Multi-Table Real-Time Sync Task
Through the multi-table real-time sync task, you can synchronize the entire database to the Lakehouse, including full synchronization of historical data and real-time incremental synchronization of changed data. The multi-table real-time synchronization function can achieve end-to-end timeliness at the second level, providing you with better data freshness.
When using multi-table sync tasks, please note the following limitations and preparation work.
Supported Data Source Types and Versions
| Type | Incremental Reading Mode | Database Version |
|---|---|---|
| MySQL | Binlog | 5.6 and above, 8.x |
| PostgreSQL | WALs Log | 14 and above |
Source Database Preparation
Database Parameter Configuration
PostgreSQL
Note: Modifying the following parameters requires restarting the PostgreSQL Server to take effect.
| Configuration | Description | Default Value (Unit) |
|---|---|---|
| wal_level | Write-Ahead Logging (WAL) level, determines how much information is written to the WAL. replica: writes enough data to support WAL archiving and replication, including running read-only queries on standby servers minimal: removes all records except those needed for recovery from a crash or immediate shutdown logical: adds information needed to support logical decoding. To support real-time synchronization, set wal_level to logical | replica |
| max_replication_slots | Number of slots allowed to be created on the server. | 10 |
| max_wal_senders | Maximum number of wal sender processes that can run simultaneously on the server, corresponding to the number of real-time synchronization tasks that can be performed simultaneously. | 10 |
| max_slot_wal_keep_size | Size of wal kept per slot. -1 means unlimited. | -1 (MB) |
| wal_sender_timeout | Replication connections exceeding this configuration time will be terminated. | 60000 (ms) |
MySQL
| Attribute | Description | Required Configuration | Query Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| log_bin | Whether to enable binlog | ON or on | SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'log_bin' |
| binlog_format | Binlog log format. There are three possible values: statement mode: records the SQL statements. The advantage is that the binlog content is small, but the disadvantage is that it may sometimes lead to inaccurate synchronization results because the same SQL function may produce different results on the master and server, leading to incorrect synchronization results. row: records the complete row data before and after the SQL execution. The advantage is that the data is accurate, but the disadvantage is that the binlog data volume is large. mixed: MySQL decides whether to use statement mode or row mode to save records based on the executed SQL content. | ROW or row | SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'binlog_format' |
| binlog_row_image | The way binlog records before and after images | FULL or full (records all fields of both images) | SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'binlog_row_image' |
| binlog_expire_logs_seconds | binlog automatic cleanup time | Configure according to business requirements, it is recommended to set it to 86400 (seconds) or more |
Database Permission Configuration
When synchronizing change events from different types of data sources, appropriate permissions need to be configured on the respective data source servers to ensure normal data synchronization. Although directly assigning an administrator or superuser permission is sufficient to ensure the task runs normally, it is usually desirable to minimize the permissions that need to be assigned to the user synchronizing the data. The specific permission configurations required for each operation step are described as follows.
PostgreSQL
Please note that when executing the authorization SQL statements, ensure that the executing account itself has the permissions to grant the required permissions. It is recommended to use an administrator account. To ensure the smooth operation of the task, it is recommended to execute the authorizations for all the scenarios listed below.
Scenario: Configure task (retrieve metadata: schema list, table list, table field list)
Required permissions:
Authorization Method
- Grant a role permission to read
information_schema: - Grant a role permission to read a specific table:
Scenario: Synchronize WAL Logs
Required Permissions
Authorization Statement
Scenario: Synchronize Historical Full Data (Optional)
Required Permissions
Authorization Statement
- Grant a role permission to read a table:
- Grant a role permission to read all tables under a schema:
Scenario: Change Data Capture, Create Publication
Required Permissions
Authorization Statement
- Grant CREATE permission
MySQL
Please note that when executing the grant SQL statement, ensure that the executing account itself has the GRANT OPTION privilege. It is recommended to use a super admin account such as root. To ensure the smooth operation of the task, it is recommended to execute the authorization for all the scenarios below.
Usage Scenario: Configure Task (Retrieve Metadata: database list, table list, table field list)
Required Permissions
Authorization Statement
- Grant the user permission to query the database list:
- Grant users the permission to query the table list and table details (SELECT includes the permission for SHOW TABLES):
Usage Scenario: Synchronizing Change Data Based on Binlog Logs
Required Permissions
Authorization Statement
Usage Scenario: Synchronize Historical Full Data
Required Permissions
Authorization Statement
- Grant the user permission to query the table:
Task Creation
Operation Entry
In the task development interface, click on the new operation and select the "Multi-table Real-time Synchronization" task type.
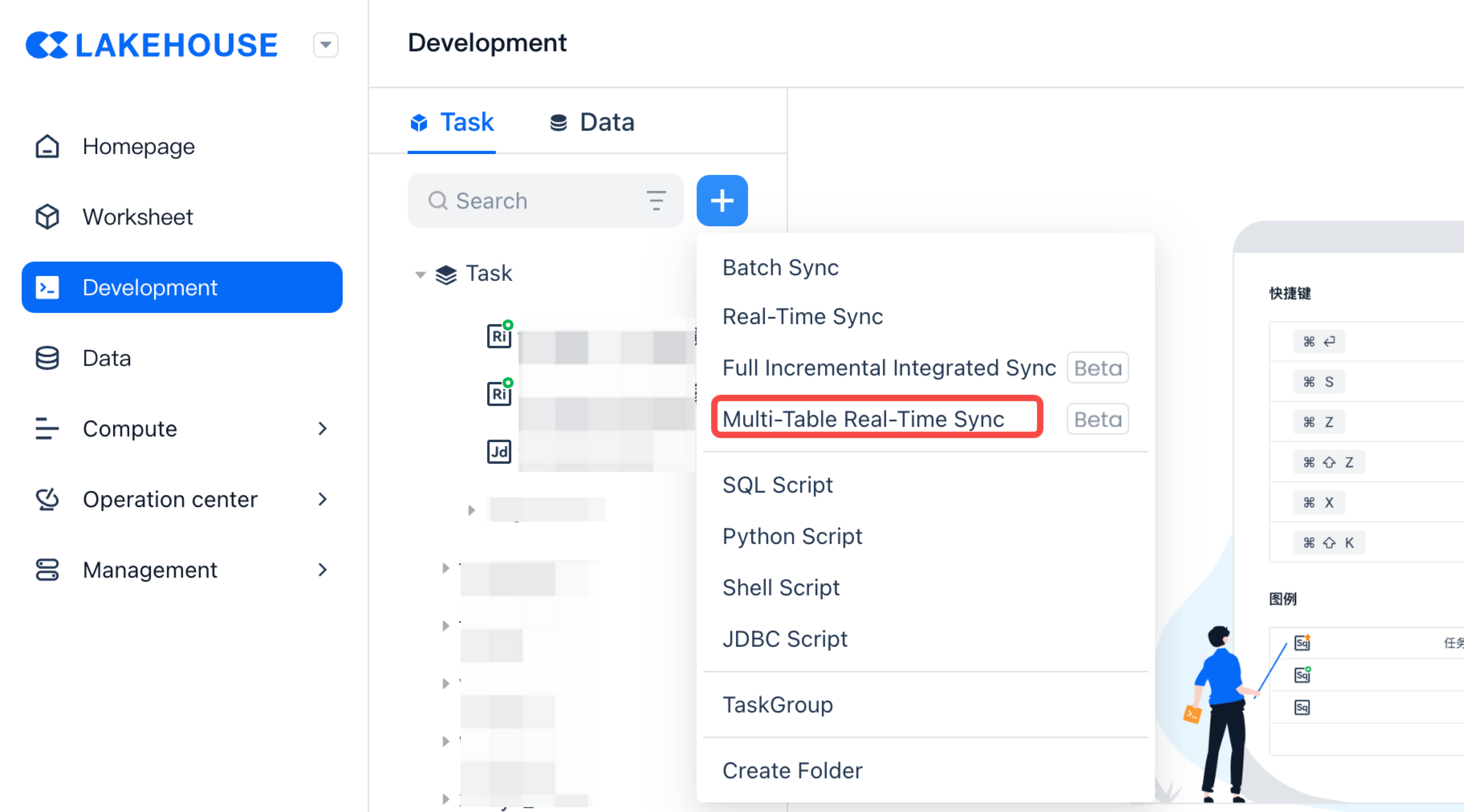
Configure Source Data Type
Select a source data type that needs to be synchronized. Currently supported source data types are as follows:
Select Synchronization Type
Two task types are supported, please choose as needed:
- Real-time Synchronization - Multi-table Mirroring: Used to mirror source data to the target end.
- Real-time Synchronization - Multi-table Merging: Used to merge data from multiple databases and tables into a single target table.
Multi-table Mirroring
Source Configuration
-
Select Data Source
-
For multi-table mirroring synchronization, please select a data source. If it is not displayed here, please create a new data source, see Data Source Configuration.
-
Ensure that the account in the data source has sufficient permissions, see the permission description below.
-
Configure Read Mode
-
MySQL currently only supports BINLOG mode.
-
PostgreSQL currently only supports WALs mode.
-
Select Synchronization Objects
-
First select the database to be synchronized, then select the tables to be synchronized.
-
The page provides a batch configuration function. Based on the configuration template, fill in the configuration file according to the format requirements, and after uploading, the page will select the objects to be synchronized according to the content given in the file. After selection, you can make fine adjustments as needed. Please note to delete the comment instructions in the template file.
-
Configure Slot
-
Only PostgreSQL needs to configure the slot, which refers to PostgreSQL's replication slot, see Documentation.
-
Each database needs to configure a slot. Currently, decoderbufs and pgoutput plugin types are supported.
-
You can choose an existing slot to use; or create a new one on the page. In the creation window, you can modify the creation statement in the lower area as needed. Click OK to create. The username configured in the data source must have the permission to create a slot, otherwise, the creation will fail, see the permission description below.
-
Special attention, do not reuse the same slot for different tasks. When the task starts, if the slot is occupied by other running tasks, it will fail to start. If other tasks are in a stopped state, because the data in the slot will be shared for consumption, the point is shared. The incremental data consumed by the new task may not be fully synchronized to the target table.
Target Configuration
The target end currently only supports writing to Lakehouse.
- Target Data Source
- The default is the Lakehouse data source corresponding to the current workspace, no modification is needed.
- Namespace Rules
- Currently, only selecting a specific namespace is supported. In the future, it will be expanded to support mirroring naming or custom naming based on the source end.
- Select a specific namespace (workspace) as needed.
- Target Table Naming Rules
- Currently, only mirroring the source name is supported. In the future, it will be expanded to support adding prefixes or custom naming rules.
- Compute Cluster
- Select an available cluster in the workspace, it is recommended to use an AP type cluster.
Preview Configuration
- After completing the above source and target configurations, you can preview the mapping relationship of the synchronized tables and fields. If modifications are needed, please go back to the previous step to adjust.
Synchronization Rules
- In the synchronization rules, you can configure rules such as Schema Evolution to define the handling behavior after changes in the source tables and fields.
Multi-table Merging
Source Configuration
- Select Data Source
- Same as above, similar to multi-table mirroring synchronization.
- Configure Read Mode
- Same as above, similar to multi-table mirroring synchronization.
- Select Synchronization Objects Multi-table merging synchronization will use a "virtual table" as an intermediate transition to receive data from specified objects. Two methods are supported for configuration:
- Method 1: Based on rule configuration, filter through regular expressions, such as selecting all tables starting with abc, just fill in abc in the regular expression.
- Method 2: Based on file batch configuration, fill in the configuration file according to the format requirements in the template, and after uploading, the page will select the objects to be synchronized according to the content given in the file. After selection, you can make fine adjustments as needed. Please note to delete the comment instructions in the template file.
Target Configuration
- Same as above, similar to multi-table mirroring synchronization.
Preview Configuration
- Same as above, similar to multi-table mirroring synchronization.
Synchronization Rules
- Same as above, similar to multi-table mirroring synchronization.
Submit
Click the submit button to submit the task to the production environment for execution. Please note that the task will not start by default after submission and needs to be started manually.
Task Operations and Maintenance
Start Task
Enter the task details page to operate and start the task. Please choose one of the following startup methods as needed. After the task starts, during the initialization phase, depending on the number of tables, it may take a few minutes or longer, please be patient.
Startup Methods
- Stateless Start (only supported for the first task start): Fully synchronize all data, first perform a full synchronization, then start incremental synchronization.
- Resume from Last Saved State (only supported for restarting stopped tasks): If the last synchronization was stopped, it will resume from the stopping point.
- Custom Start Position: Synchronize from a given point, which can be used for data rollback. This applies uniformly to all tables configured in the task.
- MySQL: Choose to start from a specified file or a specified time. The last file position can be obtained in the page monitoring area.
- PostgreSQL: Specify the LSN value, which can be viewed in the instance monitoring section below.
Full Synchronization
- This configuration controls whether to perform a full data synchronization before incremental synchronization. Please note that if you choose not to perform full synchronization, you can choose full synchronization again after stopping and restarting the task.
- Maximum Concurrency: When initiating a task with full data synchronization enabled, this parameter controls the number of concurrent subtasks for bulk data migration. It establishes corresponding JDBC connections to the source database. A higher value theoretically increases synchronization throughput (until the source database's load capacity is saturated) but proportionally amplifies the pressure on the source system.
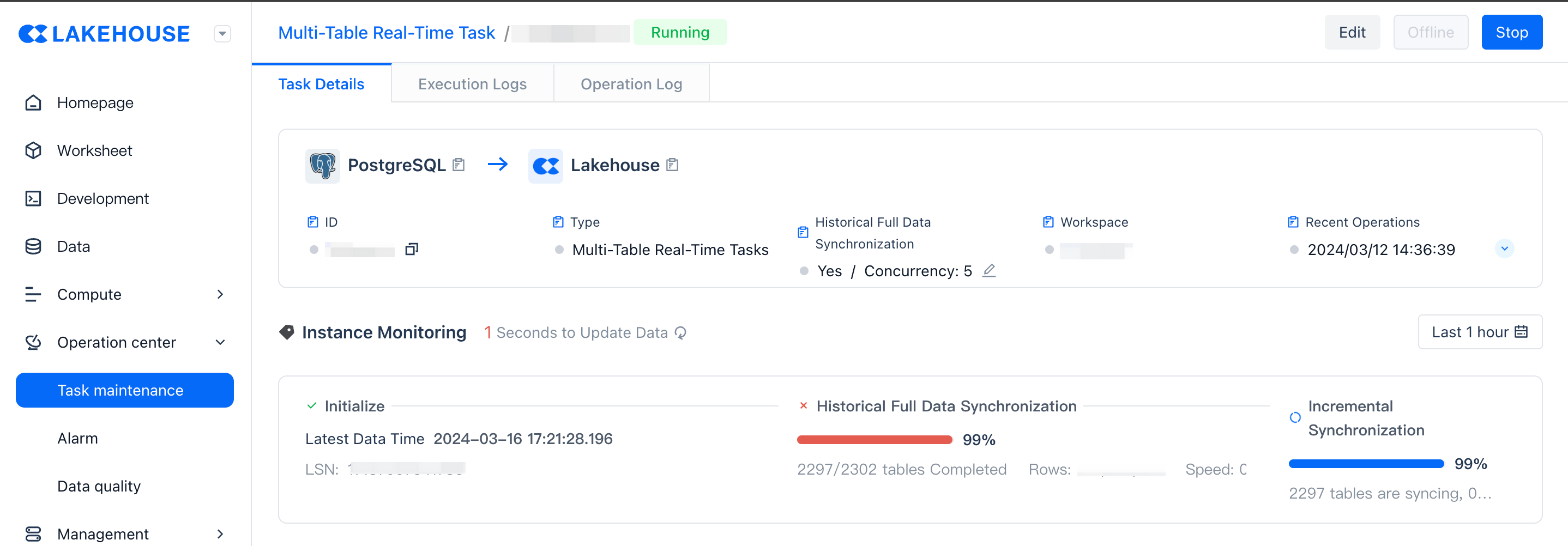
Instance Monitoring
Stage Monitoring
After the task starts, it will go through three stages: initialization, full synchronization, and incremental synchronization. You can view the running status of these three stages in the instance monitoring area.
Metrics Monitoring
In the metrics monitoring area, you can view key monitoring metrics for full synchronization and incremental synchronization.
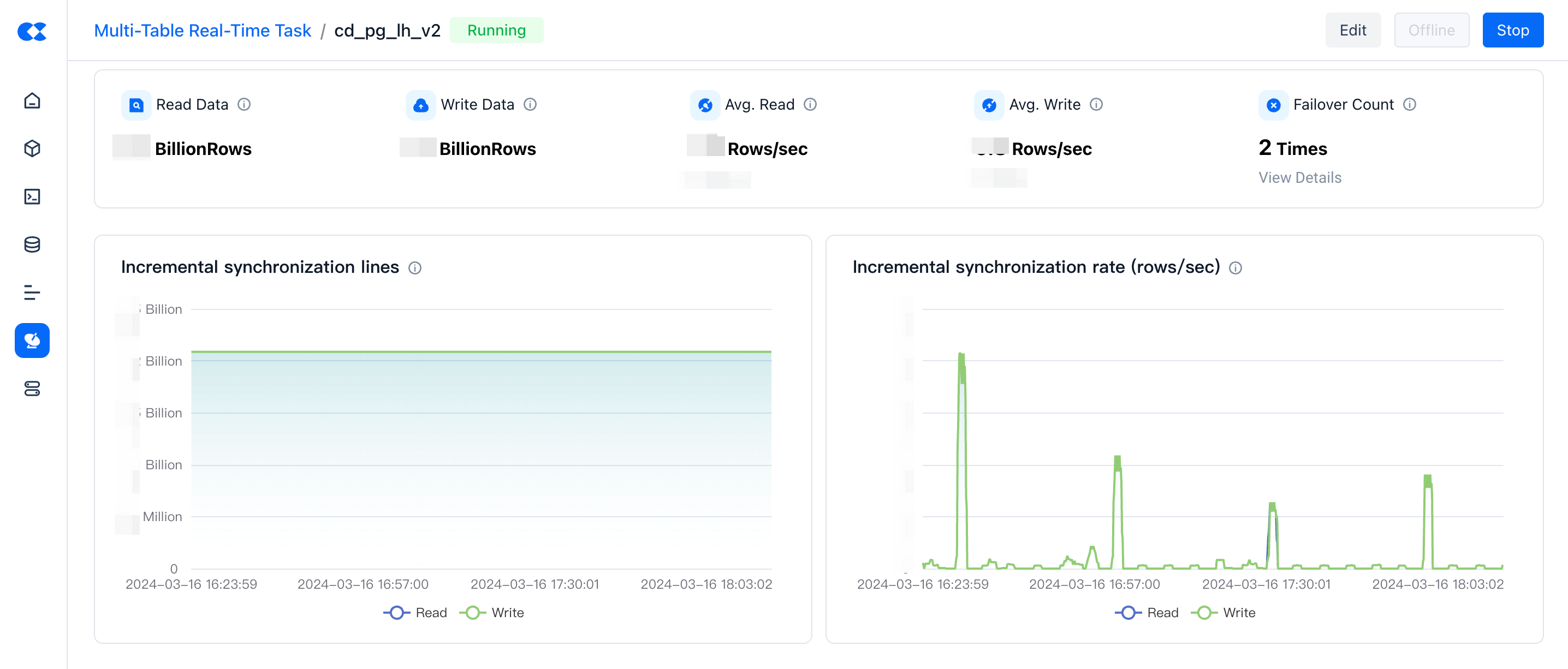
| Metric Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Read | The number of records read from the data source by the data synchronization task during the statistical period. |
| Data Written | The number of records written to the target data source by the data synchronization task during the statistical period. |
| Average Read Rate | The average read rate of the data synchronization task during the statistical period. (Total records read during the period / period time) |
| Average Write Rate | The average write rate of the data synchronization task during the statistical period. (Total records written during the period / period time) |
| Failover Count | Number of Failover Occurrences for Data Synchronization Tasks During the Statistical Period。The failover count is not solely attributable to data conditions but also relates to the operational stability of the data synchronization service itself. By default, only information regarding the last 10 failover instances is displayed. |
Synchronization Objects
In the synchronization objects area, you can view the final state of single table synchronization and perform corresponding maintenance operations.
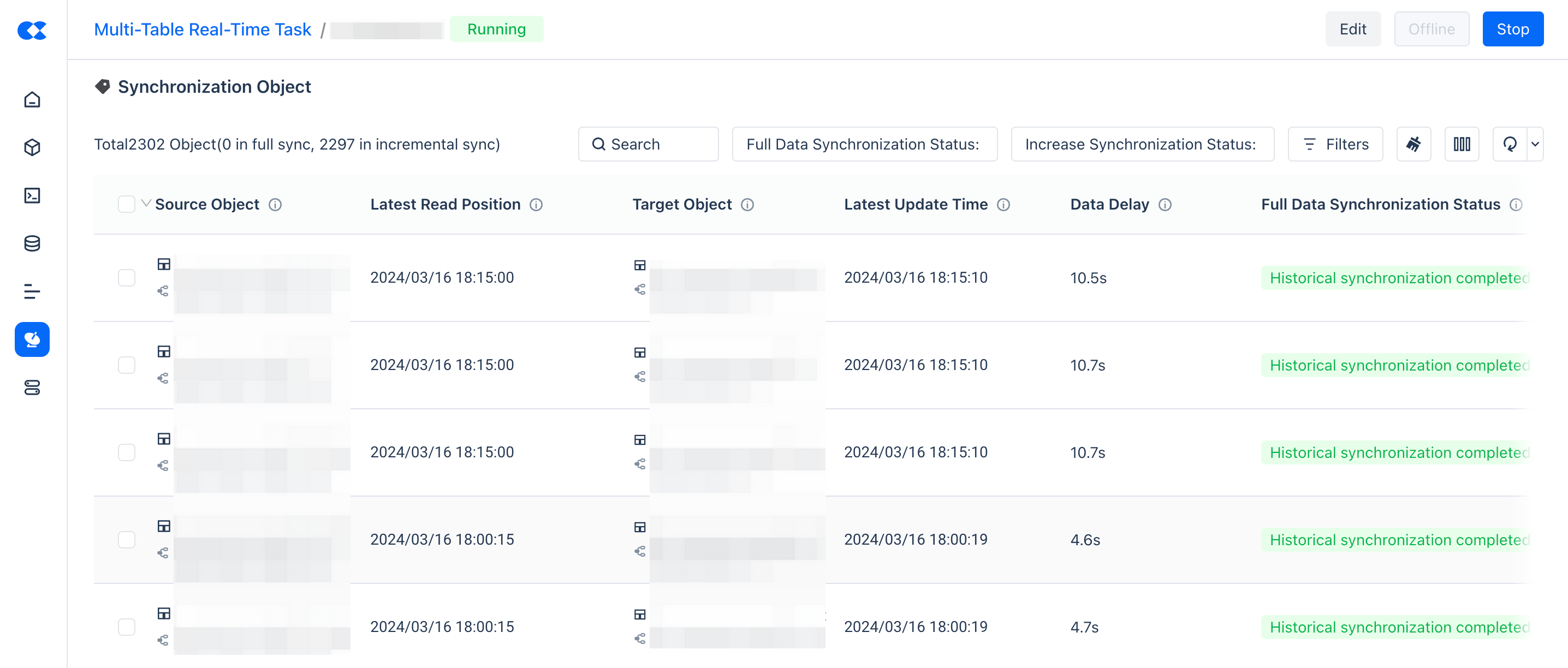
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Latest Read Position | The synchronization task reads data from the source object in real-time and writes it to the target table, using the write time of the latest record in the target table as the read position. |
| Latest Update Time | The last time data was written to the target table. |
| Data Latency | The time interval from when the data is committed at the source end to when it is visible at the target end. |
| Operation | Behavior Definition |
|---|---|
| Full Sync Details | Click to jump to the full synchronization task interface to view details. |
| Prioritize | During the full synchronization stage, this operation can increase the synchronization priority of the table, making it execute first. |
| Cancel Execution | For tables that are being synchronized, this operation cancels the current table synchronization. |
| Force Stop | For tables that are being synchronized, this operation forcibly stops the synchronization subtask process of the table. Since multiple tables may be in the same subtask, this operation may affect the synchronization of other tables, so please operate with caution. |
| Resynchronize | Resynchronize the table for both full and incremental synchronization. |
| View Exceptions | Click to view the exception information of the table's incremental synchronization task, such as Schema Evolution exceptions. |
| Data Supplement Synchronization | For this table, you can perform a full synchronization after giving a filter condition, such as filtering out part of the data based on the id value. |
Stop Task
Stopping the task will stop the ongoing full synchronization and incremental synchronization. The incremental synchronization position state will be automatically saved when stopping.
- If the table is in the full synchronization stage when stopping, after restarting, the table that has not been fully synchronized will undergo a new full synchronization.
- If the table is in the incremental synchronization stage when stopping, after restarting, it will continue to synchronize from the position where it stopped by default.
Offline Task
Taking a task offline is a high-risk operation. After the task is taken offline, the current synchronization position will not be saved. If the task is brought online and started again, it will start synchronizing data from the beginning.
- Taking a task offline will not clean the data that has already been synchronized to the target end, but it will clean the intermediate process cache data and position information.
- Resynchronization will not recreate the table. Full data synchronization will overwrite the old table, and incremental synchronization will update the target table with a merge into.
Known Limitations
-
Schema Evolution, does not currently support changing field types or automatically adding new tables.
-
In multi-table real-time synchronization tasks, if there are data with the same primary key in different source tables, the synchronization result will be abnormal.
-
Unsupported field types for MySQL synchronization:
| Field Type | Behavior After Synchronization |
|---|---|
| year | Value does not correspond |
- Unsupported field types for PostgreSQL synchronization:
| Field Type | Behavior After Synchronization |
|---|---|
| varbit | Value does not correspond |
| bytea | Value does not correspond |
| TIMETZ | Value does not correspond |
| interval | Value does not correspond |
| NAME | Value does not correspond |
| NUMERIC | Precision does not correspond, target end precision will be higher |
| decimal | Precision does not correspond, target end precision will be higher |
More
You can refer to this document for more SOP guide.
