Data Type Conversion
Data type conversion refers to the process of converting a value of one data type to another data type. Data type conversion can be divided into implicit conversion and explicit conversion. Implicit conversion refers to the data type conversion that the system automatically performs when executing certain operations, such as arithmetic operations, comparison operations, function calls, etc. Explicit conversion refers to the data type conversion specified by the user using specific functions or syntax, such as CAST, etc. Different database systems may have different data type conversion rules and functions. This article will introduce the characteristics and usage of data type conversion in lakehouse.
Explicit Conversion
The following table shows the behavior of using cast conversion,
| Source\Target | tinyint | Smallint | Int | Bigint | Float | Double | Decimal | String | Date | Timestamp_ltz | Timestamp_ntz | Interval | Boolean | Binary | Array | Map | Struct |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tinyint | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N |
| Smallint | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N |
| Int | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N |
| Bigint | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | N |
| Float | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Double | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Decimal | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| String | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N |
| Date | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Timestamp_ltz | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| timestmap_ntz | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Interval | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N |
| Boolean | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N |
| Binary | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N |
| Array | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N |
| Map | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N |
| Struct | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y |
Bold black text indicates that an error or conversion to null may occur. It should be noted that to prevent users from failing to write SQL conversion values, Singdata adopts a more lenient conversion behavior. The bold black parts that cause exceptions will be converted to null. Of course, you can also set the standard behavior for the bold black parts to strict mode, which can also report errors. To enable strict mode, set cz.sql.cast.mode=strict;. After enabling, you can directly use the try_cast function, and the error behavior will return null. For details, please refer to parameter management.
- CAST(Numeric AS Numeric): If the value exceeds the range of the target data type, Singdata will default to converting it to null.
- Converting FLOAT to INTEGER truncates the value.
- Converting TIMESTAMP to DATE removes the time information of the day.
Implicit Conversion
When two values of different types are involved in arithmetic or comparison operations, Singdata SQL will perform implicit conversion according to a certain priority to ensure the precision and range of the operation results. The priority order is shown in the figure below. In other words, if the types of the two values are different, the value of the lower type will be converted to the higher type to match the type of the other value. For example, when an integer and a decimal are added, the integer will be converted to a decimal to avoid precision loss. When a date and a timestamp are compared, the date will be converted to a timestamp to ensure consistency in time granularity.
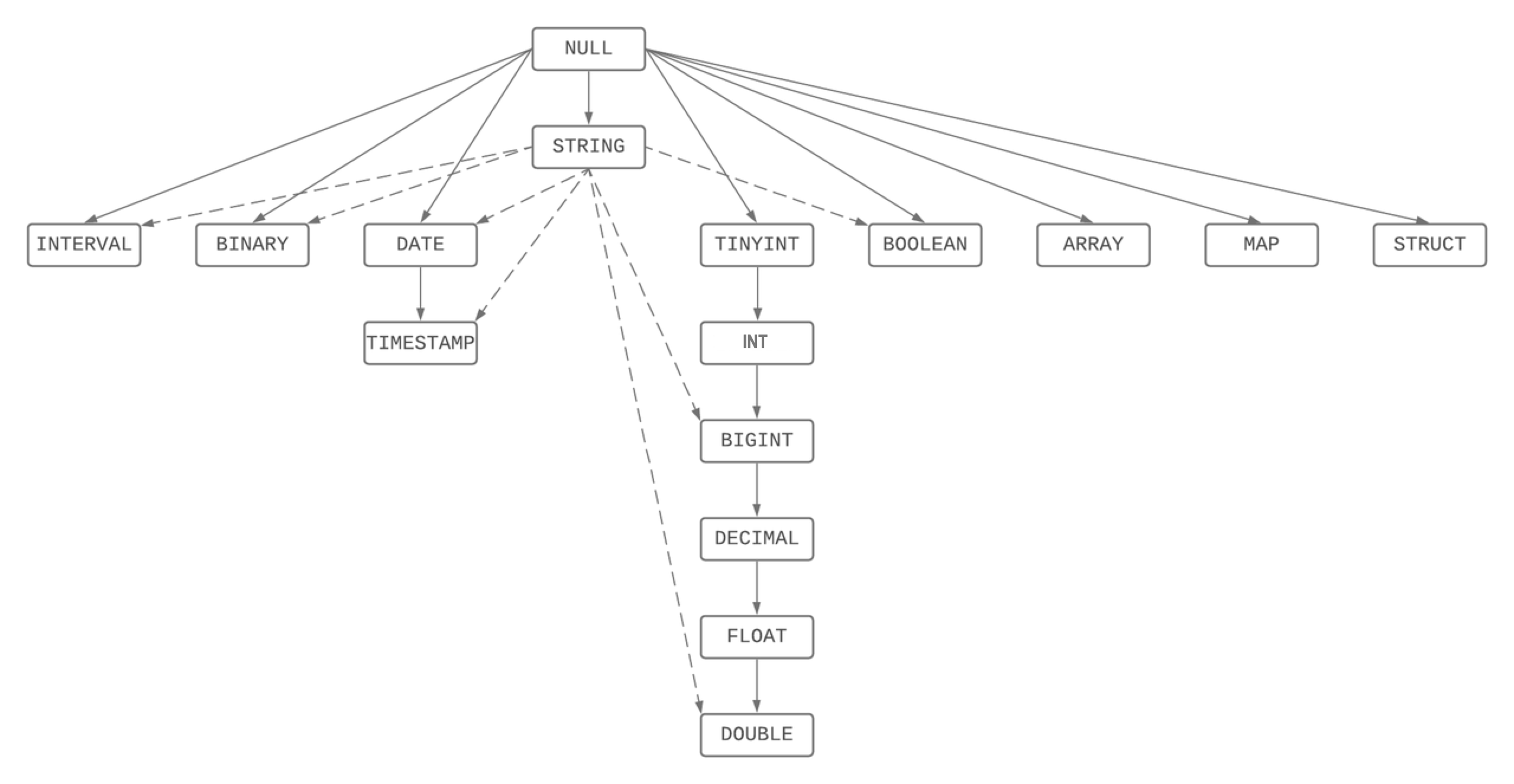
The types in the figure are arranged from low to high, with the topmost being the lowest type.
Special Note
To prevent users from failing to write SQL conversion values, Singdata adopts a more lenient conversion behavior for both implicit and explicit conversions. Exceptions will be converted to null. You can enable strict mode by setting cz.sql.cast.mode=strict;. For details, please refer to parameter management.
For example
Example
Implicit Conversion
