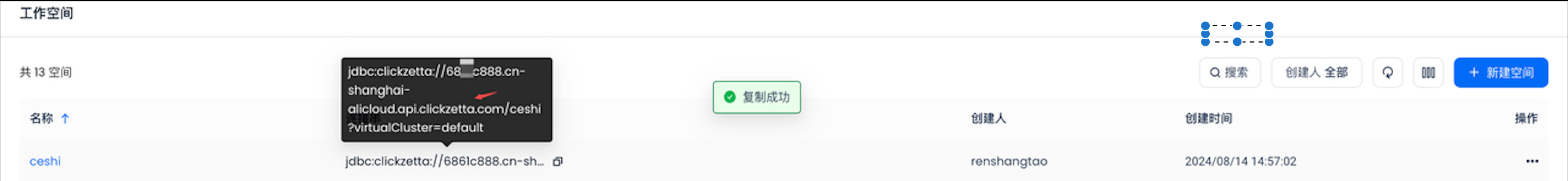 |
| username | Y | Username |
| password | Y | Password |
| workspace | Y | Workspace used |
| virtualCluster | Y | Virtual cluster used |
| schema | Y | Schema name accessed |
| table | Y | Name of the table being accessed |
Connect to Lakehouse using Spark Command Line
- Download the Spark 3.4 jar package from the Spark official website. In this case, the download is spark-3.4.3-bin-hadoop3.tgz
- Use the spark-shell command line to connect to Lakehouse locally
bin/spark-shell --jars ./spark_conenctor/spark-clickzetta-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar
import org.apache.spark.sql.functions.col
import com.clickzetta.spark.clickzetta.ClickzettaOptions
val readDf = spark.read.format("clickzetta").option(ClickzettaOptions.CZ_ENDPOINT, "lakehouse_url").option(ClickzettaOptions.CZ_USERNAME, "user").option(ClickzettaOptions.CZ_PASSWORD, "password").option(ClickzettaOptions.CZ_WORKSPACE, "quikc_start").option(ClickzettaOptions.CZ_VIRTUAL_CLUSTER, "default").option(ClickzettaOptions.CZ_SCHEMA, "public").option(ClickzettaOptions.CZ_TABLE, "birds_test").load()
readDf.show()
2. Use the spark-sql command line to connect to Lakehouse
bin/spark-sql --jars ./jars/spark-clickzetta-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar
CREATE TABLE lakehouse_table
USING clickzetta
OPTIONS (
endpoint 'lakehouse_url',
username 'user',
password 'password',
workspace 'quikc_start',
virtualCluster 'default',
schema 'public',
table 'birds_test'
);
3. Use the pyspark command line to connect to Lakehouse
bin/pyspark --jars ./jars/spark-clickzetta-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar
df=spark.read.format("clickzetta").option("endpoint", "jnsxwfyr.api.singdata.com").option("username", "user").option("password", "password").option("workspace","quick_start").option("virtualCluster", "default").option("schema", "public")option("table","birds_test").load()
df.show()
Lakehouse Spark Connector Usage Restrictions
- Writing to pk tables is not supported
- Must write all fields, partial field writing is not supported
Practical Case of Using Spark Connector
Using Spark to Write Data to Lakehouse
Overview
Seamless data transfer between different platforms is crucial for effective data management and analysis. A common scenario we help many customers solve is using Spark to process data and write it into Lakehouse, with BI reports connecting to Lakehouse for queries.
We will write a Spark program and run it in the Spark environment, using the Connector provided by Lakehouse to write data into Lakehouse.
Environment Requirements
-
Proficiency in Spark programming. You can refer to Developing Spark with IntelliJ IDEA
-
The dataset used in this case is the movie rating dataset from Spark's GitHub. You can download it by clicking the download button on this link
-
Create a table in Lakehouse
-
Download the Spark Connector package provided by Lakehouse (currently the download package is provided by Lakehouse support). After downloading, add the jar to the local maven repository to facilitate referencing and packaging in maven projects.
-
Modify the pom.xml file and add the following dependencies
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
<spark.version>3.4.0</spark.version>
<scala.version>2.12.17</scala.version>
<scala.binary.version>2.12</scala.binary.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.scala-lang</groupId>
<artifactId>scala-library</artifactId>
<version>${scala.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-core_${scala.binary.version}</artifactId>
<version>${spark.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-sql_${scala.binary.version}</artifactId>
<version>${spark.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-catalyst_${scala.binary.version}</artifactId>
<version>${spark.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.scala-lang</groupId>
<artifactId>scala-compiler</artifactId>
<version>${scala.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.clickzetta</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-clickzetta</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.scala-lang</groupId>
<artifactId>scala-library</artifactId>
<version>${scala.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<!-- scala compilation plugin -->
<plugin>
<groupId>net.alchim31.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>scala-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
</plugin>
<!-- java compilation plugin -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<!-- plugin version -->
<version>3.8.1</version>
<!-- compilation level forced to jdk1.8 -->
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<!-- encoding format -->
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<!-- maven packaging plugin -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.4.3</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>shade</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<transformers>
<transformer implementation="org.apache.maven.plugins.shade.resource.ManifestResourceTransformer">
<!-- specify the location of main -->
<mainClass>*</mainClass>
</transformer>
</transformers>
<filters>
<filter>
<artifact>*:*</artifact>
<!-- filter out unnecessary jar packages -->
<excludes>
<exclude>META-INF/*.SF</exclude>
<exclude>META-INF/*.DSA</exclude>
<exclude>META-INF/*.RSA</exclude>
</excludes>
</filter>
</filters>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
import com.clickzetta.spark.clickzetta.ClickzettaOptions
import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession
object SparkLH {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val spark = SparkSession.builder
.master("local")
.appName("ClickzettaSourceSuite")
.getOrCreate()
// Read data file
val rdd = spark.sparkContext.textFile("./Downloads/sample_movielens_data.txt")
// Split data
val rddSplit = rdd.map(line => line.split("::"))
// Convert to DataFrame
import spark.implicits._
val df= rddSplit.map(arr => (arr(0).toInt, arr(1).toInt, arr(2).toFloat)).toDF()
// Write to Lakehouse
df.write.format("clickzetta")
.option(ClickzettaOptions.CZ_ENDPOINT, "jnsxwfyr.api.clickzetta.com")
.option(ClickzettaOptions.CZ_USERNAME, "username")
.option(ClickzettaOptions.CZ_PASSWORD, "paswword")
.option(ClickzettaOptions.CZ_WORKSPACE, "quick_start")
.option(ClickzettaOptions.CZ_VIRTUAL_CLUSTER, "default")
.option(ClickzettaOptions.CZ_SCHEMA, "public")
.option(ClickzettaOptions.CZ_TABLE, "sample_movie_data")
.mode("overwrite")
.save()
spark.stop()
}
}
Using Spark ML to Process Lakehouse Data
Objective:
By reading data existing in the Lakehouse, use Spark ML to train a recommendation model to predict user ratings for movies, and use ranking metrics to evaluate the model's performance.
Environment Preparation
-
The data used in this case is the movie rating dataset from Spark's GitHub. You can download it by clicking the download button on this link. Use the Spark write to Lakehouse data case to write it into the Lakehouse.
-
Create a table in the Lakehouse
-
Install Python package version greater than 3.6
-
Install Pyspark
-
Download the Spark Connector package provided by Lakehouse,
-
If running in cluster mode, you can use --jars to specify the required dependency jar packages
-
Writing Python Code
# $example off$
from pyspark import SparkConf, SparkContext
from pyspark.sql import SQLContext
from pyspark.sql.types import *
# $example on$
from pyspark.mllib.recommendation import ALS, Rating
from pyspark.mllib.evaluation import RegressionMetrics
import os
os.environ['PYSPARK_SUBMIT_ARGS'] = '--jars 。/Downloads/spark-clickzetta-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar pyspark-shell'
if __name__ == "__main__":
sc = SparkContext("local", "Simple App")
spark = SQLContext(sc)
df=spark.read.format("clickzetta").option("endpoint", "jnsxwfyr.api.clickzetta.com").option("username", "user").option("password", "password").option("workspace", "qucik_start").option("virtualCluster", "default").option("schema", "public").option("table", "sample_movie_data").load()
# Convert DataFrame to RDD and parse as Rating objects
ratings = df.rdd.map(lambda row: Rating(row.user_id, row.movie_id, row.rating-2.5))
# Continue with subsequent model training and evaluation steps
model = ALS.train(ratings, rank=10, iterations=10, lambda_=0.01)
usersProducts = ratings.map(lambda r: (r.user, r.product))
predictions = model.predictAll(usersProducts).map(lambda r: ((r.user, r.product), r.rating))
ratingsTuple = ratings.map(lambda r: ((r.user, r.product), r.rating))
scoreAndLabels = predictions.join(ratingsTuple).map(lambda tup: tup[1])
metrics = RegressionMetrics(scoreAndLabels)
# Root mean squared error
print("RMSE = %s" % metrics.rootMeanSquaredError)
# R-squared
print("R-squared = %s" % metrics.r2)
# $example off$



