Using Data Sources in Python/Shell Task
Overview
Python/Shell tasks support the use of pre-configured data sources. By leveraging the built-in clickzetta-dbutils package in the runtime environment, tasks can directly reuse the connection configurations from Management -> Data Sources, eliminating the need to repeatedly set up connections via code within the node. This approach enhances the security of sensitive information and streamlines development and management processes.
Currently supported data sources include:
- Lakehouse Data Source
- MySQL Data Source
- PostgreSQL Data Source
Interface Operation Guide
Selecting Data Sources in Python/Shell Tasks
In the configuration panel of Python/Shell tasks, you can select one or more data sources (ensure that the data sources have been created and tested for connectivity in Management -> Data Sources). This configuration will apply to both ad-hoc runs and scheduled runs of the current task:
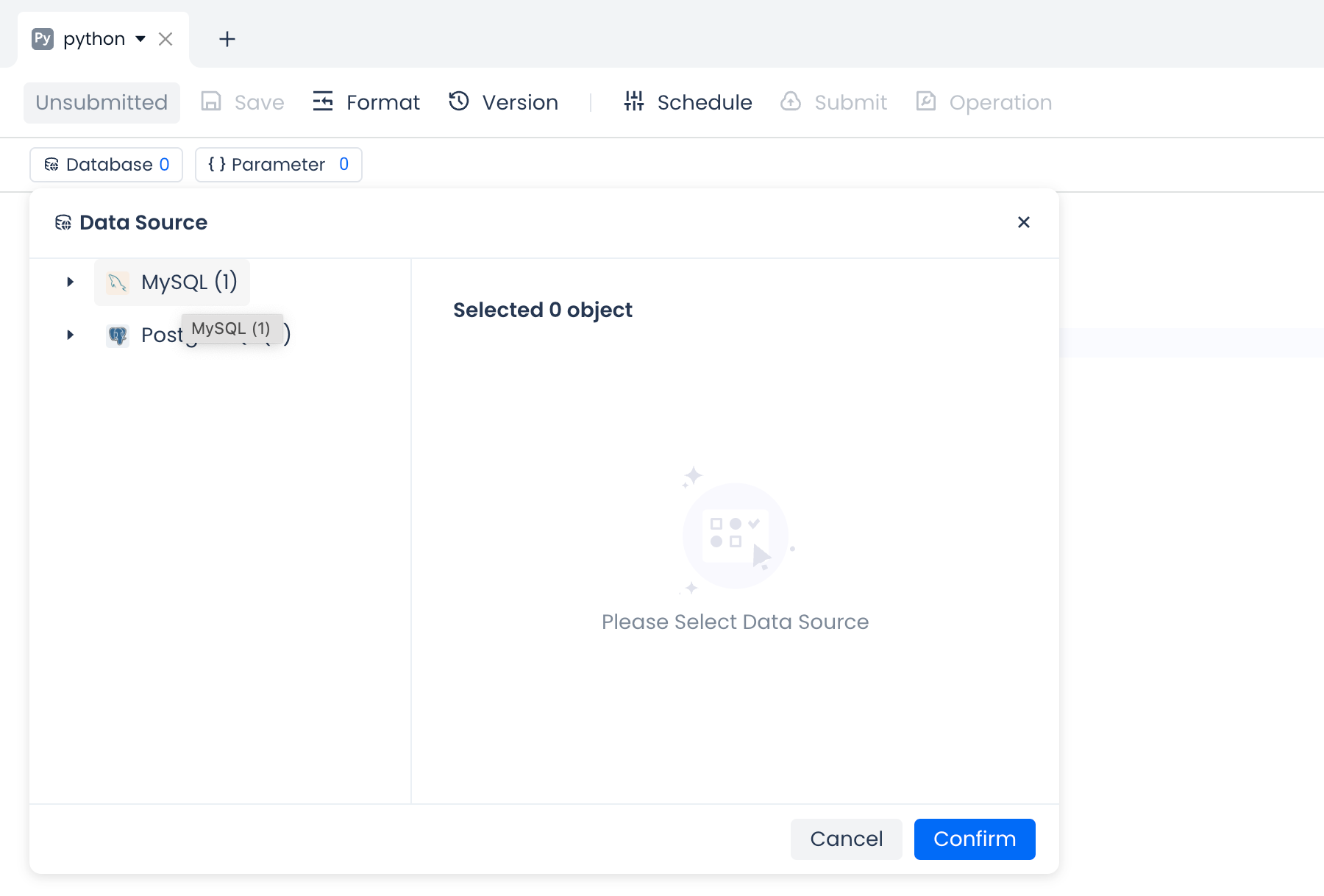
Note: The default Lakehouse data source of the current workspace can be accessed directly in the code without needing to add it here.
Accessing Data Sources in Code
After adding the data source, you can begin writing Python/Shell task code. To connect to a data source, call the get_active_engine("your_datasource_name") function from the clickzetta_dbutils Python library. You only need to provide the data source name, without specifying connection details such as the data source URL or password. Additionally, the Builder pattern is supported, as detailed in the following API usage guide and code examples.
API Usage Guide
get_active_engine
A convenient function for creating a database engine in Studio Python nodes (currently supports MySQL, PostgreSQL and Lakehouse data sources).
Function Signature
Parameter Description
ds_name(str): The name of the data source, which must match the name inManagement -> Data Sources.vcluster(str, optional): The virtual cluster name for ClickZetta data sources (required for ClickZetta).workspace(str, optional): The workspace name, defaulting to the current workspace.schema(str, optional): The name of the schema to connect to, defaulting to 'public'.options(dict, optional): Additional connection options.query(dict, optional): Additional query parameters for the SQLAlchemy URL.
Return Value
- An SQLAlchemy Engine instance.
Example
- A PostgreSQL data source named "qiliang_test_pg" has been added in
Management -> Data Sources. - The database "answer" with schema "public" is selected for "qiliang_test_pg" in the current Python node.
- Accessing tables within
qiliang_test_pg -> answer -> publicusingget_active_engine:
- Accessing tables in other databases within
qiliang_test_pgusingget_active_engine(requires configuring access to other permitted databases inManagement -> Data Sources, e.g., database "sample" with schema "public"):
get_active_lakehouse_engine
A convenient function for creating a Lakehouse data source database engine.
Function Signature
Parameter Description
vcluster(str, optional): The virtual cluster name for ClickZetta data sources (required).workspace(str, optional): The workspace name, defaulting to the current workspace.schema(str, optional): The name of the schema to connect to, defaulting to 'public'.options(dict, optional): Additional connection options.query(dict, optional): Additional query parameters for the SQLAlchemy URL.driver(str, optional): The driver name for the connection.
Return Value
- An SQLAlchemy Engine instance.
Exception
DatabaseConnectionError: Raised when the Lakehouse data source is not found in the configuration.
Example
- The cluster name to be used is "default" in
Compute -> Clusters. - The data to be accessed is in the schema "brazilianecommerce" within the workspace "ql_ws", specifically the table "olist_customers".
- Accessing tables within
qiliang_test_pg -> answer -> publicusingget_active_lakehouse_engine:
DatabaseConnectionManager
A database connection manager that supports chainable configuration of connection parameters. The actual SQLAlchemy connection is triggered only when build(self, *args, **kwargs) is called.
use_workspace
Sets the workspace for the connection, required only for Lakehouse data sources.
use_schema
Sets the schema for the connection.
Note: For PostgreSQL, `` should be set to the database name due to SQLAlchemy design.
use_vcluster
Sets the virtual cluster for the connection, required only for Lakehouse data sources.
use_options
Sets additional connection options.
Note: For PostgreSQL, schema should be set using undefined"}).
use_query
Sets additional query parameters for the connection.
build
Creates an SQLAlchemy engine based on the data source name and optional configurations.
Usage Example
Code Examples
Example of Using PostgreSQL Data Source in Python Node
Example of retrieving all PostgreSQL tables for postgres_source_name:
Example of Using MySQL Data Source in Python Node
Example of Using Lakehouse Data Source in Python Node
Example of Using Data Sources in Shell Node
In Shell nodes, data sources can be used by creating a Python script file:
Precautions
- Data source configurations support both Adhoc execution and scheduled execution scenarios.
- Using a non-existent data source name will result in an error. Please ensure that before using it, the corresponding data source is selected in the Studio under
Development -> Python Task -> Data Source. For Postgres and MySQL data sources, they must be created and tested for connectivity underManagement -> Data Sourceto ensure successful connection. - When using Lakehouse data sources, the
vclusterparameter must be configured. Lakehouse data sources directly use the built-in Lakehouse data source seen inManagement -> Data Sources. - Connection information for data sources is securely handled to prevent plaintext password leaks.
- Multiple data sources of different types can be used within the same node.
