Complete Guide to Importing Data into Singdata Lakehouse
Data Ingestion: Batch Loading via Singdata Lakehouse Studio (Public Network Connection)
Overview
Use Cases
When the existing data source (including databases, data warehouses) has a publicly accessible address (such as through public NAT mapping), the single table data volume is large, and the synchronization cost is low, with low requirements for data freshness (often on an hourly or even daily basis), the data from the source table can be synchronized to the Lakehouse table.
Implementation Steps
Navigate to Development -> Tasks, click "+", select "Offline Sync", and create a new "Offline Sync" job.
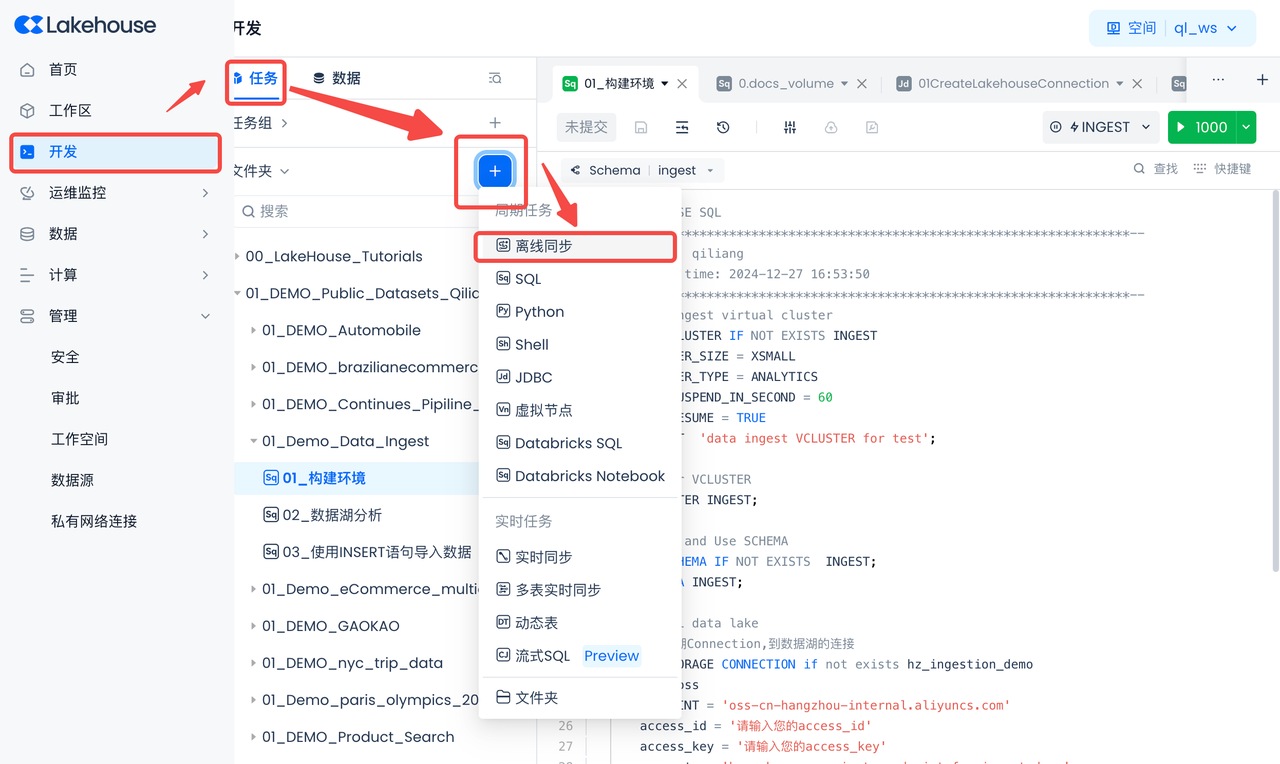
Other parameter configurations are as follows:
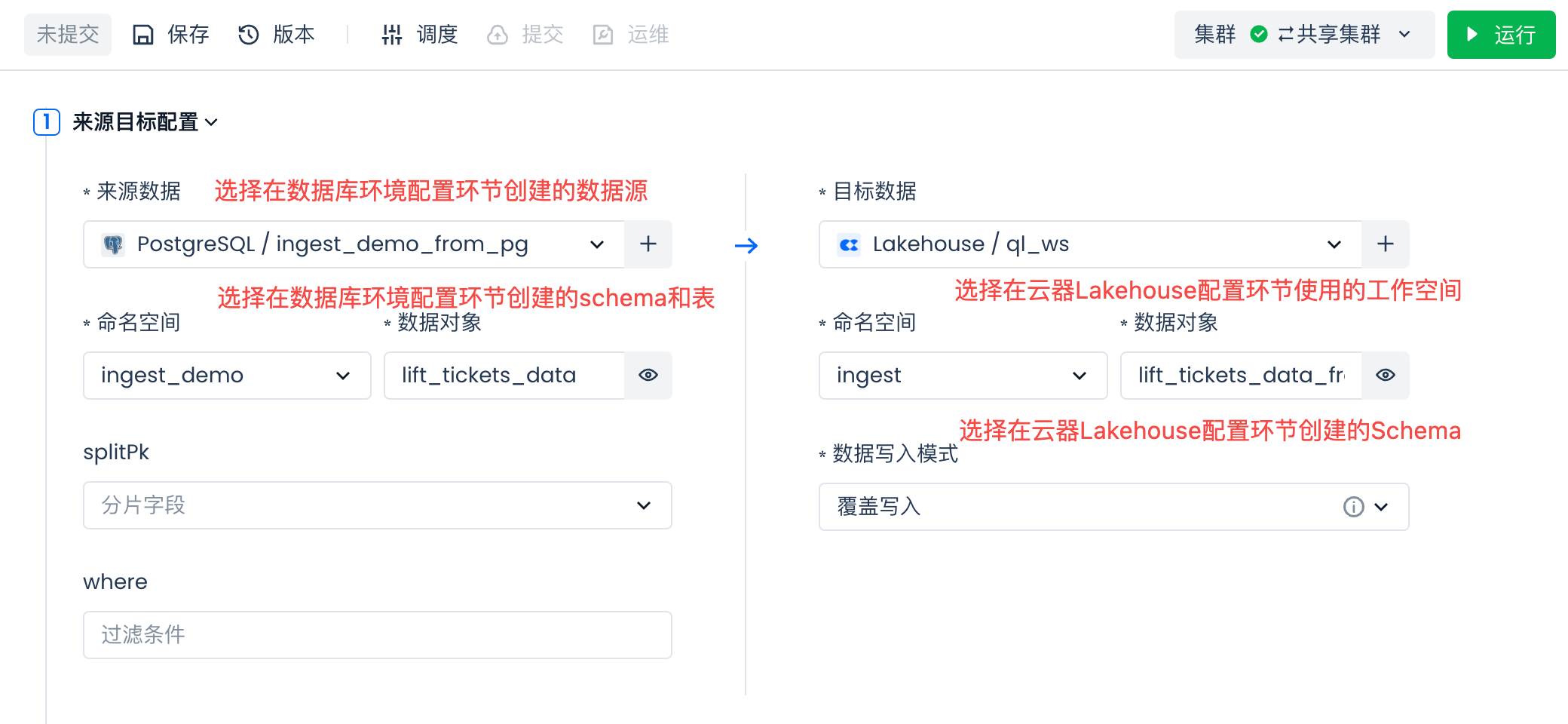
Then select to create a new data table: lift_tickets_data_from_pg_batch.
In the "Create New Data Table" SQL code, change the table name to "lift_tickets_data_from_pg_batch".
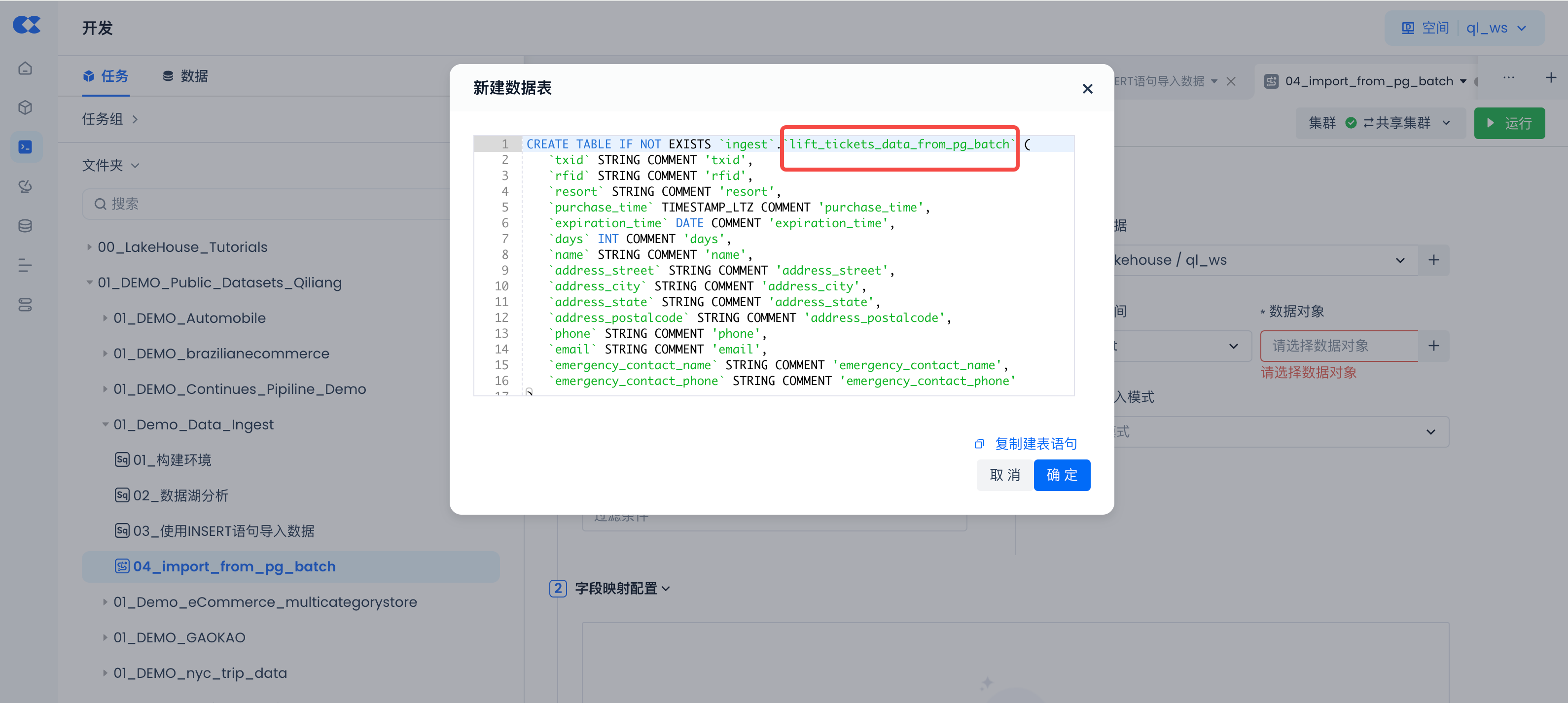
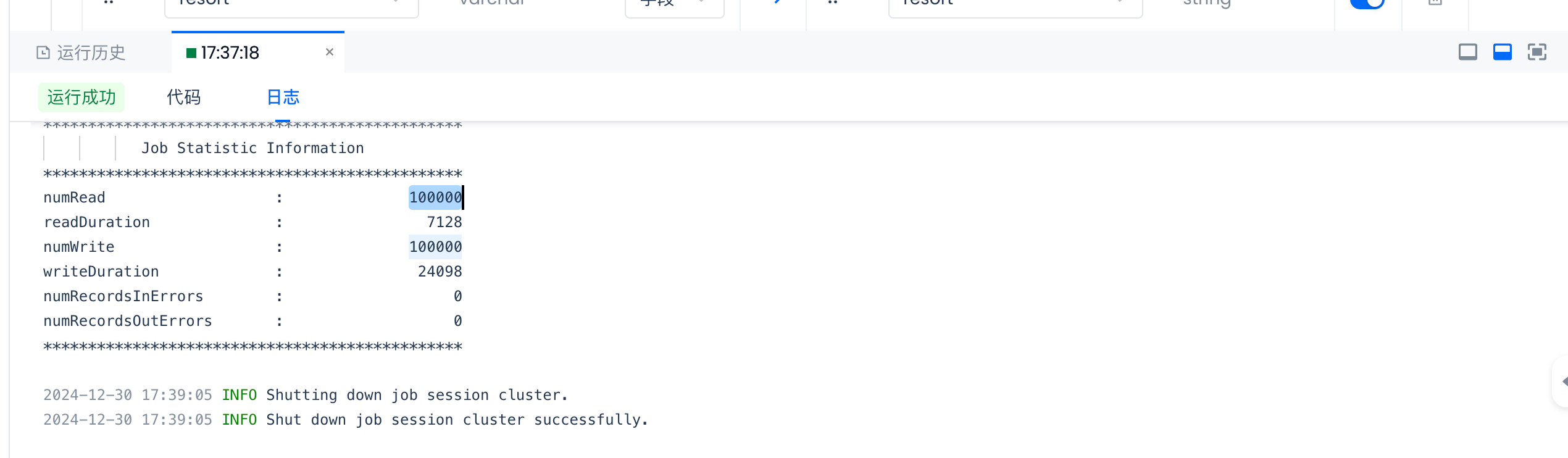
Check if the field mapping meets expectations, then test run the sync task:
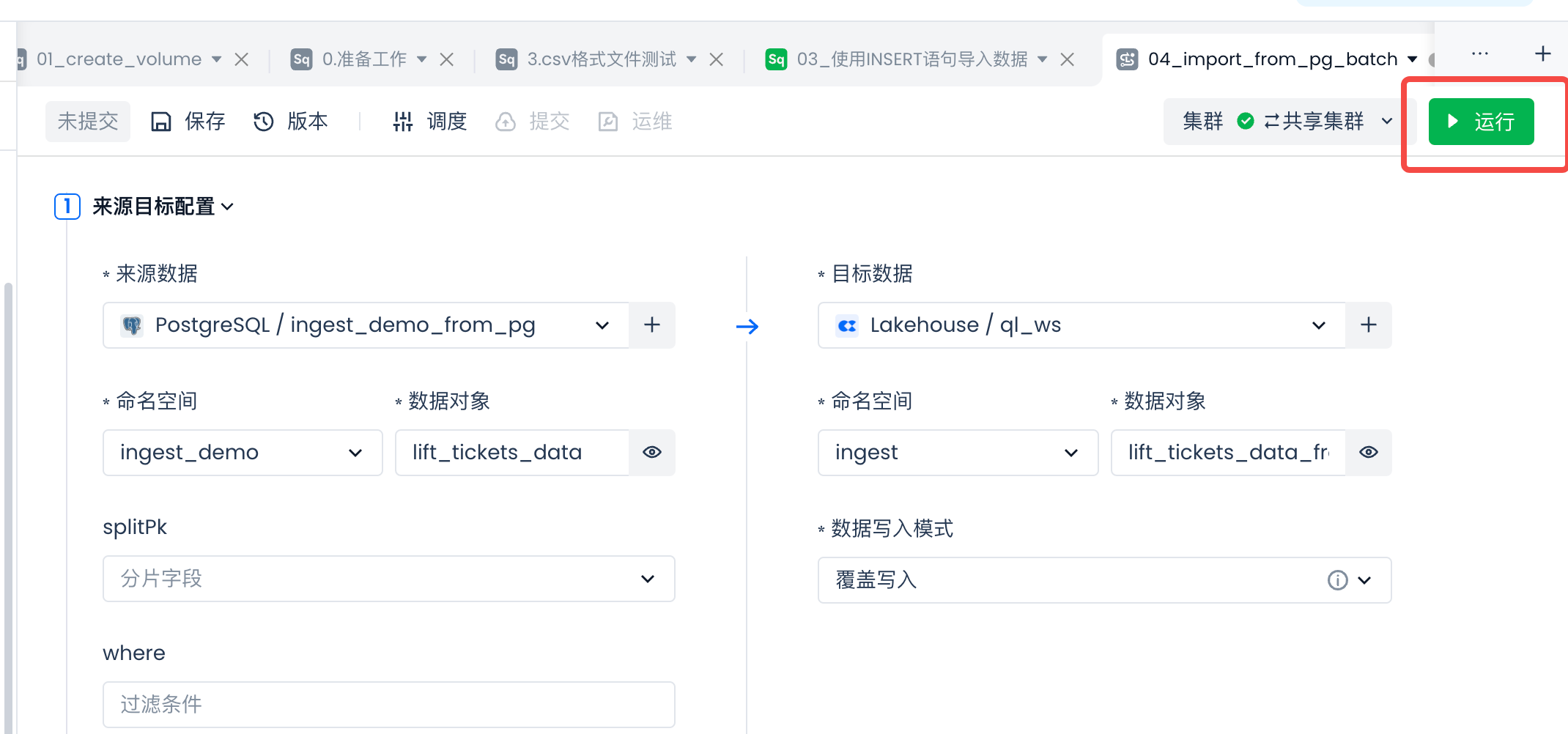
Check the test results:
View the test task logs and check if the number of nubWrite matches the number of rows in the source table.
Next Steps Recommendations
-
Configure the where condition to set the data to be synchronized for each run, rather than the full amount. This is generally based on filtering by time fields.
-
Configure scheduling parameters and submit, operate, and maintain periodic data synchronization.
- If it is suitable for small volume dimension table data, there is no need to set the where condition, set the data write mode to "overwrite", and perform a full overwrite each time.
- If it is large volume fact table data, set the where condition, set the data write mode to "append", and perform incremental append writes each time to reduce the amount of data synchronized and the synchronization cost each time. Avoid the high cost of full synchronization each time.
-
Offline sync tasks serve as the beginning of data extraction (E) and loading (L) in data ELT, and further cleaning and transformation (T) of the data loaded into the warehouse can be performed through SQL tasks.
