Power BI to connect to Lakehouse
Lakehouse implements the MySQL client-server communication protocol, so you can use MySQL drivers to connect to Lakehouse. However, Lakehouse does not implement MySQL syntax and data types. You can connect to Lakehouse using a MySQL client, but the SQL statements executed should use Lakehouse syntax, not MySQL syntax. For example, the mysqldump command is not available in Lakehouse. This article uses the MySQL driver in PowerBI to connect to Lakehouse, providing a quick guide on how to connect to Lakehouse. We use a financial sample dataset.
Prerequisites
-
Currently, a password reset is required, even for newly created accounts. This is because MySQL version 5.x uses the
mysql_native_passwordkey, and Lakehouse needs to save MySQL's encryption algorithm. Currently, Lakehouse only saves MySQL key encryption algorithms when the password is changed. You can keep the same password as before when changing it to avoid affecting other task connections. -
Set a compute cluster for the user. Since there is no way to set the cluster in the MySQL protocol, users can use SQL commands to add a default compute cluster for the user. This way, the cluster will be used during the MySQL connection. It should be noted that BI scenarios often have performance requirements for analysis, so it is recommended to choose an appropriate specification of the analytical compute cluster for the BI tool connection user to provide the best query performance.
-
Prepare the username. When using the MySQL protocol connection address, only one URL can be passed, making it impossible to concatenate the Lakehouse instance name and workspace name. Therefore, the instance name and workspace name need to be concatenated into the username.
- The username format requirements are as follows:
-
-
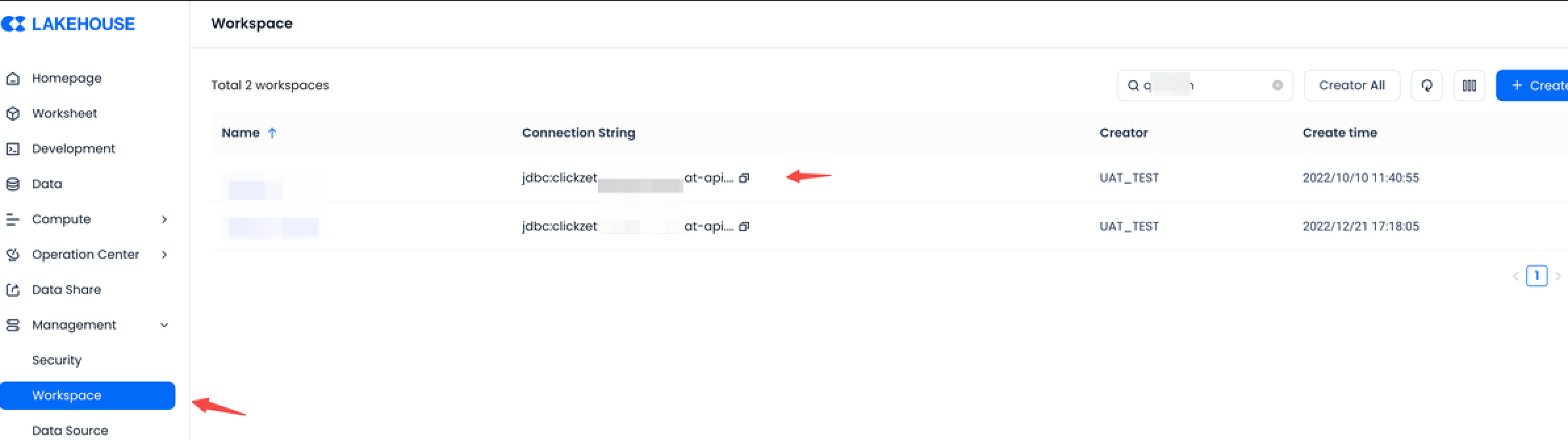
instance_name acquisition: Obtain the JDBC connection string on the Workspace page. For example, in
jdbc:clickzetta://``jnsxwfyr.api.clickzetta.com/quick_start?virtualCluster=default,jnsxwfyris the instance_name.-
-
workspace_name acquisition: The name of the workspace.
-
-
Create schema and table in Lakehouse, upload data
Connect to Powerbi
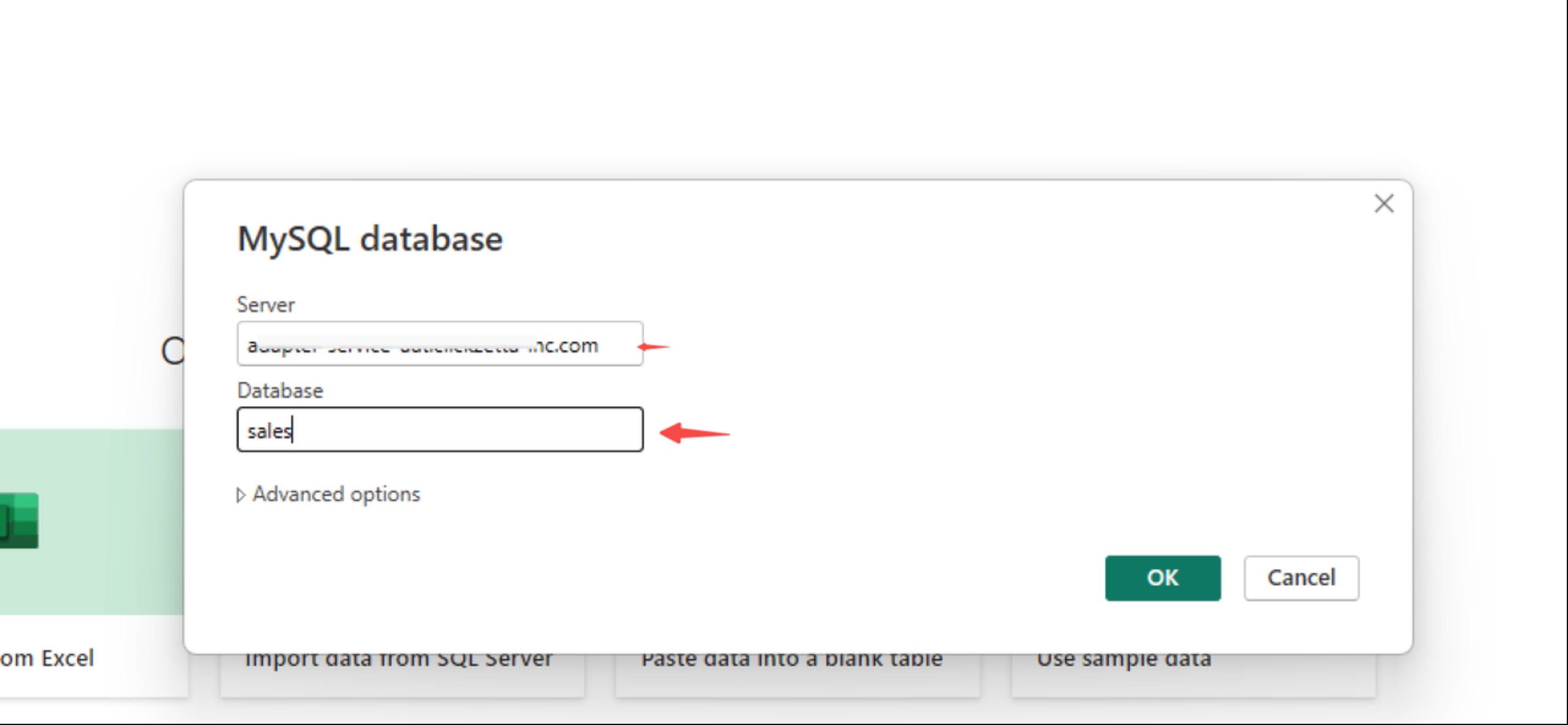
- Click to get data source, search for Mysql
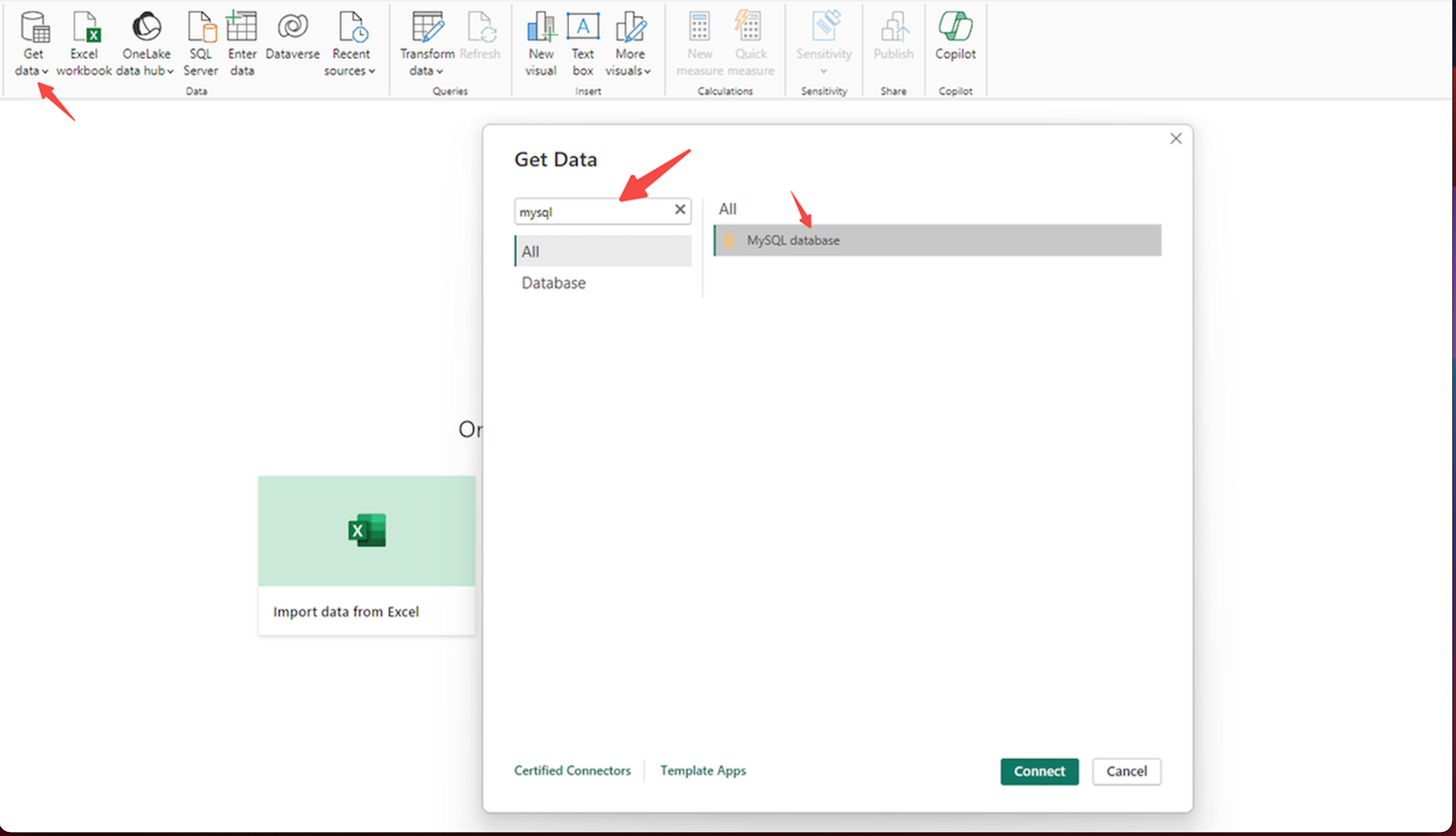
-
Enter the mysql connection address and schema name of Lakehouse, the schema in this case is public
Connection addresses for each region
| Cloud Service Provider | Region | Connection Address |
| Alibaba Cloud | Shanghai | cn-shanghai-alicloud-mysql.api.clickzetta.com |
| Singapore | ap-southeast-1-alicloud-mysql.api.singdata.com | |
| Tencent Cloud | Shanghai | ap-shanghai-tencentcloud-mysql.api.clickzetta.com |
| Beijing | ap-beijing-tencentcloud-mysql.api.clickzetta.com | |
| Guangzhou | ap-guangzhou-tencentcloud-mysql.api.clickzetta.com | |
| Amazon | Beijing | cn-north-1-aws.api-mysql.clickzetta.com |
| Singapore | ap-southeast-1-aws-mysql.api.singdata.com |
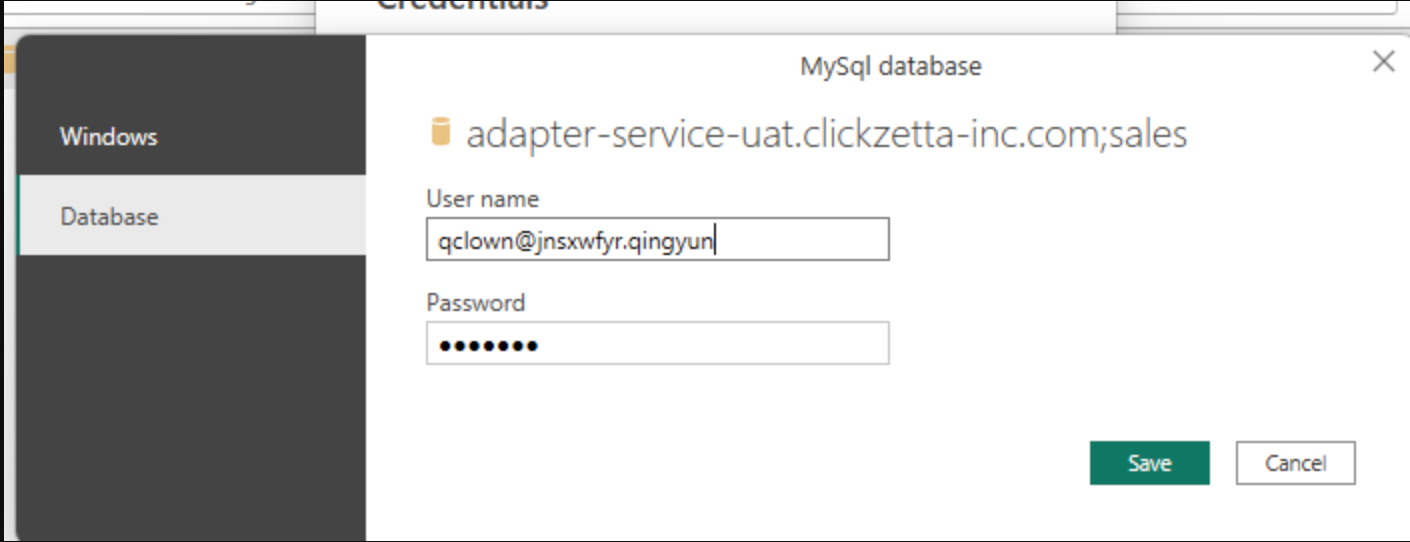
- Configure username and password. When connecting with the MySQL protocol, only one URL can be passed in and the instance name and workspace name of Lakehouse cannot be concatenated. Therefore, the instance name and workspace name need to be concatenated into the username. The username format requirements are as follows:
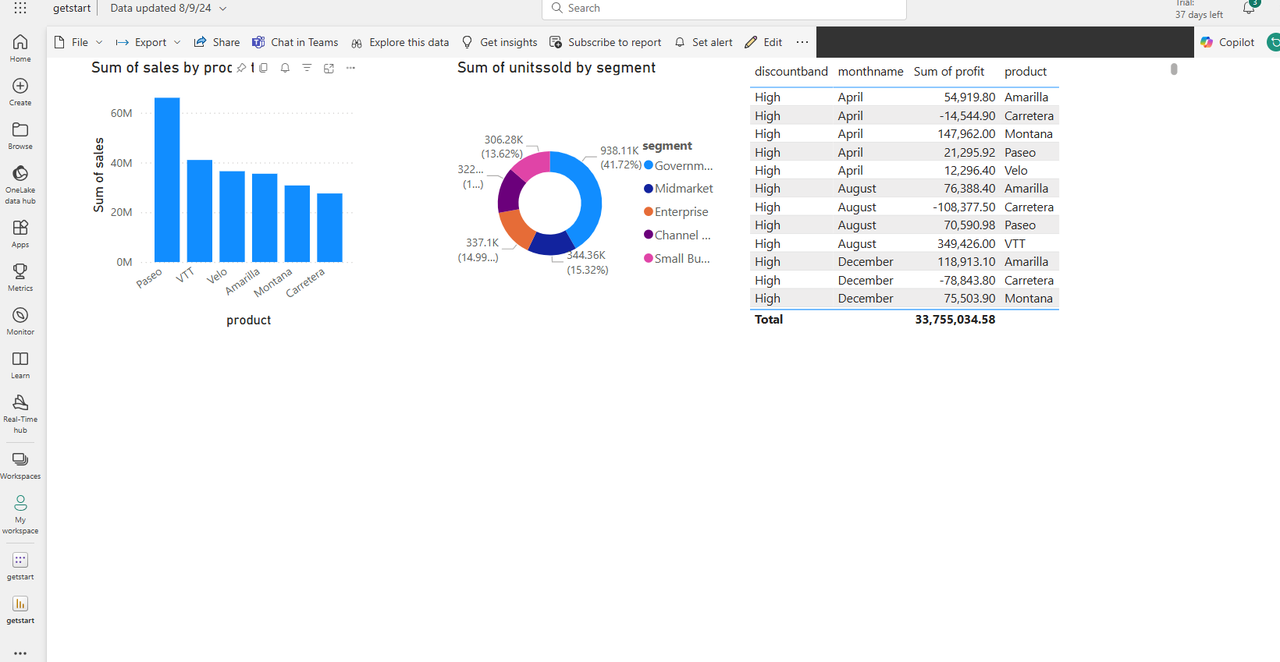
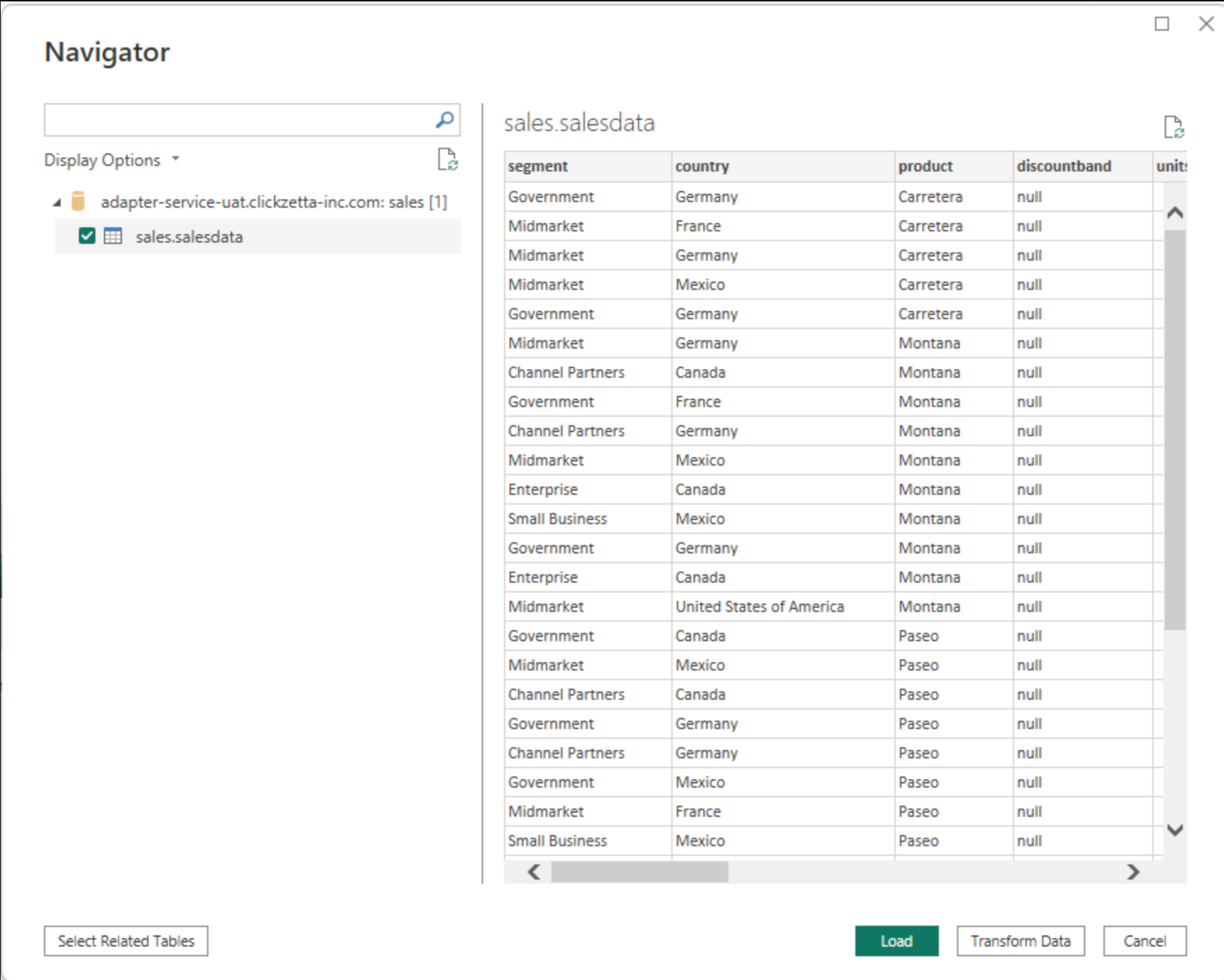
- Retrieve Lakehouse Table
- Configure Dashboard
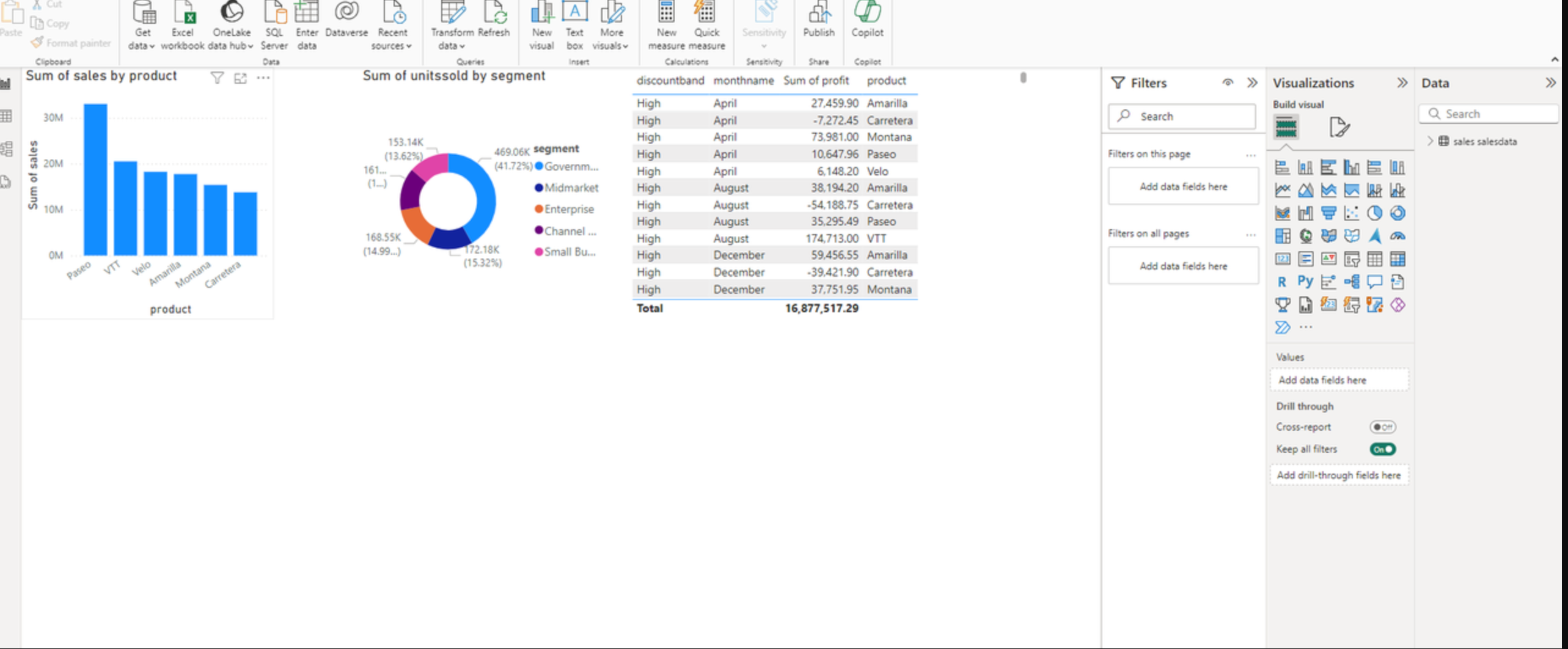
-
Publish Dashboard to Power Service
-
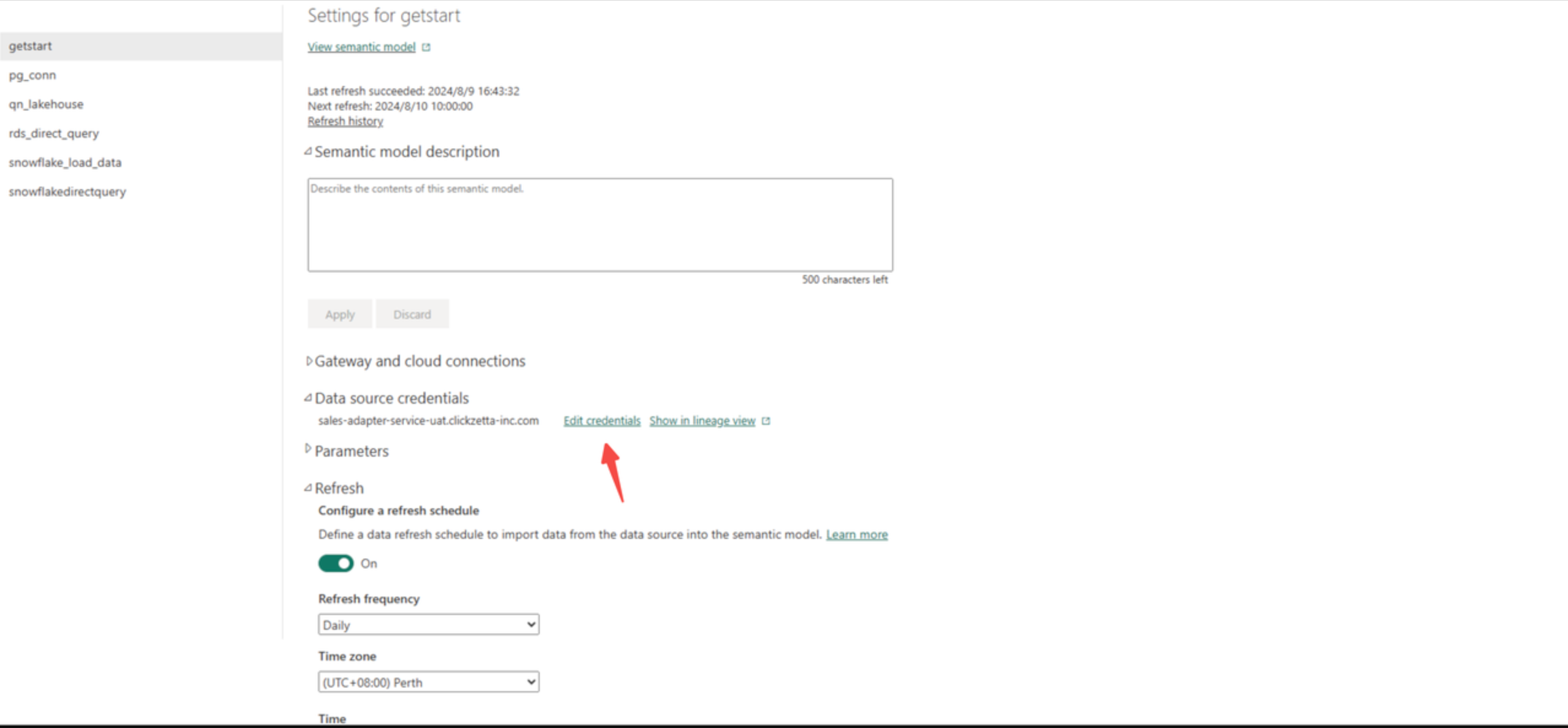
Find the recently published dashboard in Power Service and configure scheduling information and password authentication information
-
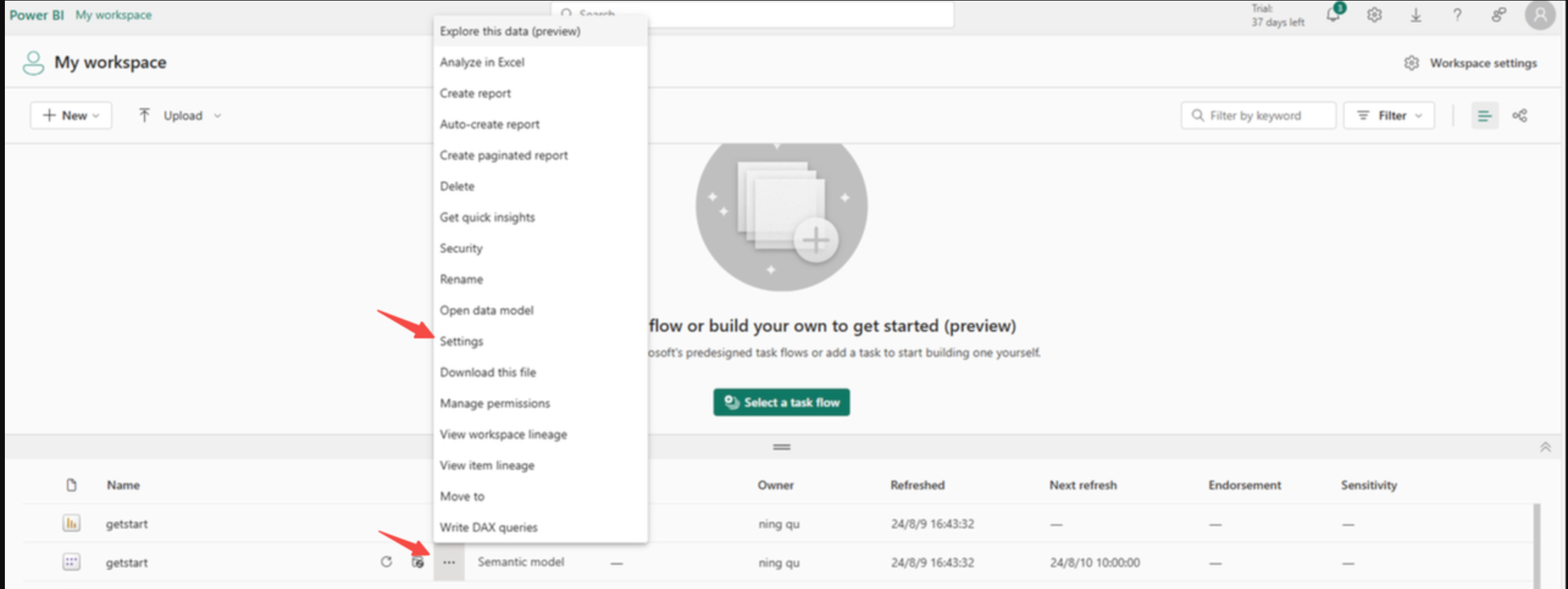
-
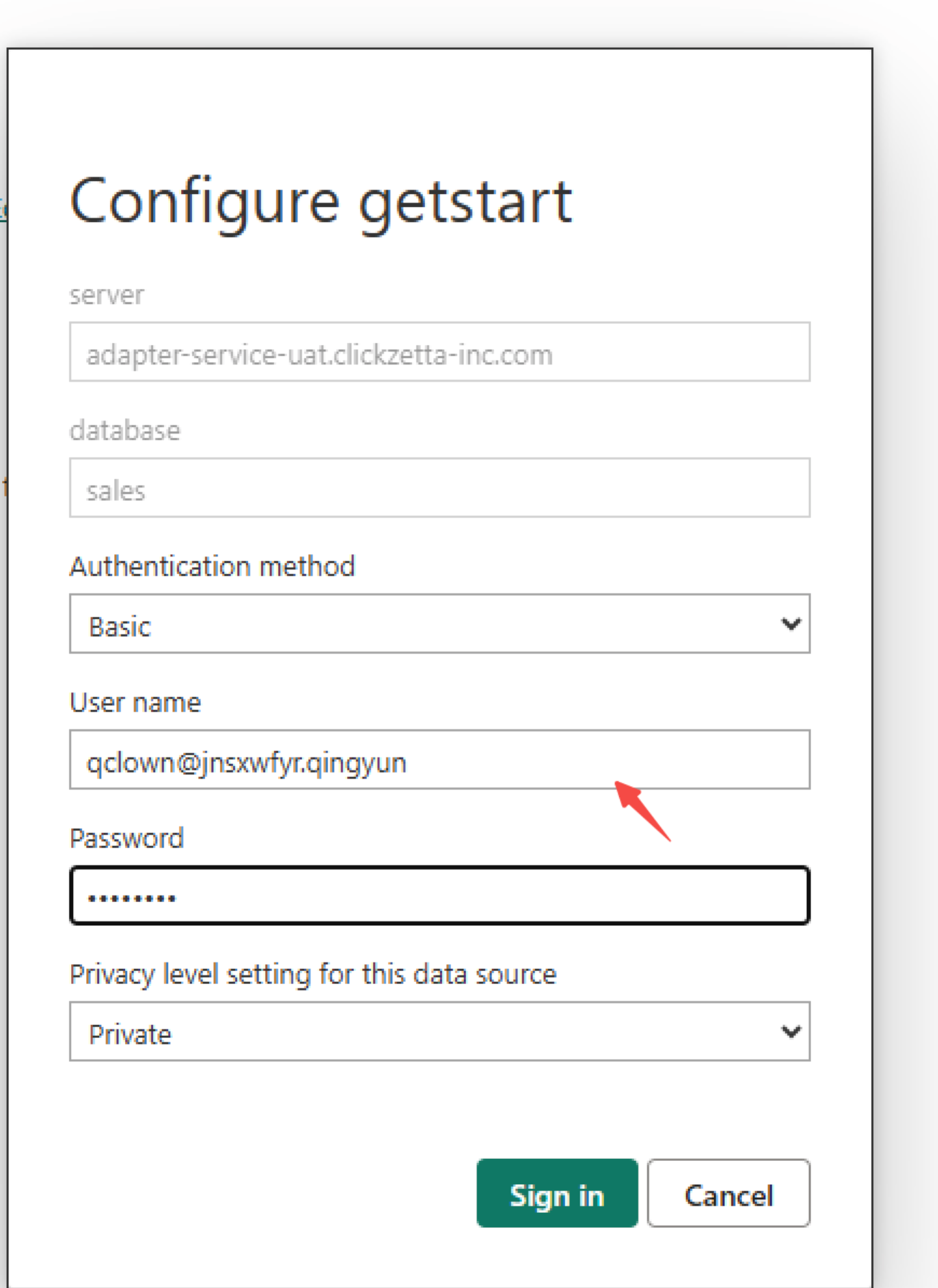
Edit Username and Password
-
Edit Scheduling Information
-
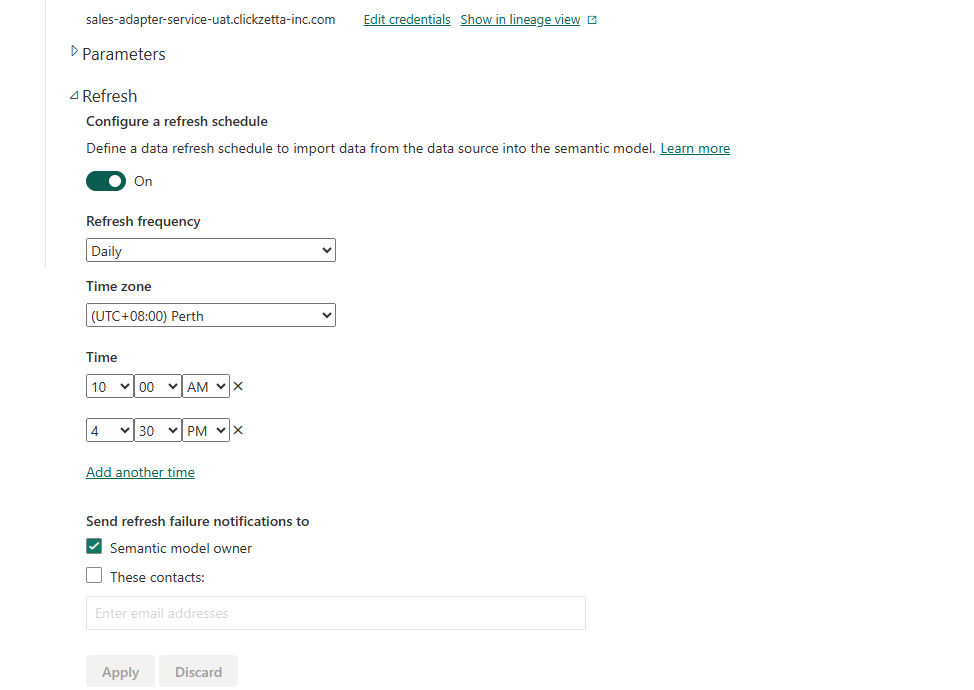
-
-
View Dashboard in Power Service